
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a military conflict or prepared political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can produce destruction in a much shorter time and can have a long-lasting radiological result. A major nuclear exchange would likely have long-term effects, primarily from the fallout released, and could also lead to secondary effects, such as "nuclear winter", nuclear famine, and societal collapse. A global thermonuclear war with Cold War-era stockpiles, or even with the current smaller stockpiles, may lead to various scenarios including the extinction of the human species.

World War III or the Third World War are names given to a hypothetical worldwide large-scale military conflict subsequent to World War I and World War II. The term has been in use since at least as early as 1941. Some apply it loosely to limited or more minor conflicts such as the Cold War or the war on terror. In contrast, others assume that such a conflict would surpass prior world wars in both scope and destructive impact.
The Cold War was a geopolitical, ideological, and economic struggle after World War II between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Détente is the relaxation of strained relations, especially political ones, through verbal communication. The diplomacy term originates from around 1912, when France and Germany tried unsuccessfully to reduce tensions.
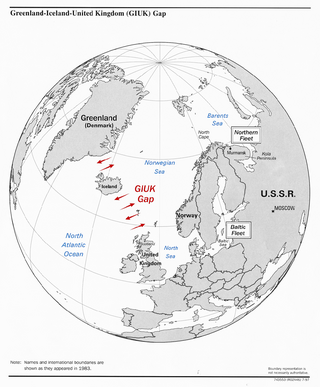
The GIUK gap is an area in the northern Atlantic Ocean that forms a naval choke point. Its name is an acronym for Greenland, Iceland, and the United Kingdom, the gap being the two stretches of open ocean among these three landmasses. It separates the Norwegian Sea and the North Sea from the open Atlantic Ocean. The term is typically used in relation to military topics. The area has for some nations been considered strategically important since the beginning of the 20th century.

David Koepp is an American screenwriter. He is the ninth most successful screenwriter of all time in terms of U.S. box office receipts with a total gross of over $2.3 billion. Koepp has achieved both critical and commercial success in a wide variety of genres: thriller, science fiction, comedy, action, drama, crime, superhero, horror, adventure, and fantasy.

Royal Air Force Greenham Common or more simply RAF Greenham Common is a former Royal Air Force station in the civil parishes of Greenham and Thatcham in the English county of Berkshire. The airfield was southeast of Newbury, about 55 miles (89 km) west of London.

Obba Babatundé is an American actor. A native of Queens, New York City, he has appeared in more than seventeen stage productions, thirty theatrical films, sixty made-for-television films, and two prime-time series.

The Geneva Summit of 1955 was a Cold War-era meeting in Geneva, Switzerland. Held on July 18, 1955, it was a meeting of "The Big Four": President Dwight D. Eisenhower of the United States, Prime Minister Anthony Eden of Britain, Premier Nikolai A. Bulganin of the Soviet Union, and Prime Minister Edgar Faure of France. They were accompanied by the foreign ministers of the four powers : John Foster Dulles, Harold Macmillan, Vyacheslav Molotov, and Antoine Pinay. Also in attendance was Nikita Khrushchev, de facto leader of the Soviet Union.
A cold war is a state of conflict between nations that does not involve direct military action but is pursued primarily through economic and political actions, propaganda, acts of espionage or proxy wars waged by surrogates. This term is most commonly used to refer to the American-Soviet Cold War of 1947–1991. The surrogates are typically states that are satellites of the conflicting nations, i.e., nations allied to them or under their political influence. Opponents in a cold war will often provide economic or military aid, such as weapons, tactical support or military advisors, to lesser nations involved in conflicts with the opposing country.
The green beret was the headgear of the British Commandos of World War II.
The Cold War was reflected in culture through music, movies, books, television, and other media, as well as sports, social beliefs, and behavior. Major elements of the Cold War included the threat of communist expansion, a nuclear war, and – connected to both – espionage. Many works use the Cold War as a backdrop or directly take part in a fictional conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union. The period 1953–62 saw Cold War themes becoming mainstream as a public preoccupation.

Canada–Soviet Union relations were the bilateral relations between Canada and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
The New Cold War may refer to:

Marines, Let's Go is a 1961 CinemaScope DeLuxe Color Korean War film about three Marine buddies on shore leave in Japan and at war in Korea. It was produced and directed by Raoul Walsh, who also wrote the story. Walsh had previously had successes with films about the U.S. Marine Corps in World War I, the 1920s, and World War II. This was the next-to-last film of Walsh's long directing career.

"Cold War" is a song recorded by American musician Janelle Monáe, released as the second single from her debut studio album The ArchAndroid (2010). The song was written and produced by Monáe, Nathaniel Irvin III, and Charles Joseph II. It was released via Monáe's website on February 12, 2010, one day after the release of the album's first single, "Tightrope". A fast-paced new wave and Afro-funk track with a futuristic feel, its drum pattern has received several comparisons to that of the 2000 single "B.O.B" by OutKast, whose member Big Boi was one of her mentors and was featured on "Tightrope". Music critics acclaimed the song as one of the best tracks from The ArchAndroid. The music video, consisting of a single shot of Monáe against a black wall and expressing various emotions as the song progresses, has been praised by critics as a unique piece of art.

The Crusade for Freedom was an American propaganda campaign operating from 1950–1960. Its public goal was to raise funds for Radio Free Europe; it also served to conceal the CIA's funding of Radio Free Europe and to generate domestic support for American Cold War policies.
The Second Cold War, Cold War II, or the New Cold War are terms that refer to heightened geopolitical tensions in the 21st century. They have been used to describe the tense relations between the United States and China and, similarly, between the United States and Russia, the primary successor state of the former Soviet Union, which took part in the original Cold War.
The Arab–Israeli war normally refers to:











