Dynamics or dynamic may refer to:

A gluon is an elementary particle that acts as the exchange particle for the strong force between quarks. It is analogous to the exchange of photons in the electromagnetic force between two charged particles. Gluons bind quarks together, forming hadrons such as protons and neutrons.
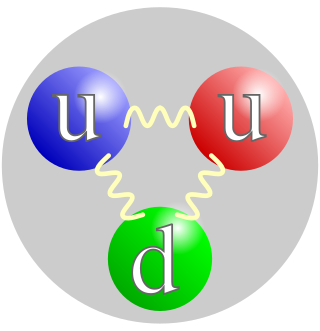
A quark is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks, down quarks and electrons. Owing to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never found in isolation; they can be found only within hadrons, which include baryons and mesons, or in quark–gluon plasmas. For this reason, much of what is known about quarks has been drawn from observations of hadrons.

In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the theory of the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons. Quarks are fundamental particles that make up composite hadrons such as the proton, neutron and pion. QCD is a type of quantum field theory called a non-abelian gauge theory, with symmetry group SU(3). The QCD analog of electric charge is a property called color. Gluons are the force carriers of the theory, just as photons are for the electromagnetic force in quantum electrodynamics. The theory is an important part of the Standard Model of particle physics. A large body of experimental evidence for QCD has been gathered over the years.
Quantum theory may refer to:

The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles. It was developed in stages throughout the latter half of the 20th century, through the work of many scientists worldwide, with the current formulation being finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, proof of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and the Higgs boson (2012) have added further credence to the Standard Model. In addition, the Standard Model has predicted various properties of weak neutral currents and the W and Z bosons with great accuracy.

In quantum chromodynamics (QCD), color confinement, often simply called confinement, is the phenomenon that color-charged particles cannot be isolated, and therefore cannot be directly observed in normal conditions below the Hagedorn temperature of approximately 2 terakelvin. Quarks and gluons must clump together to form hadrons. The two main types of hadron are the mesons and the baryons. In addition, colorless glueballs formed only of gluons are also consistent with confinement, though difficult to identify experimentally. Quarks and gluons cannot be separated from their parent hadron without producing new hadrons.

Color charge is a property of quarks and gluons that is related to the particles' strong interactions in the theory of quantum chromodynamics (QCD).

In physics, lattice gauge theory is the study of gauge theories on a spacetime that has been discretized into a lattice.

In physics, lattice field theory is the study of lattice models of quantum field theory, that is, of field theory on a space or spacetime that has been discretised onto a lattice.
Moo-Young Han was a South Korean-born American physicist. He was a professor of physics at Duke University. Along with Yoichiro Nambu of the University of Chicago, he is credited with introducing the SU(3) symmetry of quarks, today known as the color charge. The color charge is the basis of the strong force as explained by quantum chromodynamics.
The J. J. Sakurai Prize for Theoretical Particle Physics, is presented by the American Physical Society at its annual April Meeting, and honors outstanding achievement in particle physics theory. The prize consists of a monetary award, a certificate citing the contributions recognized by the award, and a travel allowance for the recipient to attend the presentation. The award is endowed by the family and friends of particle physicist J. J. Sakurai. The prize has been awarded annually since 1985.
The Colourfield were an English band formed in 1984 in Manchester, England, when former Specials and Fun Boy Three frontman Terry Hall joined up with ex-Swinging Cats members Toby Lyons and Karl Shale. Despite the fact that all three members were from Coventry, the band was based in Manchester.
In physics, a charge is any of many different quantities, such as the electric charge in electromagnetism or the color charge in quantum chromodynamics. Charges correspond to the time-invariant generators of a symmetry group, and specifically, to the generators that commute with the Hamiltonian. Charges are often denoted by the letter Q, and so the invariance of the charge corresponds to the vanishing commutator , where H is the Hamiltonian. Thus, charges are associated with conserved quantum numbers; these are the eigenvalues q of the generator Q.
In physics, a quantum is the minimum amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude of the physical property can take on only discrete values consisting of integer multiples of one quantum.
Technicolor is a color film process. Technicolour (BrE) or Technicolor (AmE) may also refer to:
Quantum chromodynamics binding energy, gluon binding energy or chromodynamic binding energy is the energy binding quarks together into hadrons. It is the energy of the field of the strong force, which is mediated by gluons. Motion-energy and interaction-energy contribute most of the hadron's mass.

In theoretical particle physics, the gluon field strength tensor is a second order tensor field characterizing the gluon interaction between quarks.
Quantum hadrodynamics is an effective field theory pertaining to interactions between hadrons, that is, hadron-hadron interactions or the inter-hadron force. It is "a framework for describing the nuclear many-body problem as a relativistic system of baryons and mesons". Quantum hadrodynamics is closely related and partly derived from quantum chromodynamics, which is the theory of interactions between quarks and gluons that bind them together to form hadrons, via the strong force.
The quantum vacuum state or simply quantum vacuum refers to the quantum state with the lowest possible energy.




