
Wernicke's aphasia, also known as receptive aphasia, sensory aphasia, or posterior aphasia, is a type of aphasia in which individuals have difficulty understanding written and spoken language. Patients with Wernicke's aphasia demonstrate fluent speech, which is characterized by typical speech rate, intact syntactic abilities, and effortless speech output. Writing often reflects speech in that it tends to lack content or meaning. In most cases, motor deficits do not occur in individuals with Wernicke's aphasia. Therefore, they may produce a large amount of speech without much meaning. Wernicke's aphasia was named after Carl Wernicke who is credited with discovering the area of the brain responsible for language comprehension. Individuals with Wernicke's aphasia are typically unaware of their errors in speech and do not realize their speech may lack meaning. They typically remain unaware of even their most profound language deficits.

Nursing homes, also known as old people's homes, care homes, rest homes, and convalescent homes, provide residential care for elderly or disabled people that often includes around-the-clock nursing care. Often these terms have slightly different meanings in the same or different English-speaking countries to indicate that the institutions are public or private or provide mostly assisted living or more or less nursing care and emergency medical care. A nursing home is a place for people who do not need to be in a hospital but cannot be cared for at home. The nursing home facility nurses have the responsibility of caring for the patients medical needs and also the responsibility of being in charge of other employees, depending on ranks. Most nursing homes have nursing aides and skilled nurses on hand 24 hours a day.
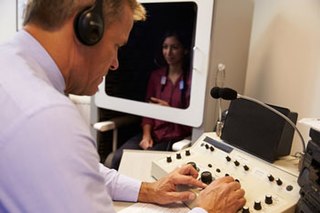
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies, audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing are affected, to what degree, and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found. If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present he or she will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation.
Transcortical motor aphasia (TMoA), also known as commissural dysphasia or white matter dysphasia, results from damage in the anterior superior frontal lobe of the language-dominant hemisphere. This damage is typically due to cerebrovascular accident (CVA). TMoA is generally characterized by reduced speech output, which is a result of dysfunction of the affected region of the brain. The left hemisphere is usually responsible for performing language functions, although left-handed individuals have been shown to perform language functions using either their left or right hemisphere depending on the individual. The anterior frontal lobes of the language-dominant hemisphere are essential for initiating and maintaining speech. Because of this, individuals with TMoA often present with difficulty in speech maintenance and initiation.

The American Speech–Language–Hearing Association (ASHA) is a professional association for speech–language pathologists, audiologists, and speech, language, and hearing scientists in the United States and internationally. It has more than 197,856 members and affiliates.
Speech-language pathology, also known as communication sciences and disorders in the United States, is a fast-growing profession that, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, offers about 120,000 jobs in the United States alone. The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) has 166,000 members, who are audiologists, speech-language pathologists, speech, language, and hearing scientists, and speech language pathology assistants. To begin practice in most areas of the United States, a prospective therapist must have an undergraduate degree and a graduate degree in speech pathology. A 9-month, supervised clinical fellowship year is then completed, after which the Certificate of Clinical Competence (CCC) in speech pathology from the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) is granted. In order to be certified clinically competent the Praxis exam must be passed. In some areas the master's degree is not required. In some areas additional requirements must be met: an additional certification from ASHA in school speech pathology and audiology, certification in special education instruction, and/or and must have passed any other federal or state examinations for licensure and certification. To retain the ASHA license a minimum amount of continuing education must be completed. A doctorate is not currently required, but that may change, as it has for many other areas of therapy. Speech-language pathology overlaps with many educational disciplines, such as communication sciences, linguistics, special education, and health care. This article will explore some of the fundamental elements of speech-language pathology, looking at the career in an educational setting.

The All India Institute of Speech and Hearing, commonly known as AIISH (AYE-SH), is located in Manasagangotri, Mysore, India. It is an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. The institute was established in 1966 with a focus on training professionals for speech and hearing sciences.
Speech-Language Pathology is a field of expertise practiced by a clinician known as a speech-language pathologist (SLP). or a speech therapist. SLP is considered a "related health profession" or "allied health profession" along with audiology, behavior analysis, optometry, occupational therapy, clinical psychology, physical therapy, and others.
The Hanen Centre is a not-for-profit registered charitable organization, based in Toronto, Canada. It defines its mission as, “providing the important people in a child’s life with the knowledge and training they need to help the child develop the best possible language, social and literacy skills”.
Aural rehabilitation is the process of identifying and diagnosing a hearing loss, providing different types of therapies to clients who are hard of hearing, and implementing different amplification devices to aid the client’s hearing abilities. Aural rehab includes specific procedures in which each therapy and amplification device has as its goal the habilitation or rehabilitation of persons to overcome the handicap (disability) caused by a hearing impairment or deafness.
Apraxia of speech (AOS) is an acquired oral motor speech disorder affecting an individual's ability to translate conscious speech plans into motor plans, which results in limited and difficult speech ability. By the definition of apraxia, AOS affects volitional movement patterns, however AOS usually also affects automatic speech.

Speech and language impairment are basic categories that might be drawn in issues of communication involve hearing, speech, language, and fluency.
Speech-Language & Audiology Canada (SAC), formerly known as the Canadian Association of Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologists (CASLPA), is a national organization supporting and representing speech-language pathologists, audiologists and communication health assistants. The association adopted its new name and logo on February 5, 2014.
Speech Pathology Australia (SPA) is the national peak body for the speech pathology profession in Australia.
Online speech therapy or telepractice is the use of technology to provide speech therapy via high speed internet, webcam, headset with microphone or any other form of communication. Online therapy is a clinical arrangement where the patient and a speech-language certified pathologist communicate and interact face-to-face over the Internet. The session involves a suite of therapeutic exercises including listening, speaking, reading and writing. The recorded videos are assessed by the pathologist to generate an activity report for evaluating progress and usage.
The International Institute of Rehabilitation Sciences and Research is managed by ASTHA Trust, founded by Mrs.Bishnupriya Mishra. The campus is located at KHANDAGIRI, in Bhubaneswar, Orissa, India. The institution provides 3+1 year degree course called BASLP.
The British Columbia Association of Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologists (BCASLPA) is a Canadian non-profit society that supports over 1200 speech-language pathologists, audiologists, and supportive personnel in British Columbia. BCASLPA also provides information to the public about speech and hearing disorders and treatments, and connects people who have speech, language, swallowing, and hearing disorders with highly trained speech and hearing health professionals across BC.
Low-functioning autism (LFA) is a term applied to people with autism who have a Intellectual disability. Symptoms may include impaired social communications or interactions, bizarre behavior, and lack of social or emotional reciprocity. Sleep problems, aggressiveness, and self-injurious behavior are also possible frequent occurrences. LFA is not a recognized diagnosis in the DSM-5 or ICD-10.
Currently there is no cure for Rett syndrome. Treatment is directed towards improving function and addressing symptoms throughout life. A multi-disciplinary team approach is typically used to treat the person throughout life. This team may include primary care physician, physical therapist, occupational therapist, speech-language pathologist, nutritionist, and support services in academic and occupational settings.

Caroline Bowen AM, Ph.D. is a speech therapist who was born in New Zealand, and who has lived and worked in Australia most of her life. She specialises in children's speech sound disorders. Her clinical career as a speech-language pathologist spanned 42 years from 1970 to 2011.









