The Confederate Congress created the position of Quartermaster-General on 26 February 1861 and the Secretary of War was allowed one Colonel and six Majors to serve as Quartermasters. [1] The first Quartermaster General was Col. Abraham C. Myers; his appointment would appear to have been a foregone conclusion as he was signing himself as Acting Quartermaster General on 2 January 1861. [2] In May 1861 when the Confederate government moved to Richmond, Virginia, the headquarters of the Quartermaster General were located on the corner of Ninth and Main Street.
Quartermaster depots were created at Richmond, Virginia; Staunton, Virginia; Raleigh, North Carolina; Atlanta, Georgia; Columbus, Georgia; Huntsville, Alabama; Montgomery, Alabama; Jackson, Mississippi; Little Rock, Arkansas; Alexandria, Louisiana; and San Antonio, Texas.
In 1863 Myers resigned from his position as Quartermaster General and in August Jefferson Davis appointed the successor to serve in that capacity for the rest of the war; Brig. Gen. Alexander Lawton. Confederate railroads in the American Civil War were in the Department's purview.

The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or the South, was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 5, 1865. It was composed of eleven U.S. states that declared secession; South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. These states warred against the United States during the American Civil War.

The flags of the Confederate States of America have a history of three successive designs during the American Civil War. The flags were known as the "Stars and Bars", used from 1861 to 1863; the "Stainless Banner", used from 1863 to 1865; and the "Blood-Stained Banner", used in 1865 shortly before the Confederacy's dissolution. A rejected national flag design was also used as a battle flag by the Confederate Army and featured in the "Stainless Banner" and "Blood-Stained Banner" designs. Although this design was never a national flag, it is the most commonly recognized symbol of the Confederacy.

Joseph Eggleston Johnston was an American career army officer, who served in the United States Army during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) and the Seminole Wars. After Virginia declared secession from the United States, he entered the Confederate States Army as one of its most senior general officers. From 1888 to 1889 he was a vice president, from 1889 to 1890 president, of the Aztec Club of 1847.

The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighting against the United States forces to win the independence of the Southern states and uphold and expand the institution of slavery. On February 28, 1861, the Provisional Confederate Congress established a provisional volunteer army and gave control over military operations and authority for mustering state forces and volunteers to the newly chosen Confederate States president, Jefferson Davis (1808-1889). Davis was a graduate of the United States Military Academy, on the Hudson River at West Point, New York, and colonel of a volunteer regiment during the Mexican–American War (1846-1848). He had also been a United States senator from Mississippi and served as U.S. Secretary of War under 14th President Franklin Pierce. On March 1, 1861, on behalf of the new Confederate States government, Davis assumed control of the military situation at Charleston Harbor in Charleston, South Carolina, where South Carolina state militia had besieged the longtime Federal Fort Sumter in Charleston harbor, held by a small U.S. Army garrison under the command of Major Robert Anderson (1805-1871). By March 1861, the Provisional Congress of the Confederate States meeting in the temporary capital of Montgomery, Alabama, expanded the provisional military forces and established a more permanent regular Confederate States Army.

The Confederate States Marine Corps (CSMC), also referred to as the Confederate States Marines, was a branch of the Confederate Navy during the American Civil War. It was established by an act of the Provisional Congress of the Confederate States on March 16, 1861. The Corps' manpower was initially authorized at 46 officers and 944 enlisted men, and was increased on September 24, 1862, to 1,026 enlisted men. The organization of the Corps began at Montgomery, Alabama, and was completed at Richmond, Virginia, when the capital of the Confederate States was moved to that location. The headquarters and main training facilities remained in Richmond throughout the war, located at Camp Beall on Drewry's Bluff and at the Gosport Shipyard in Portsmouth, Virginia. The last Marine unit surrendered to the Union army on April 9, 1865, with the Confederacy itself capitulating a month later.

The Confederate States Congress was both the provisional and permanent legislative assembly / legislature of the Confederate States of America that existed from February 1861 to April / June 1865, during the American Civil War. Its actions were, for the most part, concerned with measures to establish a new national government for the Southern proto-state in the current Southern United States region, and to prosecute a war that had to be sustained throughout the existence of the Confederacy. At first, it met as a provisional congress both in the first capital city of Montgomery, Alabama, and the second in Richmond, Virginia. As was the case for the provisional Congress after it moved northeast to Richmond, the permanent Congress met in the existing Virginia State Capitol, a building which it also shared with the secessionist Virginia General Assembly.

The Provisional Congress of the Confederate States, fully the Provisional Congress of the Confederate States of America, was a unicameral congress of deputies and delegates called together from the Southern States which became the governing body of the Provisional Government of the Confederate States from February 4, 1861, to February 17, 1862. It sat in Montgomery, Alabama, until May 21, 1861, when it adjourned to meet in Richmond, Virginia, on July 20, 1861. In both cities, it met in the existing state capitols which it shared with the respective secessionist state legislatures. It added new members as other states seceded from the Union and directed the election on November 6, 1861, at which a permanent government was elected.

Alexander Robert Lawton was a Confederate lawyer, politician, diplomat, and brigadier general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.
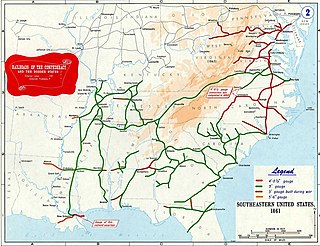
The American Civil War was the first conflict where large armies heavily relied on railroads for transporting supplies. The Confederate States Army's railroad system was fragile and primarily designed for short hauls of cotton to nearby rivers or ocean port. Due to the South's limited manufacturing and industrial capacity, obtaining new parts during the war was challenging. Consequently, the railroad system deteriorated due to overuse, lack of maintenance, and systematic destruction by Union raiders.

John Gregg was an American politician who served as a deputy from Texas to the Provisional Congress of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1862. He served as a brigade commander officer of the Confederate States Army and was killed in action during the Siege of Petersburg.

Thomas H. Cripps was a native of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania who was awarded the U.S. Medal of Honor during the American Civil War. While serving in the Union Navy as a quartermaster aboard the USS Richmond, he operated one of that's ship's guns under heavy enemy fire for two hours during the Battle of Mobile Bay, Alabama on August 5, 1864, helping to damage the CSS Tennessee and destroy artillery batteries of the Confederate States Army at Fort Morgan, even as the enemy's shell and shot damaged his ship and killed several of his fellow crewmen. For those actions, he was awarded his nation's highest honor for bravery on December 31, 1864.

The military forces of the Confederate States, also known as Confederate forces or the Confederate Armed Forces and Confederate States Armed Forces, were the military services responsible for the defense of the Confederacy during its existence (1861–1865).

The Confederate States War Department was a cabinet-level department in the government of the Confederate States of America responsible for the administration of the affairs of the Confederate States Army. The War Department was led by the Confederate States Secretary of War. During its existence, the War Department was the largest department of the Civil Service in the Confederacy.

Abraham Myers was a military officer in the United States and Confederate States Armies.
The Jeff. Davis Legion was a cavalry regiment of the Confederate States Army. Made up of companies from Mississippi, Alabama, and Georgia; it fought primarily in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. In 1865, it was reassigned to the Army of Tennessee, surrendering at Greensboro, N.C.

The 9th Arkansas Infantry Regiment was a regiment of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. It served in the Western Theater, seeing action in the Vicksburg, Tennessee and Georgia campaigns. Due to attrition; the 9th Arkansas was consolidated several times with other Arkansas regiments, finally merging in 1865 into the 1st Arkansas Consolidated Mounted Rifles.
The following list is a bibliography of American Civil War Confederate military unit histories and are generally available through inter-library loan. More details on each book are available at WorldCat. For an overall national view, see Bibliography of the American Civil War. For histories of the Union, see Bibliography of American Civil War Union military unit histories. For a guide to web sources see: Carter, Alice E.; Jensen, Richard. The Civil War on the Web: A Guide to the Very Best Sites—Completely Revised and Updated (2003).

Ira Roe Foster was a teacher, medical doctor, attorney, soldier, businessman, and politician from South Carolina. During the 1840s, Foster served as brigadier general in the Georgia Militia.

The Virginia Secession Convention of 1861 was called in the state capital of Richmond to determine whether Virginia would secede from the United States, govern the state during a state of emergency, and write a new Constitution for Virginia, which was subsequently voted down in a referendum under the Confederate Government.
Subscription required