
Romanos I Lakapenos or Lekapenos, Latinized as Romanus I Lecapenus, was Byzantine emperor from 920 until his deposition in 944, serving as regent for and senior co-ruler of the young Constantine VII.

Romanos II was Byzantine Emperor from 959 to 963. He succeeded his father Constantine VII at the age of twenty-one and died suddenly and mysteriously four years later. His wife Theophano helped their sons Basil II and Constantine VIII to ultimately succeed him in 976.

Romanos III Argyros, or Argyropoulos was Byzantine Emperor from 1028 until his death. He was a Byzantine noble and senior official in Constantinople when the dying Constantine VIII forced him to divorce his wife and marry the emperor's daughter Zoë. Upon Constantine's death three days later, Romanos took the throne.
This is an alphabetical index of people, places, things, and concepts related to or originating from the Byzantine Empire. Feel free to add more, and create missing pages. You can track changes to the articles included in this list from here.

The Catepanateof Italy was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 965 until 1071. At its greatest extent, it comprised mainland Italy south of a line drawn from Monte Gargano to the Gulf of Salerno. North of that line, Amalfi and Naples also maintained allegiance to Constantinople through the catepan. The Italian region of Capitanata derives its name from katepanikion.
Argyrus was a Lombard nobleman and Byzantine general, son of the Lombard hero Melus. He was born in Bari.

Mihailo Vojislavljević was a medieval Serbian king and the ruler of Dioclea (Duklja), from 1046 to 1081 initially as a Byzantine vassal holding the title of protospatharios, then after 1077 as nominally serving Pope Gregory VII, addressed as "King of the Slavs". He had alienated himself from the Byzantines when he supported a Bulgarian Uprising of Georgi Voyteh, after which he then sought to gain support in the West. In 1077 he received a royal insignia by Gregory VII in the aftermath of the Church schism of 1054.

The history of Islam in Sicily and southern Italy began with Arab colonization in Sicily, at Mazara, which was captured in 827. The subsequent rule of Sicily and Malta started in the 10th century. The Emirate of Sicily lasted from 831 until 1061, and controlled the whole island by 902. Though Sicily was the primary Muslim stronghold in Italy, some temporary footholds, the most substantial of which was the port city of Bari, were established on the mainland peninsula, especially in mainland southern Italy, though Arab raids, mainly those of Muhammad I ibn al-Aghlab, reached as far north as Naples, Rome and the northern region of Piedmont. The Arab raids were part of a larger struggle for power in Italy and Europe, with Christian Byzantine, Frankish, Norman and indigenous Italian forces also competing for control. Arabs were sometimes allied with various Christian factions against other factions.
Michael Spondyles was a high-ranking Byzantine courtier who became governor of Antioch, and then Apulia and Calabria.
Michael Protospatharios was the Byzantine catepan of Italy from 1031 to 1033. He was sent to Bari after his predecessor, Pothos Argyrus, was killed in battle with the Saracens who took Cassano allo Ionio in Calabria. Michael was high and lofty official in the imperial court of Constantinople. He held several high-ranking titles. At the height of his career, his full title was: ἐπὶ τῶν οἰκιακῶν, κατεπάνω Ἰταλίας, κριτὴς τοῦ βήλου καί τοῦ ἱπποδρόμου, that is, "Chamberlain, catepan of Italy, and kritēs of the vēlon and the Hippodrome". The kritēs was probably an officer in charge of processing requests for the audience of the emperor. Michael arrived in Italy early in 1032 with a new army, composed not only of recruits from the West or the auxiliaries, but also from the elite troops of Asia Minor and Syria. It is unknown what became of this grand army, however, as Michael was replaced in 1033 by Constantinos Opos.
Constantine Lips was a Byzantine aristocrat and admiral who lived in the later 9th and early 10th centuries. He was killed in 917 at the Battle of Acheloos against Bulgaria. Constantine Lips is most notable for his foundation of the convent bearing his name at Constantinople.
The Excubitors were founded in c. 460 as an imperial guard-unit by the Byzantine emperor Leo I the Thracian. The 300-strong force, originally recruited from among the warlike mountain tribe of the Isaurians, replaced the older Scholae Palatinae as the main imperial bodyguards. The Excubitors remained an active military unit for the next two centuries, although, as imperial bodyguards, they did not often go on campaign. Their commander, the Count of the Excubitors, soon acquired great influence. Justin I was able to use this position to rise to the throne in 518, and thereafter the Counts of the Excubitors were among the main political power-holders of their day; two more, Tiberius II Constantine and Maurice, rose to become emperors in the late 6th century.

The Byzantine Empire was ruled by the Isaurian dynasty from 717 to 802. The Isaurian emperors were successful in defending and consolidating the empire against the caliphates after the onslaught of the early Muslim conquests, but were less successful in Europe, where they suffered setbacks against the Bulgars, had to give up the Exarchate of Ravenna, and lost influence over Italy and the papacy to the growing power of the Franks.
The Hikanatoi, sometimes Latinized as Hicanati, were one of the Byzantine tagmata, the elite guard units based near the imperial capital of Constantinople. Founded in the early 9th century, it survived until the late 11th century.
Michael Lachanodrakon was a distinguished Byzantine general and fanatical supporter of the policy of iconoclasm under Emperor Constantine V. As a result of his iconoclast zeal, in 766 he rose to high office as governor of the Thracesian Theme, and instigated a series of repressive measures against iconophile practices, particularly targeting the monasteries. A talented general, he also led a series of campaigns against the Arabs of the Abbasid Caliphate before being dismissed from office in about 782. Restored to imperial favour in 790, he fell at the Battle of Marcellae against the Bulgars in 792.
Constantine Opos was a notable Byzantine general and aristocrat in the first half of the reign of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos. He participated in the wars against the Normans and the Seljuk Turks, eventually reaching the rank of megas doux.
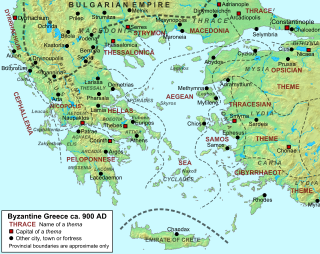
The Theme of Samos was a Byzantine military-civilian province, located in the eastern Aegean Sea, established in the late 9th century. As one of the Byzantine Empire's three dedicated naval themes, it served chiefly to provide ships and troops for the Byzantine navy.

Byzantine Anatolia refers to the peninsula of Anatolia during the rule of the Byzantine Empire. Anatolia was of vital importance to the empire following the Muslim invasion of Syria and Egypt during the reign of the Byzantine Emperor Heraclius in the years 634–645 AD. Over the next two hundred and fifty years, the region suffered constant raids by Arab Muslim forces raiding mainly from the cities of Antioch, Tarsus, and Aleppo near the Anatolian borders. However, the Byzantine Empire maintained control over the Anatolian peninsula until the High Middle Ages, when imperial authority in the area began to collapse.
Marianos Argyros was a Byzantine aristocrat and member of the Argyros family. A monk, in 944 he supported the assumption of sole rule by Constantine VII, and was allowed to leave the monastery and enter imperial service. He held a succession of senior military commands, fighting in southern Italy against local rebels and the Fatimids, and in the Balkans against the Magyars. In 963, he tried to oppose the takeover of the imperial throne by the general Nikephoros Phokas by assuming control over Constantinople and arresting his father, Bardas Phokas the Elder. During the ensuing clashes, he was hit on the head by a platter and died on the next day, 16 August.








