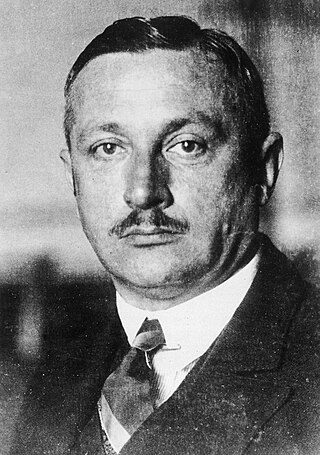The chancellor of Austria, officially the federal chancellor the Republic of Austria, is the head of government of the Republic of Austria.

The president of Austria is the head of state of the Republic of Austria.

The Constitution of the German Reich, usually known as the Weimar Constitution, was the constitution that governed Germany during the Weimar Republic era (1919–1933). The constitution declared Germany to be a democratic parliamentary republic with a legislature elected under proportional representation. Universal suffrage was established, with a minimum voting age of 20. The constitution technically remained in effect throughout the Nazi era from 1933 to 1945 as well as during the Allied occupation of Germany from 1945 to 1949, though practically it had been repealed by the Enabling Act of 1933 and thus its various provisions and protections went unenforced for the duration of Nazi rule, and after World War II, the power of the Allied Control Council and four occupying powers once again stood above the provisions of the constitution.

Gustav Adolf Bauer was a German Social Democratic Party leader and the chancellor of Germany from June 1919 to March 1920. Prior to that, he was minister of labour in the last cabinet of the German Empire and during most of the German Revolution that preceded the formal establishment of the Weimar Republic.

The president of the Reich was the German head of state under the Weimar constitution, which was officially in force from 1919 to 1945. In English he was usually simply referred to as the president of Germany.

A Landtag is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non-federal matters.

Karl Josef Seitz was an Austrian politician of the Social Democratic Workers' Party. He served as member of the Imperial Council, President of the National Council and Mayor of Vienna.

The Parlamentarischer Rat was the West German constituent assembly in Bonn that drafted and adopted the constitution of West Germany, the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, promulgated on 23 May 1949.

The Federal Constitution of Austria is the body of all constitutional law of the Republic of Austria on the federal level. It is split up over many different acts. Its centerpiece is the Federal Constitutional Law (Bundes-Verfassungsgesetz) (B-VG), which includes the most important federal constitutional provisions.
The Christian Social Party was a major conservative political party in the Cisleithanian crown lands of Austria-Hungary and under the First Austrian Republic, from 1891 to 1934. The party was affiliated with Austrian nationalism that sought to keep Catholic Austria out of the State of Germany founded in 1871, which it viewed as Protestant and Prussian-dominated; it identified Austrians on the basis of their predominantly Catholic religious identity as opposed to the predominantly Protestant religious identity of the Prussians.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 19 January 1919, although members of the standing army in the east did not vote until 2 February. The elections were the first of the new Weimar Republic, which had been established after World War I and the Revolution of 1918–19, and the first with women's suffrage. The previous constituencies, which heavily overrepresented rural areas, were scrapped, and the elections held using a form of proportional representation. The voting age was also lowered from 25 to 20. Austrian citizens living in Germany were allowed to vote, with German citizens living in Austria being allowed to vote in the February 1919 Constitutional Assembly elections.

The First Austrian Republic, officially the Republic of Austria, was created after the signing of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye on 10 September 1919—the settlement after the end of World War I which ended the Habsburg rump state of Republic of German-Austria—and ended with the establishment of the Austrofascist Federal State of Austria based upon a dictatorship of Engelbert Dollfuss and the Fatherland's Front in 1934. The Republic's constitution was enacted on 1 October 1920 and amended on 7 December 1929. The republican period was increasingly marked by violent strife between those with left-wing and right-wing views, leading to the July Revolt of 1927 and the Austrian Civil War of 1934.
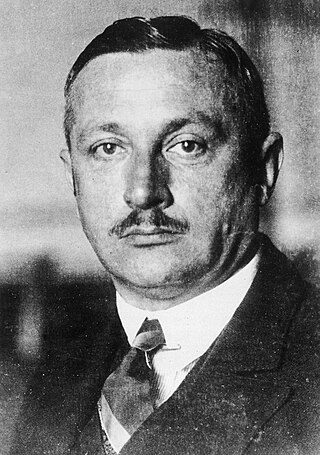
Rudolf Ramek was an Austrian Christian Social politician, who served as Chancellor of Austria from 1924 to 1926.

The Government of Austria is the executive cabinet of the Republic of Austria. It consists of the chancellor, who is the head of government, the vice chancellor and the ministers.

The Council of the People's Deputies was the provisional government of Germany during the first part of the German Revolution, from 10 November 1918 to 13 February 1919. Formed initially by three members each from Germany's two main socialist parties, it shaped the transition from the Empire to the Weimar Republic.

Michael Mayr was an Austrian politician, who served as Chancellor of Austria in the First Austrian Republic from July 1920 to June 1921. He was a member of the Christian Social Party, and by profession a historian.

The Weimar National Assembly, officially the German National Constitutional Assembly, was the popularly elected constitutional convention and de facto parliament of Germany from 6 February 1919 to 21 May 1920. As part of its duties as the interim government, it debated and reluctantly approved the Treaty of Versailles that codified the peace terms between Germany and the victorious Allies of World War I. The Assembly drew up and approved the Weimar Constitution that was in force from 1919 to 1933. With its work completed, the National Assembly was dissolved on 21 May 1920. Following the election of 6 June 1920, the new Reichstag met for the first time on 24 June 1920, taking the place of the Assembly.

The chancellor of Germany, officially the federal chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany, is the head of the federal government of Germany, and the commander-in-chief of the German Armed Forces during wartime. The chancellor is the chief executive of the Federal Cabinet and heads the executive branch. The chancellor is elected by the Bundestag on the proposal of the federal president and without debate.

The Prussian Constitution of 1920 formed the legal framework for the Free State of Prussia, a constituent state of the Weimar Republic, from 1918 to 1947. It was based on democratic parliamentary principles and replaced the Constitution of 1848/50. During the National Socialist era, it was eroded to the point of irrelevance and following World War II lost legal force when the state of Prussia was abolished by the Allies in 1947.

The Federal Constitutional Law is a federal constitutional law in Austria serving as the centerpiece of the Constitution. It establishes Austria as a democratic federal parliamentary republic.