Related Research Articles

A central processing unit (CPU)—also called a central processor or main processor—is the most important processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs).
The control unit (CU) is a component of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) that directs the operation of the processor. A CU typically uses a binary decoder to convert coded instructions into timing and control signals that direct the operation of the other units.
In computing, a context switch is the process of storing the state of a process or thread, so that it can be restored and resume execution at a later point, and then restoring a different, previously saved, state. This allows multiple processes to share a single central processing unit (CPU), and is an essential feature of a multiprogramming or multitasking operating system. In a traditional CPU, each process - a program in execution - utilizes the various CPU registers to store data and hold the current state of the running process. However, in a multitasking operating system, the operating system switches between processes or threads to allow the execution of multiple processes simultaneously. For every switch, the operating system must save the state of the currently running process, followed by loading the next process state, which will run on the CPU. This sequence of operations that stores the state of the running process and the loading of the following running process is called a context switch.

In digital computers, an interrupt is a request for the processor to interrupt currently executing code, so that the event can be processed in a timely manner. If the request is accepted, the processor will suspend its current activities, save its state, and execute a function called an interrupt handler to deal with the event. This interruption is often temporary, allowing the software to resume normal activities after the interrupt handler finishes, although the interrupt could instead indicate a fatal error.
In processor design, microcode serves as an intermediary layer situated between the central processing unit (CPU) hardware and the programmer-visible instruction set architecture of a computer, also known as its machine code. It consists of a set of hardware-level instructions that implement the higher-level machine code instructions or control internal finite-state machine sequencing in many digital processing components. While microcode is utilized in general-purpose CPUs in contemporary desktops, it also functions as a fallback path for scenarios that the faster hardwired control unit is unable to manage.

The Original Chip Set (OCS) is a chipset used in the earliest Commodore Amiga computers and defined the Amiga's graphics and sound capabilities. It was succeeded by the slightly improved Enhanced Chip Set (ECS) and the greatly improved Advanced Graphics Architecture (AGA).

The CDC 6600 was the flagship of the 6000 series of mainframe computer systems manufactured by Control Data Corporation. Generally considered to be the first successful supercomputer, it outperformed the industry's prior recordholder, the IBM 7030 Stretch, by a factor of three. With performance of up to three megaFLOPS, the CDC 6600 was the world's fastest computer from 1964 to 1969, when it relinquished that status to its successor, the CDC 7600.
The Motorola 68000 series is a family of 32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessors. During the 1980s and early 1990s, they were popular in personal computers and workstations and were the primary competitors of Intel's x86 microprocessors. They were best known as the processors used in the early Apple Macintosh, the Sharp X68000, the Commodore Amiga, the Sinclair QL, the Atari ST and Falcon, the Atari Jaguar, the Sega Genesis, the Philips CD-i, the Capcom System I (Arcade), the AT&T UNIX PC, the Tandy Model 16/16B/6000, the Sun Microsystems Sun-1, Sun-2 and Sun-3, the NeXT Computer, NeXTcube, NeXTstation, and NeXTcube Turbo, early Silicon Graphics IRIS workstations, computers from MASSCOMP, the Texas Instruments TI-89/TI-92 calculators, the Palm Pilot, the Control Data Corporation CDCNET Device Interface, and the Space Shuttle. Although no modern desktop computers are based on processors in the 680x0 series, derivative processors are still widely used in embedded systems.

The Intel 8085 ("eighty-eighty-five") is an 8-bit microprocessor produced by Intel and introduced in March 1976. It is software-binary compatible with the more-famous Intel 8080 with only two minor instructions added to support its added interrupt and serial input/output features. However, it requires less support circuitry, allowing simpler and less expensive microcomputer systems to be built. The "5" in the part number highlighted the fact that the 8085 uses a single +5-volt (V) power supply by using depletion-mode transistors, rather than requiring the +5 V, −5 V and +12 V supplies needed by the 8080. This capability matched that of the competing Z80, a popular 8080-derived CPU introduced the year before. These processors could be used in computers running the CP/M operating system.
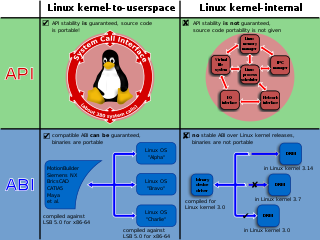
In computing, a system call is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the operating system on which it is executed. This may include hardware-related services, creation and execution of new processes, and communication with integral kernel services such as process scheduling. System calls provide an essential interface between a process and the operating system.
In computer science, subnormal numbers are the subset of denormalized numbers that fill the underflow gap around zero in floating-point arithmetic. Any non-zero number with magnitude smaller than the smallest positive normal number is subnormal, while denormal can also refer to numbers outside that range.

A memory management unit (MMU), sometimes called paged memory management unit (PMMU), is a computer hardware unit that examines all memory references on the memory bus, translating these requests, known as virtual memory addresses, into physical addresses in main memory.

PIC is a family of microcontrollers made by Microchip Technology, derived from the PIC1650 originally developed by General Instrument's Microelectronics Division. The name PIC initially referred to Peripheral Interface Controller, and is currently expanded as Programmable Intelligent Computer. The first parts of the family were available in 1976; by 2013 the company had shipped more than twelve billion individual parts, used in a wide variety of embedded systems.
JTAG is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture.
In digital electronics, especially computing, hardware registers are circuits typically composed of flip flops, often with many characteristics similar to memory, such as:

The Clipper architecture is a 32-bit RISC-like instruction set architecture designed by Fairchild Semiconductor. The architecture never enjoyed much market success, and the only computer manufacturers to create major product lines using Clipper processors were Intergraph and High Level Hardware, although Opus Systems offered a product based on the Clipper as part of its Personal Mainframe range. The first processors using the Clipper architecture were designed and sold by Fairchild, but the division responsible for them was subsequently sold to Intergraph in 1987; Intergraph continued work on Clipper processors for use in its own systems.

The Signetics 2650 was an 8-bit microprocessor introduced in July 1975. According to Adam Osborne's book An Introduction to Microprocessors Vol 2: Some Real Products, it was "the most minicomputer-like" of the microprocessors available at the time. A combination of missing features and odd memory access limited its appeal, and the system saw little use in the market.
The Task Control Block (TCB) contains the state of a task in, e.g., OS/360 and successors on IBM System/360 architecture and successors.
ntoskrnl.exe, also known as the kernel image, contains the kernel and executive layers of the Microsoft Windows NT kernel, and is responsible for hardware abstraction, process handling, and memory management. In addition to the kernel and executive mentioned earlier, it contains the cache manager, security reference monitor, memory manager, scheduler (Dispatcher), and blue screen of death.
The IBM System/360 architecture is the model independent architecture for the entire S/360 line of mainframe computers, including but not limited to the instruction set architecture. The elements of the architecture are documented in the IBM System/360 Principles of Operation and the IBM System/360 I/O Interface Channel to Control Unit Original Equipment Manufacturers' Information manuals.