Open Graphics Library (OpenGL) is a cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics. The API is typically used to interact with a graphics processing unit (GPU), to achieve hardware-accelerated rendering.

Windows Millennium Edition, or Windows Me, is a graphical operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of operating systems. It is the successor to Windows 98, and was released to manufacturing on June 19, 2000, with general availability on September 14, 2000.
GeForce is a brand of graphics processing units (GPUs) designed by Nvidia. As of the GeForce 20 Super series, there have been sixteen iterations of the design. The first GeForce products were discrete GPUs designed for add-on graphics boards, intended for the high-margin PC gaming market, and later diversification of the product line covered all tiers of the PC graphics market, ranging from cost-sensitive GPUs integrated on motherboards, to mainstream add-in retail boards. Most recently, GeForce technology has been introduced into Nvidia's line of embedded application processors, designed for electronic handhelds and mobile handsets.

The GeForce FX or "GeForce 5" series is a line of graphics processing units from the manufacturer NVIDIA.

The GeForce 6 Series is Nvidia's sixth generation of GeForce graphic processing units. Launched on April 14, 2004, the GeForce 6 family introduced PureVideo post-processing for video, SLI technology, and Shader Model 3.0 support.

Alienware is an American computer hardware subsidiary of Dell. Their products are designed for gaming and can be identified by their alien-themed designs. Alienware was founded in 1996 by Nelson Gonzalez and Alex Aguila. The company's corporate headquarters is located in The Hammocks, in Miami, Florida.

The nForce4 is a motherboard chipset released by Nvidia in October 2004. The chipset supports AMD 64-bit processors and Intel Pentium 4 LGA 775 processors.
Dell XPS is a line of high performance computers manufactured by Dell.

Quadro is Nvidia's brand for graphics cards intended for use in workstations running professional computer-aided design (CAD), computer-generated imagery (CGI), digital content creation (DCC) applications, scientific calculations and machine learning.

The Radeon R100 is the first generation of Radeon graphics chips from ATI Technologies. The line features 3D acceleration based upon Direct3D 7.0 and OpenGL 1.3, and all but the entry-level versions offloading host geometry calculations to a hardware transform and lighting (T&L) engine, a major improvement in features and performance compared to the preceding Rage design. The processors also include 2D GUI acceleration, video acceleration, and multiple display outputs. "R100" refers to the development codename of the initially released GPU of the generation. It is the basis for a variety of other succeeding products.

Tweak UI is a free application, released in 1996 by Microsoft for customizing the Microsoft Windows operating system's user interface. Tweak UI modifies the Windows Registry in the same way as a user could edit it manually with a program such as RegEdit, but provides a simple graphical user interface that does not need knowledge of the registry structure, is quicker and easier to use, and not susceptible to registry damage due to user error.

Omega Drivers were unofficial, third-party device drivers for ATI and NVIDIA graphics cards, created by Angel Trinidad. They differed from the official drivers in that they offer more customization and extra features. They are compatible with some ATI graphics cards and some NVIDIA cards that use Detonator drivers.
The AMD 700 chipset series is a set of chipsets designed by ATI for AMD Phenom processors to be sold under the AMD brand. Several members were launched in the end of 2007 and the first half of 2008, others launched throughout the rest of 2008.
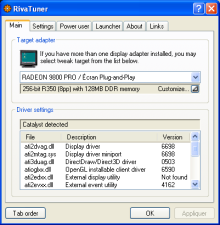
RivaTuner is a freeware overclocking and hardware monitoring program that was first developed by Alexey Nicolaychuk in 1997 for the NVIDIA video cards. It was a pioneering application that influenced the design of subsequent freeware graphics card overclocking and monitoring utilities. It supports nVidia GPUs from the Riva TNT to the GeForce 700 Series, and also has limited support for the ATI/AMD Radeon series of video cards from the Radeon 8500 and above.
ATI Tray Tools (ATT) is a freeware program developed by Ray Adams for ATI Radeon video cards.
The graphics processing unit (GPU) codenamed Radeon R600 is the foundation of the Radeon HD 2000 series and the FireGL 2007 series video cards developed by ATI Technologies. The HD 2000 cards competed with nVidia's GeForce 8 series.
The R200 is the second generation of GPUs used in Radeon graphics cards and developed by ATI Technologies. This GPU features 3D acceleration based upon Microsoft Direct3D 8.1 and OpenGL 1.3, a major improvement in features and performance compared to the preceding Radeon R100 design. The GPU also includes 2D GUI acceleration, video acceleration, and multiple display outputs. "R200" refers to the development codename of the initially released GPU of the generation. It is the basis for a variety of other succeeding products.
The GeForce 800M Series is a family of graphics processing units by Nvidia for laptop PCs. It consists of rebrands of mobile versions of the GeForce 700 series and some newer chips that are lower end compared to the rebrands.

Serving as the high-end introduction to Maxwell, named after James Clerk Maxwell, the GeForce 900 series is a family of graphics processing units developed by Nvidia, succeeding the GeForce 700 series. They are produced with TSMC's 28 nm process.