Copper chloride may refer to:
- Copper(I) chloride (cuprous chloride), CuCl, mineral name nantokite
- Copper(II) chloride (cupric chloride), CuCl2, mineral name eriochalcite
Copper chloride may refer to:
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of cations and anions. Salts are composed of related numbers of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral. These component ions can be inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate ; and can be monatomic, such as fluoride (F−) or polyatomic, such as sulfate.
A halide is a binary phase, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a, e.g., fluoride, chloride, or theoretically tennesside compound. The alkali metals combine directly with halogens under appropriate conditions forming halides of the general formula, MX. Many salts are halides; the hal- syllable in halide and halite reflects this correlation. All Group 1 metals form halides that are white solids at room temperature.

Iron(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula. Also called ferric chloride, it is a common compound of iron in the +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous compound is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 307.6 °C. The color depends on the viewing angle: by reflected light the crystals appear dark green, but by transmitted light they appear purple-red.

Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) is an inorganic compound which is a white solid under ambient conditions. It is poorly soluble in water. Lead(II) chloride is one of the most important lead-based reagents. It also occurs naturally in the form of the mineral cotunnite.

Atacamite is a copper halide mineral: a copper(II) chloride hydroxide with formula Cu2Cl(OH)3. It was first described for deposits in the Atacama Desert of Chile in 1801 by D. de Fallizen. The Atacama Desert is also the namesake of the mineral.

In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.

Aluminium chloride (AlCl3), also known as aluminium trichloride, describe compounds with the formula AlCl3(H2O)n (n = 0 or 6). They consist of aluminium and chlorine atoms in a 1:3 ratio, and one form also contains six waters of hydration. Both are white solids, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving a yellow color.

Verdigris is the common name for a green pigment obtained through the application of acetic acid to copper plates or the natural patina formed when copper, brass or bronze is weathered and exposed to air or seawater over time. It is usually a basic copper carbonate (Cu
2CO
3(OH)2), but near the sea will be a basic copper chloride (Cu2(OH)3Cl). If acetic acid is present at the time of weathering, it may consist of copper(II) acetate.

Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2).
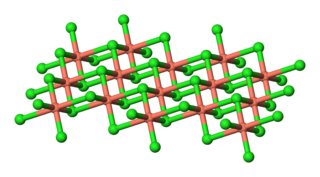
Copper(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. This is a light brown solid, which slowly absorbs moisture to form a blue-green dihydrate.

Tenorite is a copper oxide mineral with the chemical formula CuO.
Cell notation or cell representation in chemistry is a shorthand method of expressing a reaction in an electrochemical cell.
Bronze disease is an irreversible and nearly inexorable corrosion process that occurs when chlorides come into contact with bronze or other copper-bearing alloys. It can occur as both a dark green coating, or as a much lighter whitish fuzzy or furry green coating. It is not a bacterial infection, but the result of a chemical reaction with the chlorides that usually occurs due to contamination of the bronze object by saltwater or from burial in specific types of soil where chloride salts are present. If not treated, complete destruction of the affected artifact is possible. Treatment is very difficult, costly and not always effective. Transfer of chlorides from the contaminated artefact to other artefacts can spread the condition.

Boleite is a complex halide mineral with formula: KPb26Ag9Cu24(OH)48Cl62. It was first described in 1891 as an oxychloride mineral. It is an isometric mineral which forms in deep-blue cubes. There are numerous minerals related to boleite, such as pseudoboleite, cumengite, and diaboleite, and these all have the same complex crystal structure. They all contain bright-blue cubic forms and are formed in altered zones of lead and copper deposits, produced during the reaction of chloride bearing solutions with primary sulfide minerals.

Calumetite is a natural rarely occurring mineral. It was discovered in 1963 at the Centennial Mine near Calumet, Michigan, United States. Calumetite was first discovered along with anthonyite. It has a chemical formula of Cu(OH,Cl)
2•2(H
2O).

Anthonyite is a hydrous secondary copper halide mineral with chemical formula of Cu(OH,Cl)2•3(H2O).
Dicopper chloride trihydroxide is the chemical compound with the formula Cu2(OH)3Cl. It is often referred to as tribasic copper chloride (TBCC), copper trihydroxyl chloride or copper hydroxychloride. It is a greenish crystalline solid encountered in mineral deposits, metal corrosion products, industrial products, art and archeological objects, and some living systems. It was originally manufactured on an industrial scale as a precipitated material used as either a chemical intermediate or a fungicide. Since 1994, a purified, crystallized product has been produced at the scale of thousands of tons per year, and used extensively as a nutritional supplement for animals.
Chrysothallite is a rare thallium-bearing chloride mineral with the formula K6Cu6Tl3+Cl17(OH)4•H2O. Chrysothallite is unique in being only the second mineral with essential trivalent thallium, a feature shared with natural thallium(III) oxide, avicennite. Another examples of natural thallium chlorides are steropesite, Tl3BiCl6, and lafossaite, TlCl. Chrysothallite is one of numerous fumarolic minerals discovered among fumarolic sites of the Tolbachik volcano, Kamchatka, Russia The mineral is named in allusion to its colour and thallium content.
Potassium tetrachloridocuprate(II) is a salt with chemical formula K
2CuCl
4, also written as (K+
)2·[CuCl
4]2−.