
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement.
A halide is a binary phase, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a, e.g., fluoride, chloride, or theoretically tennesside compound. The alkali metals combine directly with halogens under appropriate conditions forming halides of the general formula, MX. Many salts are halides; the hal- syllable in halide and halite reflects this correlation. All Group 1 metals form halides that are white solids at room temperature.
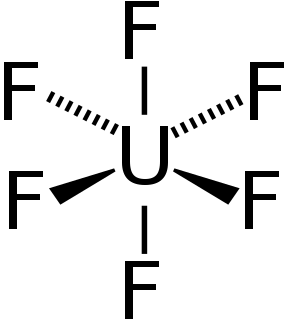
Uranium hexafluoride (UF6), colloquially known as "hex" in the nuclear industry, is a compound used in the process of enriching uranium, which produces fuel for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.

Copper(II) sulfate, also known as copper sulphate, are the inorganic compounds with the chemical formula CuSO4(H2O)x, where x can range from 0 to 5. The pentahydrate (x = 5) is the most common form. Older names for this compound include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper, and Roman vitriol.

Copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula CuO. A black solid, it is one of the two stable oxides of copper, the other being Cu2O or copper(I) oxide (cuprous oxide). As a mineral, it is known as tenorite. It is a product of copper mining and the precursor to many other copper-containing products and chemical compounds.
A gas laser is a laser in which an electric current is discharged through a gas to produce coherent light. The gas laser was the first continuous-light laser and the first laser to operate on the principle of converting electrical energy to a laser light output. The first gas laser, the Helium–neon laser (HeNe), was co-invented by Iranian-American physicist Ali Javan and American physicist William R. Bennett, Jr., in 1960. It produced a coherent light beam in the infrared region of the spectrum at 1.15 micrometres.
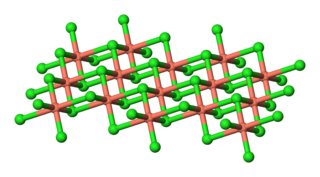
Copper(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. This is a light brown solid, which slowly absorbs moisture to form a blue-green dihydrate.

In coordination chemistry, metal ammine complexes are metal complexes containing at least one ammonia (NH3) ligand. "Ammine" is spelled this way due to historical reasons; in contrast, alkyl or aryl bearing ligands are spelt with a single "m". Almost all metal ions bind ammonia as a ligand, but the most prevalent examples of ammine complexes are for Cr(III), Co(III), Ni(II), Cu(II) as well as several platinum group metals.

Copper(II) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuF2. It is a white crystalline, hygroscopic solid with a rutile-type crystal structure, similar to other fluorides of chemical formulae MF2 (where M is a metal).
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry is a systematic method of naming inorganic chemical compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. Ideally, every inorganic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous formula can be determined. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry.

Copper monosulfide is a chemical compound of copper and sulfur. It was initially thought to occur in nature as the dark indigo blue mineral covellite. However, it was later shown to be rather a cuprous compound, formula Cu+3S(S2). CuS is a moderate conductor of electricity. A black colloidal precipitate of CuS is formed when hydrogen sulfide, H2S, is bubbled through solutions of Cu(II) salts. It is one of a number of binary compounds of copper and sulfur (see copper sulfide for an overview of this subject), and has attracted interest because of its potential uses in catalysis and photovoltaics.

Copper arsenate (Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O), also called copper orthoarsenate, tricopper arsenate, cupric arsenate, or tricopper orthoarsenate, is a blue or bluish-green powder insoluble in water and alcohol and soluble in aqueous ammonium and dilute acids. Its CAS number is 7778-41-8 or 10103-61-4.

Tellurium tetrafluoride, TeF4, is a stable, white, hygroscopic crystalline solid and is one of two fluorides of tellurium. The other binary fluoride is tellurium hexafluoride. The widely reported Te2F10 has been shown to be F5TeOTeF5 There are other tellurium compounds that contain fluorine, but only the two mentioned contain solely tellurium and fluorine. Tellurium difluoride, TeF2, and ditellurium fluoride, Te2F are not known.
Fluorosilicate glass (FSG) is a glass material composed primarily of fluorine, silicon and oxygen. It has a number of uses in industry and manufacturing, especially in semiconductor fabrication where it forms an insulating dielectric. The related fluorosilicate glass-ceramics have good mechanical and chemical properties.

Organocopper compounds in organometallic chemistry contain carbon to copper chemical bonds. Organocopper chemistry is the science of organocopper compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis and reactions. They are reagents in organic chemistry.

Copper(I) fluoride or cuprous fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuF. Its existence is uncertain. It was reported in 1933 to have a sphalerite-type crystal structure. Modern textbooks state that CuF is not known, since fluorine is so electronegative that it will always oxidise copper to its +2 oxidation state. Complexes of CuF such as [(Ph3P)3CuF] are, however, known and well characterised.
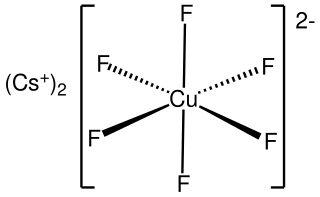
Caesium hexafluorocuprate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cs
2CuF
6. It is a red solid that degrades upon contact with water. It was first prepared be heating CsCuCl
3 and caesium fluoride at 410°C under 350 atmospheres of fluorine:
Copper hydride is a pyrophoric, inorganic compound with the chemical formula (CuH)
n. It is an odourless, metastable, red solid, rarely isolated as a pure composition, that decomposes to the elements. Copper hydride is mainly produced as a reducing agent in organic synthesis and as a precursor to extremely reactive catalysts.

Copper(II) carbonate or cupric carbonate is a chemical compound with formula CuCO
3. At ambient temperatures, it is an ionic solid consisting of copper(II) cations Cu2+
and carbonate anions CO2−
3.













