A corm is an underground part of a plant stem.
Corm may also refer to:
- Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs)
- Corm (surname), list of people with the surname
A corm is an underground part of a plant stem.
Corm may also refer to:

A corm, bulbo-tuber, or bulbotuber is a short, vertical, swollen underground plant stem that serves as a storage organ that some plants use to survive winter or other adverse conditions such as summer drought and heat (perennation).

Iridaceae is a family of plants in order Asparagales, taking its name from the irises, meaning rainbow, referring to its many colours. There are 66 accepted genera with a total of c. 2244 species worldwide. It includes a number of other well known cultivated plants, such as freesias, gladioli and crocuses.
Wesson may refer to
Elephant ear may refer to:

Konjac is a common name of the East and Southeast Asian plant Amorphophallus konjac, which has an edible corm (bulbo-tuber). It is also known as konjaku, konnyaku potato, devil's tongue, voodoo lily, snake palm, or elephant yam.

Taro (, Colocasia esculenta) is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in African, Oceanic, and South Asian cultures Taro is believed to be one of the earliest cultivated plants.

Eleocharis dulcis, the Chinese water chestnut or water chestnut, is a grass-like sedge native to Asia, tropical Africa, and Oceania. It is grown in many countries for its edible corms.
Water chestnut may refer to either of two plants :

Cocoyam is a common name for more than one tropical root crop and vegetable crop belonging to the Arum family and may refer to:

Dipterostemon is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae. Its only species is Dipterostemon capitatus, synonym Dichelostemma capitatum, known by the common names blue dicks, purplehead and brodiaea, native to the Western United States and northwest Mexico.
Éogan or Eógan is an early Irish male name, which also has the hypocoristic and diminutive forms Eoganán, Eóghainin, Eóghain and Eóghainn. In more modern forms of Irish it is written as Eóghan or Eoghan (/'oːəun/).

Cormes is a commune in the Sarthe department in the Pays de la Loire region in north-western France.

Mary McCormic was an American operatic soprano and a professor of opera at the University of North Texas College of Music (1945–1960).

Amorphophallus titanum, the titan arum, is a flowering plant in the family Araceae. It has the largest unbranched inflorescence in the world. The inflorescence of the talipot palm, Corypha umbraculifera, is larger, but it is branched rather than unbranched. A. titanum is endemic to rainforests on the Indonesian island of Sumatra.
Pulaka, Cyrtosperma merkusii, or swamp taro, is a crop grown mainly in Tuvalu and an important source of carbohydrates for the area's inhabitants. It is a "swamp crop" similar to taro, but "with bigger leaves and larger, coarser roots." The same plant is known as ‘‘pulaka’’ in Niue, babai in Kiribati, puraka in Cook Islands, pula’a in Samoa, via kan in Fiji, Pulaka in Tokelau, simiden in Chuuk, swam taro in Papua New Guinea, and navia in Vanuatu.

Cyrtosperma merkusii or giant swamp taro, is a crop grown throughout Oceania and into South and Southeast Asia. It is a riverine and "swamp crop" similar to taro, but "with bigger leaves and larger, coarser roots." There are no demonstrably wild populations today, but it is believed to be native to Indonesia. It is known as puraka in Cook Islands, lak in Yap, babai in Kiribati, iaraj in the Marshall Islands, brak in Palau, babaʻ in the Marianas Islands, pula’a in Samoa, via kana, Pulaka in Lau, Lovo in Fiji, pulaka in Tokelau and Tuvalu, mwahng in Pohnpei, pasruk in Kosrae, simiden in Chuuk, swam taro in Papua New Guinea, navia in Vanuatu and palawan in the Philippines.

In plant morphology, a cataphyll is a reduced, small leaf. Many plants have both "true leaves" (euphylls), which perform most of the photosynthesis, and cataphylls, which are modified to perform other functions.

Daoud Corm (1852–1930), David Corm in English, was an influential Lebanese painter and the father of writer, industrialist and philanthropist Charles Corm. He was a teacher and mentor to the young Khalil Gibran as well as Khalil Saleeby and Habib Srour.
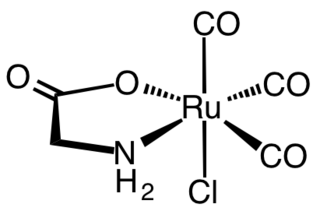
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs) are chemical compounds designed to release controlled amounts of carbon monoxide (CO). CORMs are being developed as potential therapeutic agents to locally deliver CO to cells and tissues, thus overcoming limitations of CO gas inhalation protocols.
Corm is a surname. People with the surname include: