The coulomb (symbol: C) is a unit of electric charge, named after French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb.
Contents
Coulomb may also refer to:
The coulomb (symbol: C) is a unit of electric charge, named after French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb.
Coulomb may also refer to:

The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp, is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to 1 coulomb, or 6.241509074×1018 electrons' worth of charge, moving past a point in a second. It is named after French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836), considered the father of electromagnetism along with Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted.

André-Marie Ampère was a French physicist and mathematician who was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics". He is also the inventor of numerous applications, such as the solenoid and the electrical telegraph. As an autodidact, Ampère was a member of the French Academy of Sciences and professor at the École polytechnique and the Collège de France.

Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be positive or negative. Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with no net charge is referred to as electrically neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects.
Pascal, Pascal's or PASCAL may refer to:

The coulomb (symbol: C) is the unit of electric charge in the International System of Units (SI). In the present version of the SI it is equal to the electric charge delivered by a 1 ampere constant current in 1 second and to 5×1027/801088317 elementary charges, e, (about 6.241509×1018e).
Foucault may refer to:

Charles-Augustin de Coulomb was a French officer, engineer, and physicist. He is best known as the eponymous discoverer of what is now called Coulomb's law, the description of the electrostatic force of attraction and repulsion. He also did important work on friction.
The Coulomb barrier, named after Coulomb's law, which is in turn named after physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, is the energy barrier due to electrostatic interaction that two nuclei need to overcome so they can get close enough to undergo a nuclear reaction.
Charles Coulomb may refer to:
Curie may refer to:
François is a French masculine given name and surname, equivalent to the English name Francis.
The watt is a unit of power named after Scottish engineer James Watt.
Kirchhoff, Kirchoff or Kirchhoffer is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
Charles-Augustin is a given name. Notable people with the name include:
Charles Coulombe may refer to:
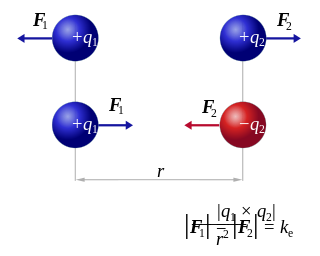
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that calculates the amount of force between two electrically charged particles at rest. This electric force is conventionally called electrostatic force or Coulomb force. Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, hence the name. Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism and maybe even its starting point, as it allowed meaningful discussions of the amount of electric charge in a particle.
Buisson is a French surname and place name. It may refer to:
Cauchy primarily refers to Augustin-Louis Cauchy (1789-1857), French mathematician.