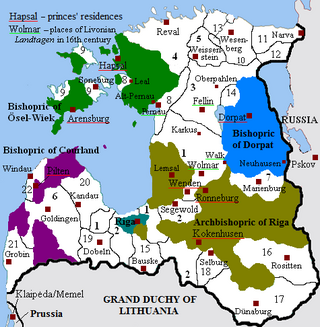
Livonia or in earlier records Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.

A viceroy is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory.

Courland is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. Courland's largest city is Liepāja, which is the third largest city in Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland as they were formerly held by the same duke.
The United Baltic Duchy, or alternatively the Grand Duchy of Livonia, was the name proposed during World War I by leaders of the local Baltic German nobility for a new monarchical state that never came into existence. The attempt to establish a new client state of the German Empire on the territory of what is now Latvia and Estonia was made in 1918, during the German occupation of the former Courland, Livonian and Estonian governorates of the Russian Empire which had ceased to exist after the Bolshevik coup in 1917. The unsuccessful proclamation of a pro-German duchy was first made in April 1918, after the Republic of Estonia had already formally declared full independence.
A viceroyalty was an entity headed by a viceroy. It dates back to the Spanish conquest of the Americas in the sixteenth century.

The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was a duchy in the Baltic region, then known as Livonia, that existed from 1561 to 1569 as a nominally vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently made part of the Crown of the Polish Kingdom from 1569 to 1726 and incorporated into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1726. On March 28, 1795, it was annexed by the Russian Empire in the Third Partition of Poland.

The Governorate of Estonia, also known as the Governorate of Esthonia was a governorate in the Baltic region, along with the Livonian and Courland Governorates. It was a part of the Imperial Russian administration (guberniya), which is located in modern-day northern Estonia and some islands in the West Estonian archipelago, including the islands of Hiiumaa and Vormsi. The Governorate was established in 1796 when Paul I's reform abolished the Viceroyalty (namestnik). Previously, the Reval Governorate existed under Peter I's reign from the Treaty of Nystad, which ceded territory from Sweden to the newly established Russian Empire, until its inexistence in 1783.

Prince Platon Alexandrovich Zubov was the last of Catherine the Great's favourites and the most powerful man in the Russian Empire during the last years of her reign.

A colonial empire is a collective of territories, either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.

The Courland Governorate, also known as the Province of Courland, Governorate of Kurland and known from 1795 to 1796 as the Viceroyalty of Courland was one of the Baltic governorates of the Russian Empire, that is now part of the Republic of Latvia.

The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was the name for a proposed client state of the German Empire during World War I which did not come into existence. It was proclaimed on 8 March 1918, in the German-occupied Courland Governorate by a council composed of Baltic Germans, who offered the crown of the once-autonomous duchy to Kaiser Wilhelm II, despite the existence of a formerly sovereign reigning family in that duchy, the Biron descendants of Ernst Johann von Biron. Although the German Reichstag supported national self-determination for the peoples of the Baltic provinces, the German High Command continued the policy of attaching these territories to the German Reich by relying on the local Baltic Germans.

The Kharkov Governorate was a governorate of the Russian Empire founded in 1835. It embraced the historical region of Sloboda Ukraine. From 1765 to 1780 and from 1796 to 1835 the governorate was called the Sloboda Ukraine Governorate. In 1780-1796 there existed the Kharkov Viceroyalty.

The Caucasus Viceroyalty was the Russian Empire's administrative and political authority in the Caucasus region exercised through the offices of glavnoupravlyayushchiy and namestnik ("viceroy"). These two terms are commonly, but imprecisely, translated into English as viceroy, which is frequently used interchangeably with governor general. More accurately, glavnoupravlyayushchiy is referred to as the High Commissioner of the Caucasus, and namestnik as Viceroy.

Dobeles apriņķis was a historic county of the Courland Governorate and of the Republic of Latvia. Its capital was Dobele (Doblen).

Bauskas apriņķis was a historic county of the Courland Governorate and of the Republic of Latvia. Its capital was Bauska (Bauske).
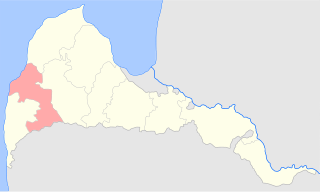
Aizpute County was a historic county of the Courland Governorate and of the Republic of Latvia. Its capital was Aizpute (Hasenpoth).

Kuldīgas apriņķis was a historic county of the Courland Governorate and of the Republic of Latvia. Its capital was Kuldīga (Goldingen).

Talsu apriņķis was a historic county of the Courland Governorate and of the Republic of Latvia. Its capital was Talsi (Talsen).

Jaunjelgavas apriņķis was a historic county of the Courland Governorate and of the Republic of Latvia. Its capital was Jaunjelgava (Friedrichstadt).
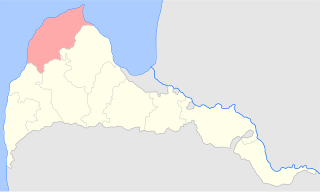
Ventspils County was a historic county of the Courland Governorate and of the Republic of Latvia. Its capital was Ventspils (Windau).
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.














