This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Byzantium or Byzantion was an ancient Greek colony in early antiquity that later became Constantinople, and then Istanbul. Byzantium was colonized by the Greeks from Megara in 657 BC.
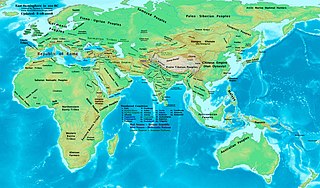
The 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC, started on the first day of 100 BC and ended on the last day of 1 BC. The AD/BC notation does not use a year zero; however, astronomical year numbering does use a zero, as well as a minus sign, so "2 BC" is equal to "year –1". This is the 100th century in the Holocene calendar; it spans the years 9,901 to 10,000. 1st century AD follows.

Perga or Perge was an ancient Anatolian city in modern Turkey, once the capital of Pamphylia Secunda, now in Antalya province on the southwestern Mediterranean coast of Turkey. Today, it is a large site of ancient ruins 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) east of Antalya on the coastal plain. An acropolis located there dates back to the Bronze Age.

Bithynia was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor, adjoining the Propontis, the Thracian Bosporus and the Euxine Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Paphlagonia to the northeast along the Pontic coast, and Phrygia to the southeast towards the interior of Asia Minor.

In Greek mythology, Byzas was the eponymous founder of Byzantium, the city later known as Constantinople and then Istanbul.

Chalcedon was an ancient maritime town of Bithynia, in Asia Minor. It was located almost directly opposite Byzantium, south of Scutari and it is now a district of the city of Istanbul named Kadıköy. The name Chalcedon is a variant of Calchedon, found on all the coins of the town as well as in manuscripts of Herodotus's Histories, Xenophon's Hellenica, Arrian's Anabasis, and other works. Except for a tower, almost no above-ground vestiges of the ancient city survive in Kadıköy today; artifacts uncovered at Altıyol and other excavation sites are on display at the Istanbul Archaeological Museum.

Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians and Celts, it was conquered by the Romans in the 1st century BC and subsequently became the capital of the Roman province of Pannonia Inferior. In 294 AD, Sirmium was proclaimed one of four capitals of the Roman Empire. It was also the capital of the Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum and of Pannonia Secunda. Sirmium was located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in northern Serbia. The site is protected as an Archaeological Site of Exceptional Importance. The modern region of Syrmia (Srem) was named after the city.

Lampsacus was an ancient Greek city strategically located on the eastern side of the Hellespont in the northern Troad. An inhabitant of Lampsacus was called a Lampsacene. The name has been transmitted in the nearby modern town of Lapseki.
Cassandreia or Kassandreia was once one of the most important cities in Ancient Macedonia, founded by and named after Cassander in 316 BC. It was located on the site of the earlier Ancient Greek city of Potidaea, at the isthmus of the Pallene peninsula. The fact that Cassander named it after himself suggests that he may have intended it to be his capital, and if the canal which cuts the peninsula at this point was dug or at least planned in his time, he may have intended to develop his naval forces using it as a base with two harbours on the east and west sides. Cassandreia soon became a great and powerful city, surpassing the other Macedonian towns in wealth. Philip V of Macedon made Cassandreia his main naval base. At the end of the Roman Republic, around 43 BC by order of Brutus a Roman colony was settled by the proconsul Q. Hortensius Hortalus, which 30 BC was resettled by August with the installation of new settlers and took the official name Colonia Iulia Augusta Cassandrensis. The territory of the colony had included within its boundaries the peninsula of Pallini and the district stretched north of the canal to the foot of the mountain Cholomontas. The colony enjoyed ius Italicum, and is mentioned in Pliny the Elder's encyclopaedia and in inscriptions. It was destroyed by the Huns and Slavs around 540 AD.
Zipoetes I, also Zipoites I or Ziboetes I, possibly Tiboetes I was the second independent ruler of Bithynia.
Rufus is one of the most common of the ancient Roman cognomina.

Martinian, who died in 325, was Roman Emperor from July to September 18, 324. He had been appointed co-emperor by Licinius.

Ariassos or Ariassus was a town in Asia Minor built on a steep hillside about 50 kilometres inland from Attaleia.

Lebedus or Lebedos was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League, located south of Smyrna, Klazomenai and neighboring Teos and before Ephesus, which is further south. It was on the coast, ninety stadia (16.65 km) to the east of Cape Myonnesus, and 120 (22.2 km) west of Colophon.
Tium was an ancient settlement, also known as Filyos, on the south coast of the Black Sea at the mouth of the river Billaeus in present-day Turkey.
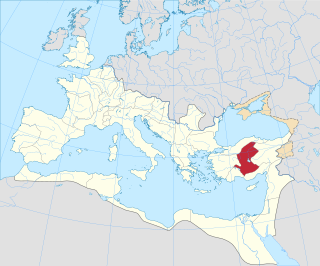
Galatia was the name of a province of the Roman Empire in Anatolia. It was established by the first emperor, Augustus, in 25 BC, covering most of formerly independent Celtic Galatia, with its capital at Ancyra.
Quintus Marcius Crispus was a Roman senator and military officer who served under Julius Caesar during the civil wars of the late republic.












