Related Research Articles

Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a treatment for depression and pain management. Ketamine is a novel compound that was derived from phencyclidine in 1962 in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with fewer hallucinogenic effects.
Treatment-resistant depression is a term used in psychiatry to describe people with major depressive disorder (MDD) who do not respond adequately to a course of appropriate antidepressant medication within a certain time. Definitions of treatment-resistant depression vary, and they do not include a resistance to psychological therapies. Inadequate response has most commonly been defined as less than 50% reduction in depressive symptoms following treatment with at least one antidepressant medication, although definitions vary widely. Some other factors that may contribute to inadequate treatment are: a history of repeated or severe adverse childhood experiences, early discontinuation of treatment, insufficient dosage of medication, patient noncompliance, misdiagnosis, cognitive impairment, low income and other socio-economic variables, and concurrent medical conditions, including comorbid psychiatric disorders. Cases of treatment-resistant depression may also be referred to by which medications people with treatment-resistant depression are resistant to. In treatment-resistant depression adding further treatments such as psychotherapy, lithium, or aripiprazole is weakly supported as of 2019.

Cycloserine, sold under the brand name Seromycin, is a GABA transaminase inhibitor and an antibiotic, used to treat tuberculosis. Specifically it is used, along with other antituberculosis medications, for active drug resistant tuberculosis. It is given by mouth.
The emphasis of the treatment of bipolar disorder is on effective management of the long-term course of the illness, which can involve treatment of emergent symptoms. Treatment methods include pharmacological and psychological techniques.

NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for human and non-human animals; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia.

Esketamine, also known as (S)-ketamine or S(+)-ketamine, is the S(+) enantiomer of ketamine. It is a dissociative hallucinogen drug used as a general anesthetic and as an antidepressant for treatment of depression. It is sold under the brand names Spravato, Ketanest, among others. Esketamine is the active enantiomer of ketamine in terms of NMDA receptor antagonism and is more potent than racemic ketamine.
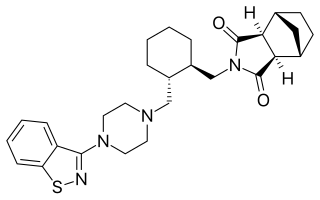
Lurasidone, sold under the trade name Latuda among others, is an antipsychotic medication used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It is taken by mouth.

Samidorphan is an opioid antagonist that in the form of olanzapine/samidorphan is used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Samidorphan reduces the weight gain associated with olanzapine. Samidorphan is taken by mouth.

Rapastinel is a novel antidepressant that was under development by Allergan as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression. It is a centrally active, intravenously administered amidated tetrapeptide that acts as a novel and selective modulator of the NMDA receptor. The drug is a rapid-acting and long-lasting antidepressant as well as robust cognitive enhancer by virtue of its ability to enhance NMDA receptor-mediated signal transduction and synaptic plasticity.

Lanicemine (AZD6765) is a low-trapping NMDA receptor antagonist that was under development by AstraZeneca for the management of severe and treatment-resistant depression. Lanicemine differs from ketamine in that it is a low-trapping NMDA receptor antagonist, showing similar rapid-acting antidepressant effects to ketamine in clinical trials but with little or no psychotomimetic side effects. However, lanicemine did not meet study endpoints, and its development was terminated by AstraZeneca in 2013.

Apimostinel is an investigational antidepressant, acting as a novel and selective modulator of the NMDA receptor. It is currently under development for the acute treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) by Gate Neurosciences, and previously by Naurex and Allergan. As of February 2015, an intravenous formulation of apimostinel has completed a phase IIa clinical trial for MDD.
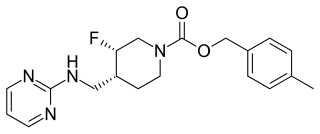
Rislenemdaz is an orally active, selective NMDA receptor subunit 2B (NR2B) antagonist which is under development by Cerecor in the United States as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). In November 2013, phase II clinical trials were initiated, and in the same month, rislenemdaz received Fast Track Designation from the Food and Drug Administration for TRD.

L-4-Chlorokynurenine is an orally active small molecule prodrug of 7-chlorokynurenic acid, a NMDA receptor antagonist. It was investigated as a potential rapid-acting antidepressant.

Dextromethorphan/bupropion (DXM/BUP), sold under the brand name Auvelity, is a combination medication for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Its active components are dextromethorphan (DXM) and bupropion. Patients who stayed on the medication had an average of 11% greater reduction in depressive symptoms than placebo in an FDA approval trial. It is taken as a tablet by mouth.

Tulrampator is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which is under development by RespireRx Pharmaceuticals and Servier for the treatment of major depressive disorder, Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and mild cognitive impairment. Tulrampator was in phase II clinical trial for depression, but failed to show superiority over placebo. There are also phase II clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease and phase I trials for dementia and mild cognitive impairment.

NV-5138 is an orally and centrally active small-molecule drug which is under development by Navitor Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). It directly and selectively activates the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling pathway by binding to and modulating sestrin2, a leucine amino acid sensor and upstream regulatory pathway. The mTORC1 pathway is the same signaling pathway that the NMDA receptor antagonist ketamine activates in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) to mediate its rapid-acting antidepressant effects. A single oral dose of NV-5138 has been found to increase mTORC1 signaling and produce synaptogenesis in the mPFC and to induce rapid antidepressant effects in multiple animal models of depression. Like those of ketamine, these actions require the signaling of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The antidepressant effects following a single dose of NV-5138 are long-lasting, with a duration of up to 7 days, and are similar to those of ketamine. Based on these promising preclinical findings, efforts are underway to assess NV-5138 in clinical trials with human subjects. By November 2019, NV-5138 had completed three phase I studies for the treatment of MDD. In these studies, preliminary evidence of efficacy, tolerability, safety, and pharmacokinetics was observed, and as of 2021 it was into Phase II trials.
Psychoplastogens are a group of small molecule drugs that produce rapid and sustained effects on neuronal structure and function, intended to manifest therapeutic benefit after a single administration. Several existing psychoplastogens have been identified and their therapeutic effects demonstrated; several are presently at various stages of development as medications including Ketamine, MDMA, Scopolamine, and the serotonergic psychedelics, including LSD, psilocin, DMT, and 5-MeO-DMT. Compounds of this sort are being explored as therapeutics for a variety of brain disorders including depression, addiction, and PTSD. The ability to rapidly promote neuronal changes via mechanisms of neuroplasticity was recently discovered as the common therapeutic activity and mechanism of action.
Ketamine-assisted psychotherapy(KAP) is the use of prescribed doses of ketamine, the drug, as an adjunct to psychotherapy sessions. KAP shows significant potential in treating mental disorders such as treatment-resistant depression (TRD), anxiety, obsessive–compulsive disorders (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorders (PTSD), and other conditions. It can also be used for those experiencing substance abuse and physical pain. While it is primarily used as a veterinary anaesthetic, ketamine has also been found to have rapid analgesic and hallucinogenic effects, which has sparked interest in its use as an antidepressant. Despite initial trials of its use in the treatment of mental disorders focussing primarily on its antidepressant effects, newer studies are attempting to harness its psychedelic effects to bring about altered states of consciousness, which will augment the adjunct psychotherapy. Ketamine's neuroplasticity-promoting effects strengthen the cognitive restructuring that takes place through traditional psychotherapy, thereby leading to long-lasting behavioural change. KAP offers promising directions for research on new antidepressant alternatives, but is still not sufficiently defined or evaluated as a treatment combination.
References
- ↑ "Official page about NeuroRX NRX100/NRX101". Archived from the original on 2020-07-09. Retrieved 2018-06-23.
- ↑ "Cycloserine/lurasidone - NeuroRx". Adis Insight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT02974010 for "Sequential Therapy for the Treatment of Severe Bipolar Depression. (STABIL-B)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Kantrowitz JT, Halberstam B, Gangwisch J (June 2015). "Single-dose ketamine followed by daily D-Cycloserine in treatment-resistant bipolar depression". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 76 (6): 737–8. doi: 10.4088/JCP.14l09527 . PMID 26132675.
- ↑ Heresco-Levy U, Gelfin G, Bloch B, Levin R, Edelman S, Javitt DC, Kremer I (April 2013). "A randomized add-on trial of high-dose D-cycloserine for treatment-resistant depression". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 16 (3): 501–6. doi: 10.1017/S1461145712000910 . PMID 23174090.