An allele is a variant form of a given gene. Sometimes, the presence of different alleles of the same gene can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. A notable example of this trait of color variation is Gregor Mendel's discovery that the white and purple flower colors in pea plants were the result of "pure line" traits which could be used as a control for future experiments. However, most genetic variations result in little or no observable variation.

Genetics is a branch of biology concerned with the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.

A genetic disorder is a genetic problem caused by one or more abnormalities formed in the genome. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions. The earliest known genetic condition in a hominid was in the fossil species Paranthropus robustus, with over a third of individuals displaying Amelogenesis imperfecta.

Eugene Allen Hackman is a retired American actor and novelist. In a career that spanned nearly five decades, Hackman was nominated for five Academy Awards, winning Best Actor in The French Connection and Best Supporting Actor in Unforgiven. He won four Golden Globes, one SAG Award and two BAFTAs.
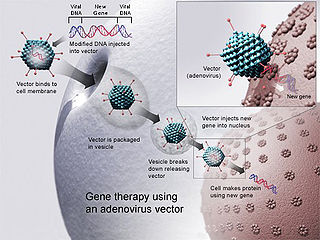
In the medicine field gene therapy is the therapeutic delivery of nucleic acid into a patient's cells as a drug to treat disease. The first attempt at modifying human DNA was performed in 1980 by Martin Cline, but the first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the National Institutes of Health, was performed in May 1989. The first therapeutic use of gene transfer as well as the first direct insertion of human DNA into the nuclear genome was performed by French Anderson in a trial starting in September 1990.

In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA . Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.

A homeobox is a DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, found within genes that are involved in the regulation of patterns of anatomical development (morphogenesis) in animals, fungi and plants. These genes encode homeodomain protein products that are transcription factors sharing a characteristic protein fold structure that binds DNA. The "homeo-" prefix in the words "homeobox" and "homeodomain" stems from the mutational phenotype known as "homeosis", which is frequently observed when these genes are mutated in animals. Homeosis is a term coined by William Bateson to describe the outright replacement of a discrete body part with another body part. Homeobox genes are not only found in animals, but have also been found in fungi, for example the unicellular yeasts, in plants, and numerous single cell eukaryotes.

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome, the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.

Gene Klein (born Chaim Witz, known professionally as Gene Simmons, is an Israeli-American musician, singer, songwriter, record producer, entrepreneur, actor, author, and television personality. Also known by his stage persona The Demon, he is the bassist and co-lead singer of Kiss, the rock band he co-founded with lead singer and rhythm guitarist Paul Stanley in the early 1970s.
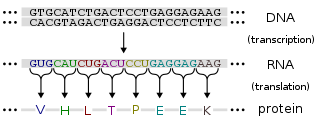
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.

Embryology is the branch of biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes, fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses. Additionally, embryology encompasses the study of congenital disorders that occur before birth, known as teratology.

Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms.

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest-evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and hemizygous except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome.
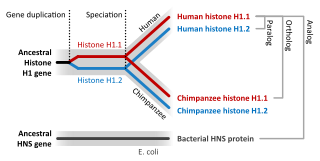
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal gene transfer event (xenologs).
Gene ontology (GO) is a major bioinformatics initiative to unify the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species. More specifically, the project aims to: 1) maintain and develop its controlled vocabulary of gene and gene product attributes; 2) annotate genes and gene products, and assimilate and disseminate annotation data; and 3) provide tools for easy access to all aspects of the data provided by the project, and to enable functional interpretation of experimental data using the GO, for example via enrichment analysis. GO is part of a larger classification effort, the Open Biomedical Ontologies (OBO).

A locus in genetics is a fixed position on a chromosome, like the position of a gene or a marker. Each chromosome carries many genes; human's estimated 'haploid' protein coding genes are 19,000–20,000, on the 23 different chromosomes. A variant of the similar DNA sequence located at a given locus is called an allele. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the locus for a particular biological trait.

KEGG is a collection of databases dealing with genomes, biological pathways, diseases, drugs, and chemical substances. KEGG is utilized for bioinformatics research and education, including data analysis in genomics, metagenomics, metabolomics and other omics studies, modeling and simulation in systems biology, and translational research in drug development.

In biology, a gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA that codes for a molecule that has a function. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic trait. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes as well as gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye color or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that constitute life.
Gene nomenclature is the scientific naming of genes, the units of heredity in living organisms. An international committee published recommendations for genetic symbols and nomenclature in 1957. The need to develop formal guidelines for human gene names and symbols was recognized in the 1960s and full guidelines were issued in 1979. Several other genus-specific research communities have adopted nomenclature standards, as well, and have published them on the relevant model organism websites and in scientific journals, including the Trends in Genetics Genetic Nomenclature Guide. Scientists familiar with a particular gene family may work together to revise the nomenclature for the entire set of genes when new information becomes available. For many genes and their corresponding proteins, an assortment of alternate names is in use across the scientific literature and public biological databases, posing a challenge to effective organization and exchange of biological information. Standardization of nomenclature thus tries to achieve the benefits of vocabulary control and bibliographic control, although adherence is voluntary. The advent of the information age has brought gene ontology, which in some ways is a next step of gene nomenclature, because it aims to unify the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species.

Zygosity is the degree of similarity of the alleles for a trait in an organism.


















