Related Research Articles

A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness.

Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a group of three conditions in which tumors grow in the nervous system. The three types are neurofibromatosis type I (NF1), neurofibromatosis type II (NF2), and schwannomatosis. In NF1 symptoms include light brown spots on the skin, freckles in the armpit and groin, small bumps within nerves, and scoliosis. In NF2, there may be hearing loss, cataracts at a young age, balance problems, flesh colored skin flaps, and muscle wasting. In schwannomatosis there may be pain either in one location or in wide areas of the body. The tumors in NF are generally non-cancerous.

Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans.

Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues.

Adenoviruses are medium-sized, nonenveloped viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953.

A glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or the spine. Gliomas comprise about 30 percent of all brain tumors and central nervous system tumours, and 80 percent of all malignant brain tumours.

Hypopituitarism is the decreased (hypo) secretion of one or more of the eight hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. If there is decreased secretion of one specific pituitary hormone, the condition is known as selective hypopituitarism. If there is decreased secretion of most or all pituitary hormones, the term panhypopituitarism is used.

Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness.
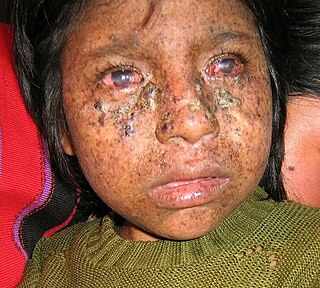
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a genetic disorder in which there is a decreased ability to repair DNA damage such as that caused by ultraviolet (UV) light. Symptoms may include a severe sunburn after only a few minutes in the sun, freckling in sun-exposed areas, dry skin and changes in skin pigmentation. Nervous system problems, such as hearing loss, poor coordination, loss of intellectual function and seizures, may also occur. Complications include a high risk of skin cancer, with about half having skin cancer by age 10 without preventative efforts, and cataracts. There may be a higher risk of other cancers such as brain cancers.

A neoplasm is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumour or tumor.

Cockayne syndrome (CS), also called Neill-Dingwall syndrome, is a rare and fatal autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by growth failure, impaired development of the nervous system, abnormal sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity), eye disorders and premature aging. Failure to thrive and neurological disorders are criteria for diagnosis, while photosensitivity, hearing loss, eye abnormalities, and cavities are other very common features. Problems with any or all of the internal organs are possible. It is associated with a group of disorders called leukodystrophies, which are conditions characterized by degradation of neurological white matter. The underlying disorder is a defect in a DNA repair mechanism. Unlike other defects of DNA repair, patients with CS are not predisposed to cancer or infection. Cockayne syndrome is a rare but destructive disease usually resulting in death within the first or second decade of life. The mutation of specific genes in Cockayne syndrome is known, but the widespread effects and its relationship with DNA repair is yet to be well understood.
Lentivirus is a genus of retroviruses that cause chronic and deadly diseases characterized by long incubation periods, in humans and other mammalian species. The genus includes the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS. Lentiviruses are distributed worldwide, and are known to be hosted in apes, cows, goats, horses, cats, and sheep as well as several other mammals.

Costello syndrome, also called faciocutaneoskeletal syndrome or FCS syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. It is characterized by delayed development and intellectual disabilities, distinctive facial features, unusually flexible joints, and loose folds of extra skin, especially on the hands and feet. Heart abnormalities are common, including a very fast heartbeat (tachycardia), structural heart defects, and overgrowth of the heart muscle. Infants with Costello syndrome may be large at birth, but grow more slowly than other children and have difficulty feeding. Later in life, people with this condition have relatively short stature and many have reduced levels of growth hormones. It is a RASopathy.

Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome (SGBS), is a rare inherited congenital disorder that can cause craniofacial, skeletal, cardiac, and renal abnormalities. The syndrome is inherited in an X-linked recessive fashion, where males express the phenotype and females usually do not. Females that possess one copy of the mutation are considered to be carriers of the syndrome and may express varying degrees of the phenotype.

David Botstein is an American biologist serving as the chief scientific officer of Calico. He served as the director of the Lewis-Sigler Institute for Integrative Genomics at Princeton University from 2003 to 2013, where he remains an Anthony B. Evnin Professor of Genomics.

Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD), also known as dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DLD gene. DLD is a flavoprotein enzyme that oxidizes dihydrolipoamide to lipoamide.

Ewing sarcoma is a type of cancer that forms in bone or soft tissue. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture. The most common areas where it begins are the legs, pelvis, and chest wall. In about 25% of cases, the cancer has already spread to other parts of the body at the time of diagnosis. Complications may include a pleural effusion or paraplegia.

Tumor protein p63, typically referred to as p63, also known as transformation-related protein 63 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TP63 gene.

Cancer is the leading cause of death in dogs. It is estimated that 1 in 3 domestic dogs will develop cancer, which is the same incidence of cancer among humans. Dogs can develop a variety of cancers and most are very similar to those found in humans. Dogs can develop carcinomas of epithelial cells and organs, sarcomas of connective tissues and bones, and lymphomas or leukemias of the circulatory system. Selective breeding of dogs has led certain pure-bred breeds to be at high-risk for specific kinds of cancer.

Lupus erythematosus is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. The most common and most severe form is systemic lupus erythematosus.
References
- 1 2 Hajjar, M; Chalovski, M; Davis, D (2011). "Identification and characterization of a novel gene family DLD/NP1 in a wide spectrum of eukaryotic species". Gene. 340 (1): 31–43. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2004.06.014. PMID 15556292.
- 1 2 "AceView: Gene:DLD/NP1, a comprehensive annotation of human, mouse and worm genes with mRNAs or ESTsAceView".