
The Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, more commonly known as The Iditarod, is an annual long-distance sled dog race held in Alaska in early March. It travels from Anchorage to Nome. Mushers and a team of between 12 and 14 dogs, of which at least 5 must be on the towline at the finish line, cover the distance in 8–15 days or more. The Iditarod began in 1973 as an event to test the best sled dog mushers and teams but evolved into today's highly competitive race.

A sled dog is a dog trained and used to pull a land vehicle in harness, most commonly a sled over snow.

Susan Howlet Butcher was an American dog musher, noteworthy as the second woman to win the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race in 1986, the second four-time winner in 1990, and the first to win four out of five sequential years. She is commemorated in Alaska by the Susan Butcher Day.

Balto was an Alaskan husky and sled dog belonging to musher and breeder Leonhard Seppala. He achieved fame when he led a team of sled dogs driven by Gunnar Kaasen on the final leg of the 1925 serum run to Nome, in which diphtheria antitoxin was transported from Anchorage, Alaska, to Nenana, Alaska, by train and then to Nome by dog sled to combat an outbreak of the disease.

The Yukon Quest, formally the Yukon Quest 1,000-mile International Sled Dog Race is a sled dog race scheduled every February since 1984 between Fairbanks, Alaska, and Whitehorse, Yukon, switching directions each year. Because of the harsh winter conditions, difficult trail, and the limited support that competitors are allowed, it is considered the "most difficult sled dog race in the world", or even the "toughest race in the world"—"even tougher, more selective and less attention-seeking than the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race." The originator envisioned it as "a race so rugged that only purists would participate."

DeeDee Ann Jonrowe is an American kennel owner and dog musher who is a three-time runner up in the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, and holds the fastest time ever recorded for a woman. She is a very popular figure in the sport, and her completion of the 1,049-mile+ race in 2003 just three weeks after completing chemotherapy for breast cancer received widespread publicity.
Emmitt Peters Sr. the "Yukon Fox", was an Alaskan American hunter, fisher, trapper, and dog musher. The last rookie to win the 1,049 mile Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, he and his lead dogs Nugget and Digger shattered the previous speed record by almost six days.
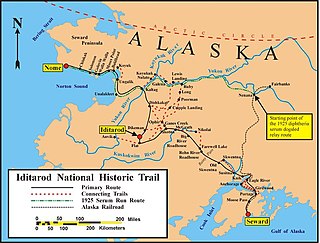
The 1925 serum run to Nome, also known as the Great Race of Mercy and The Serum Run, was a transport of diphtheria antitoxin by dog sled relay across the U.S. territory of Alaska by 20 mushers and about 150 sled dogs across 674 miles (1,085 km) in 5+1⁄2 days, saving the small town of Nome and the surrounding communities from a developing epidemic of diphtheria.

Ramy "Ray" Brooks is an Alaska Native kennel owner and operator, motivational speaker, and dog musher who specializes in long-distance races. He is a two-time runner up in the 1,049+ mi Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race across the U.S. state of Alaska, and a former winner of the 1,000 mi (1,600 km) Yukon Quest dog sled race across both Canada and the U.S.

Jujiro Wada was a Japanese adventurer and entrepreneur who achieved fame for his exploits in turn-of-the-20th-century Alaska and Yukon Territory.

Celia Hunter was an American environmentalist and conservationist. She was conferred the highest award by the Sierra Club, The John Muir Award, in 1991. She was presented the highest award by the Wilderness Society, The Robert Marshall Award, in 1998.

Lance Mackey was an American dog musher and dog sled racer from Fairbanks, Alaska. Mackey was a four-time winner of both the 1,000-mile (1,600 km) Yukon Quest and the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race.

The Iron Dog or Iron Dog Race, originally known as the Iron Dog Gold Rush Classic and for a few years the Tesoro Iron Dog, is an off-road snowmobile race across Alaska, USA. It normally starts on a Sunday in mid-February. At 2,031 miles (3,269 km), it is the longest high speed cross-country snowmachine race in the world. A record forty-two teams entered the 2008 event. In 2013 the total purse was US $210,500, with $50,000 awarded to the winners.
Charlie Biederman was a musher in Alaska best known for being the last surviving dog sled mail carrier in the United States. Charlie was born in Alaska as the son of Ed Biederman, a musher born in Bohemia who immigrated to the United States in 1874 and also delivered the mail via dog sled. The date of Charlie's birth is unclear, but contemporary U.S. Censuses indicate it likely was around 1919. Charlie had four siblings. Charlie was raised in Eagle, Alaska, but lived in an isolated cabin on the Yukon River for most of his life. From an early age, he assisted his father and brother in their winter deliveries of the mail to isolated cabins in central Alaska. In winter, the family lived in Eagle and ran the mail route between that town and Circle, another small settlement approximately 158 miles (254 km) downriver. In the summer, the family lived at their Yukon River cabin, harvesting fish for subsistence and boarding the dogs of fellow mushers. In 1938, the family were underbid for the main contract for mail delivery in the area by a bush pilot. Ed Biederman retired shortly afterward and died in 1945. The final dog sled mail route was replaced in 1963. That final route was from Gambell to Savoonga and was run by Chester Noongwook. In January 1995, he donated the mail-delivery sled he used to the National Postal Museum in Washington, D.C., where it hangs today. One month after making the delivery, he died on February 22, 1995.

The Jamaica Dogsled Team is a team of sled dogs and mushers headquartered at Chukka Caribbean Adventures in Ocho Rios, located in Saint Ann Parish, Jamaica. The dog team is made up of strays rescued by the Jamaica Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals and offers dryland dogsled rides, along with the adventure center's other outdoor experiences. In addition, the two mushers Newton Marshall and Damion Robb, compete in sled races throughout the US and Canada, using leased dog teams. Country music singer Jimmy Buffett's Margaritaville is the team's major sponsor.
Sue Henry was an American writer of mystery thriller fiction. She was also a librarian, college administrator, instructor at the University of Alaska.

Walter Bruce "Walt" Parker was an American civil servant, policy adviser, transportation adviser, academic and local politician. Parker's career focused on the development of natural resources, transportation and infrastructure in Alaska from the 1940s to the 2000s. In 1989, Alaska Governor Steve Cowper appointed Parker as the chairman of the Alaska Oil Spill Commission, which investigated the Exxon Valdez oil spill. He is credited with making important contributions to the fields of transportation, telecommunications, education, land use and urban planning within the state of Alaska. Parker was inducted into the Alaska Conservation Hall of Fame by the Alaska Conservation Foundation in 2002 for his contributions to state conservation.

Hannah Paul Solomon was an American community leader and artist. She was the first female mayor of Fort Yukon, Alaska, helped organize the Fairbanks Native Association, and was inducted into the Alaska Women's Hall of Fame in 2012. Her traditional beadwork is in the collections of several museums.














