Related Research Articles

In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradition, strongly developing during the Renaissance and in much of the common practice period, especially in the Baroque period. The term originates from the Latin punctus contra punctum meaning "point against point", i.e. "note against note".

In music, a fugue is a contrapuntal compositional technique in two or more voices, built on a subject that is introduced at the beginning in imitation and which recurs frequently in the course of the composition. It is not to be confused with a fuguing tune, which is a style of song popularized by and mostly limited to early American music and West Gallery music. A fugue usually has three main sections: an exposition, a development and a final entry that contains the return of the subject in the fugue's tonic key. Some fugues have a recapitulation.

Polytonality is the musical use of more than one key simultaneously. Bitonality is the use of only two different keys at the same time. Polyvalence or polyvalency is the use of more than one harmonic function, from the same key, at the same time.

Johann Baptist Joseph Maximilian Reger was a German composer, pianist, organist, conductor, and academic teacher. He worked as a concert pianist, as a musical director at the Leipzig University Church, as a professor at the Royal Conservatory in Leipzig, and as a music director at the court of Duke Georg II of Saxe-Meiningen.
In Western musical theory, a cadence is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards. A harmonic cadence is a progression of two or more chords that concludes a phrase, section, or piece of music. A rhythmic cadence is a characteristic rhythmic pattern that indicates the end of a phrase. A cadence can be labeled "weak" or "strong" depending on the impression of finality it gives. While cadences are usually classified by specific chord or melodic progressions, the use of such progressions does not necessarily constitute a cadence—there must be a sense of closure, as at the end of a phrase. Harmonic rhythm plays an important part in determining where a cadence occurs.

Karl Wilhelm Julius Hugo Riemann was a German musicologist and composer who was among the founders of modern musicology. The leading European music scholar of his time, he was active and influential as both a music theorist and music historian. Many of his contributions are now termed as Riemannian theory, a variety of related ideas on many aspects of music theory.
Voice leading is the linear progression of individual melodic lines and their interaction with one another to create harmonies, typically in accordance with the principles of common-practice harmony and counterpoint.

Ludus Tonalis, subtitled Kontrapunktische, tonale, und Klaviertechnische Übungen, is a piano work by Paul Hindemith that was composed in 1942 during his stay in the United States. It was first performed in 1943 in Chicago by Willard MacGregor. The piece explores "matters of technique, theory, inspiration, and communication. It is in effect, a veritable catalogue of the composer's mature style."
The organ repertoire is considered to be the largest and oldest repertory of all musical instruments. Because of the organ's prominence in worship in Western Europe from the Middle Ages on, a significant portion of organ repertoire is sacred in nature. The organ's suitability for improvisation by a single performer is well adapted to this liturgical role and has allowed many blind organists to achieve fame; it also accounts for the relatively late emergence of written compositions for the instrument in the Renaissance. Although instruments are still disallowed in most Eastern churches, organs have found their way into a few synagogues as well as secular venues where organ recitals take place.
D minor is a minor scale based on D, consisting of the pitches D, E, F, G, A, B♭, and C. Its key signature has one flat. Its relative major is F major and its parallel major is D major.
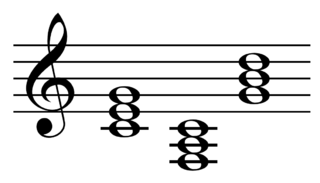
In music, a primary triad is one of the three triads, or three-note chords built from major or minor thirds, most important in tonal and diatonic music, as opposed to an auxiliary triad or secondary triad.

In music theory, a chromatic fourth, or passus duriusculus, is a melody or melodic fragment spanning a perfect fourth with all or almost all chromatic intervals filled in. The quintessential example is in D minor with the tonic and dominant notes as boundaries:

Montgomery Rufus Karl Siegfried Straube was a German church musician, organist, and choral conductor, famous above all for championing the abundant organ music of Max Reger.

Prelude and Fugue in A minor, BWV 543 is a piece of organ music written by Johann Sebastian Bach sometime around his years as court organist to the Duke of Saxe-Weimar (1708–1713).

Neo-Riemannian theory is a loose collection of ideas present in the writings of music theorists such as David Lewin, Brian Hyer, Richard Cohn, and Henry Klumpenhouwer. What binds these ideas is a central commitment to relating harmonies directly to each other, without necessary reference to a tonic. Initially, those harmonies were major and minor triads; subsequently, neo-Riemannian theory was extended to standard dissonant sonorities as well. Harmonic proximity is characteristically gauged by efficiency of voice leading. Thus, C major and E minor triads are close by virtue of requiring only a single semitonal shift to move from one to the other. Motion between proximate harmonies is described by simple transformations. For example, motion between a C major and E minor triad, in either direction, is executed by an "L" transformation. Extended progressions of harmonies are characteristically displayed on a geometric plane, or map, which portrays the entire system of harmonic relations. Where consensus is lacking is on the question of what is most central to the theory: smooth voice leading, transformations, or the system of relations that is mapped by the geometries. The theory is often invoked when analyzing harmonic practices within the Late Romantic period characterized by a high degree of chromaticism, including work of Schubert, Liszt, Wagner and Bruckner.
Richard Cohn is a music theorist and Battell Professor of Music Theory at Yale. He was previously chair of the department of music at the University of Chicago.

The Clavier-Übung III, sometimes referred to as the German Organ Mass, is a collection of compositions for organ by Johann Sebastian Bach, started in 1735–36 and published in 1739. It is considered Bach's most significant and extensive work for organ, containing some of his most musically complex and technically demanding compositions for that instrument.
Carl Friedrich Weitzmann was a German music theorist and musician.
The diatonic, Guidonian, or major hexachord (6-32) is a hexachord consisting of six consecutive pitches from the diatonic scale that are also a consecutive segment of the circle of fifths: F C G D A E = C D E F G A = "do-re-mi-fa-sol-la".

Throughout the 18th century, the appreciation of Johann Sebastian Bach's music was mostly limited to distinguished connoisseurs. The 19th century started with publication of the first biography of the composer and ended with the completion of the publication of all of Bach's known works by the Bach Gesellschaft. A Bach Revival had started from Mendelssohn's performance of the St Matthew Passion in 1829. Soon after that performance, Bach started to become regarded as one of the greatest composers of all times, if not the greatest, a reputation he has retained ever since. A new extensive Bach biography was published in the second half of the 19th century.
References
- ↑ "Chicago Press"
- ↑ "IMDb"
- ↑ ""Yale Bulletin"". Archived from the original on 2011-11-11. Retrieved 2011-11-28.
- ↑ Publications and Networking Committees, Society for Music Theory, retrieved 2014-05-16.