
A database is an organized collection of data, generally stored and accessed electronically from a computer system. Where databases are more complex they are often developed using formal design and modeling techniques.
SQL is a domain-specific language used in programming and designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS), or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data where there are relations between different entities/variables of the data. SQL offers two main advantages over older read/write APIs like ISAM or VSAM. First, it introduced the concept of accessing many records with one single command; and second, it eliminates the need to specify how to reach a record, e.g. with or without an index.

In telecommunication, a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) line code is a binary code in which ones are represented by one significant condition, usually a positive voltage, while zeros are represented by some other significant condition, usually a negative voltage, with no other neutral or rest condition. The pulses in NRZ have more energy than a return-to-zero (RZ) code, which also has an additional rest state beside the conditions for ones and zeros. NRZ is not inherently a self-clocking signal, so some additional synchronization technique must be used for avoiding bit slips; examples of such techniques are a run-length-limited constraint and a parallel synchronization signal.
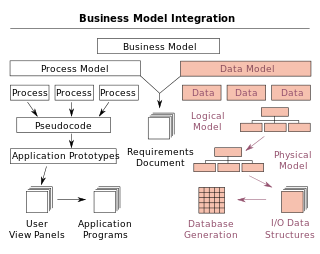
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to properties of the real world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.
A data definition or data description language (DDL) is a syntax similar to a computer programming language for defining data structures, especially database schemas. DDL statements create, modify, and remove database objects such as tables, indexes, and users. Common DDL statements are CREATE, ALTER, and DROP

A race condition or race hazard is the behavior of an electronics, software, or other system where the system's substantive behavior is dependent on the sequence or timing of other uncontrollable events. It becomes a bug when one or more of the possible behaviors is undesirable.

WinFS was the code name for a canceled data storage and management system project based on relational databases, developed by Microsoft and first demonstrated in 2003 as an advanced storage subsystem for the Microsoft Windows operating system, designed for persistence and management of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data.
In psychology and cognitive science, a schema describes a pattern of thought or behavior that organizes categories of information and the relationships among them. It can also be described as a mental structure of preconceived ideas, a framework representing some aspect of the world, or a system of organizing and perceiving new information. Schemata influence attention and the absorption of new knowledge: people are more likely to notice things that fit into their schema, while re-interpreting contradictions to the schema as exceptions or distorting them to fit. Schemata have a tendency to remain unchanged, even in the face of contradictory information. Schemata can help in understanding the world and the rapidly changing environment. People can organize new perceptions into schemata quickly as most situations do not require complex thought when using schema, since automatic thought is all that is required.
A modeling perspective in information systems is a particular way to represent pre-selected aspects of a system. Any perspective has a different focus, conceptualization, dedication and visualization of what the model is representing.
This glossary of Unified Modeling Language terms covers all versions of UML. Individual entries will point out any distinctions that exist between versions.
Kinetic Rule Language (KRL) is a rule-based programming language for creating applications on the Live Web. KRL programs, or rulesets, comprise a number of rules that respond to particular events. KRL has been promoted as language for building personal clouds.

Thermodynamic databases contain information about thermodynamic properties for substances, the most important being enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy. Numerical values of these thermodynamic properties are collected as tables or are calculated from thermodynamic datafiles. Data is expressed as temperature-dependent values for one mole of substance at the standard pressure of 101.325 kPa, or 100 kPa. Unfortunately, both of these definitions for the standard condition for pressure are in use.
The SQL/Schemata, or Information and Definition Schemas, part to the SQL standard is defined by ISO/IEC 9075-11:2008. SQL/Schemata defines the information schema and definition schema, providing a common set of tools to make SQL databases and objects self-describing. These tools include the SQL object identifier, structure and integrity constraints, security and authorization specifications, features and packages of ISO/IEC 9075, support of features provided by SQL-based DBMS implementations, SQL-based DBMS implementation information and sizing items, and the values supported by the DBMS implementations. SQL/Schemata defines a number of features, some of which are mandatory.

Metadata is "data [information] that provides information about other data". Many distinct types of metadata exist, among these descriptive metadata, structural metadata, administrative metadata, reference metadata and statistical metadata.
UML state machine, also known as UML statechart, is a significantly enhanced realization of the mathematical concept of a finite automaton in computer science applications as expressed in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) notation.

The European Climate Assessment and Dataset (ECA&D) is a database of daily meteorological station observations across Europe and is gradually being extended to countries in the Middle East and North Africa. ECA&D has attained the status of Regional Climate Centre for high-resolution observation data in World Meteorological Organization Region VI ].
QML is a user interface markup language. It is a declarative language for designing user interface–centric applications. Inline JavaScript code handles imperative aspects. It is associated with Qt Quick, the UI creation kit originally developed by Nokia within the Qt framework. Qt Quick is often used for mobile applications where touch input, fluid animations and user experience are crucial. QML is also used with Qt3D to describe a 3D scene and a "frame graph" rendering methodology. A QML document describes a hierarchical object tree. QML modules shipped with Qt include primitive graphical building blocks, modeling components, behavioral components, and more complex controls. These elements can be combined to build components ranging in complexity from simple buttons and sliders, to complete internet-enabled programs.

In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to databases:








