Related Research Articles

Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a country in Central America, bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half the country's 4 million people.

Panama is a country located in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica. Panama is located on the narrow and low Isthmus of Panama.
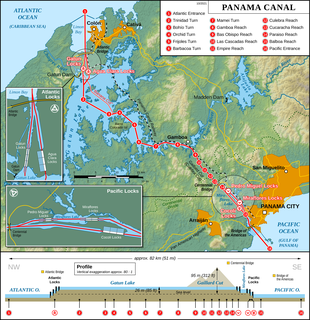
The Panama Canal is an artificial 82 km (51 mi) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. Canal locks are at each end to lift ships up to Gatun Lake, an artificial lake created to reduce the amount of excavation work required for the canal, 26 m above sea level, and then lower the ships at the other end. The original locks are 34 m wide. A third, wider lane of locks was constructed between September 2007 and May 2016. The expanded canal began commercial operation on June 26, 2016. The new locks allow transit of larger, post-Panamax ships, capable of handling more cargo.

Francisco Pizarro González was a Spanish conquistador who led an expedition that conquered the Inca Empire. He captured and killed Incan emperor Atahualpa, and claimed the lands for Spain.

Panama City is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has an urban population of 880,691, with over 1.5 million in its metropolitan area. The city is located at the Pacific entrance of the Panama Canal, in the province of Panama. The city is the political and administrative center of the country, as well as a hub for banking and commerce.

Tocumen International Airport is the international airport of Panama City, the capital of Panama. The airport serves as the homebase for Copa Airlines and is a regional hub to and from The Caribbean, South, North and Central America and additionally features routes to some European and Asian cities.

A steamboat is a boat that is propelled primarily by steam power, typically driving propellers or paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S or PS, however these designations are most often used for steamships.

The United States invasion of Panama, codenamed Operation Just Cause, occurred between mid-December 1989 and late January 1990. The invasion was led by the administration of President George H. W. Bush, ten years after the Torrijos–Carter Treaties were ratified to transfer control of the Panama Canal from the U.S. to Panama by 1 January 2000.

Colón is a city and sea port in Panama, beside the Caribbean Sea, lying near the Atlantic entrance to the Panama Canal. It is the capital of Panama's Colón Province and has traditionally been known as Panama's second city. Originally it was located entirely on Manzanillo Island, surrounded by Limon Bay, Manzanillo Bay and the Folks River; however, since the disestablishment of the Panama Canal Zone, the city's limits have been redefined to include Fort Gulick, a former U.S. Army base, as well the former Canal Zone towns of Cristobal, Margarita and Coco Solo.

The Darién Gap is a break in the Pan-American Highway consisting of a large swath of undeveloped swampland and forest within Panama's Darién Province in Central America and the northern portion of Colombia's Chocó Department in South America. The gap begins in Yaviza, Panama and ends in Turbo, Colombia, and is 106 km long. Roadbuilding through this area is expensive and the environmental cost is high. Political consensus in favor of road construction has not emerged.

Darién is a province in Panama whose capital city is La Palma. With an area of 11,896.5 km2 (4,593.3 sq mi), it is located at the eastern end of the country and bordered to the north by the province of Panamá and the region of Kuna Yala. To the south, it is bordered by the Pacific Ocean and Colombia. To the east, it borders Colombia; to the west, it borders the Pacific Ocean and the province of Panama.

Gatun Lake is a large artificial lake to the south of Colón, Panama. It forms a major part of the Panama Canal, carrying ships for 33 km (21 mi) of their transit across the Isthmus of Panama.

The Chagres River, in central Panama, is the largest river in the Panama Canal's watershed. The river is dammed twice, and the resulting reservoirs—Gatun Lake and Lake Alajuela—form an integral part of the canal and its water system. Although the river's natural course runs northwest to its mouth at the Caribbean Sea, its waters also flow, via the canal's locks, into the Gulf of Panama to the south. The Chagres has the unusual claim of drainage into two oceans.

The Pacific Mail Steamship Company was founded April 18, 1848, as a joint stock company under the laws of the State of New York by a group of New York City merchants, William H. Aspinwall, Edwin Bartlett, Henry Chauncey, Mr. Alsop, G.G. Howland and S.S. Howland. These merchants had acquired the right to transport mail under contract from the United States Government from the Isthmus of Panama to California awarded in 1847 to one Arnold Harris.

The Embera–Wounaan are a semi-nomadic indigenous people in Panama living in Darién Province on the shores of the Chucunaque, Sambú, Tuira Rivers and its water ways. The Embera-Wounaan were formerly and widely known by the name Chocó, and they speak the Embera and Wounaan languages, part of the Choco language family.
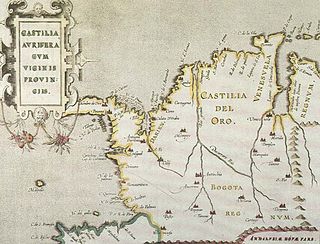
Castilla de Oro or del Oro was the name given by the Spanish settlers at the beginning of the 16th century to the Central American territories from the Gulf of Urabá, near today's Colombian-Panamanian border, to the Belén River. Beyond that river, the region was known as Veragua, and was disputed by the Spanish crown along with the Columbus family. The name "Castilla de Oro" was made official in May 1513 by King Ferdinand II of Aragon, then regent of the Crown of Castile.
The Chepo expedition was a pirate voyage led by Spanish renegades Juan Guartem, Eduardo Blomar and Bartolomé Charpes in the Spanish Main during 1679. Sailing up the Mandingua River, the expedition crossed the Isthmus of Panama into the Pacific where they raided shipping for several months as well as looting and then burning the town of Chepo, Panama. They were tried in absentia by the Viceroy of Bogotá and on his orders were burned in effigy at Santa Fe de Bogotá. However, the three continued committing piracy on both coasts of Central America and were never caught for their crimes. This was the second major expedition following the "Pacific Adventure" led by John Coxon that same year.

Panama, formerly named Rio Bravo after the Spanish name for the Kern River, Rio Bravo de San Felipe, is an unincorporated community in Kern County, California. It is located 8 miles (13 km) south-southwest of Bakersfield, at an elevation of 351 feet (107 m) in the San Joaquin Valley.
Rio Bravo is a former settlement in Kern County, California. It was located on the railroad 2 miles (3.2 km) north of Panama.

The Emberá
References
- Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993.
- CIA map, 1995.
| This article related to a river in Panama is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |