
Hampshire is a ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Berkshire to the north, Surrey and West Sussex to the east, the Isle of Wight across the Solent to the south, Dorset to the west, and Wiltshire to the north-west. The cities of Portsmouth and Southampton are the largest settlements and the county town is the city of Winchester.

Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century, the development of the computer that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is marine weather forecasting as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water.

Numerical climate models are mathematical models that can simulate the interactions of important drivers of climate. These drivers are the atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. Scientists use climate models to study the dynamics of the climate system and to make projections of future climate and of climate change. Climate models can also be qualitative models and contain narratives, largely descriptive, of possible futures.
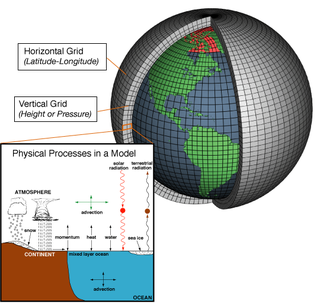
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources. These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components.

Atmospheric science is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climatology is the study of atmospheric changes that define average climates and their change over time climate variability. Aeronomy is the study of the upper layers of the atmosphere, where dissociation and ionization are important. Atmospheric science has been extended to the field of planetary science and the study of the atmospheres of the planets and natural satellites of the Solar System.

A bioregion is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a biogeographic realm, but larger than an ecoregion or an ecosystem, and is defined along watershed and hydrological boundaries. People are counted as an integral part of the definition of a bioregion.
The Carl-Gustaf Rossby Research Medal is the highest award for atmospheric science of the American Meteorological Society. It is presented to individual scientists, who receive a medal. Named in honor of meteorology and oceanography pioneer Carl-Gustaf Rossby, who was also its second (1953) recipient.

The Meteorological Office, abbreviated as the Met Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and is led by CEO Penelope Endersby, who took on the role as Chief Executive in December 2018 and is the first woman to do so. The Met Office makes meteorological predictions across all timescales from weather forecasts to climate change.

Solent University is a public university based in Southampton, United Kingdom. It has approximately 10,500 students (2019/20). Its main campus is located on East Park Terrace near the city centre and the maritime hub of Southampton.

Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs.

The Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) is a research institute that is sponsored jointly by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research (OAR) and the University of Colorado Boulder (CU). CIRES scientists study the Earth system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, biosphere, and geosphere, and communicate these findings to decision makers, the scientific community, and the public.

The Heartland Institute is an American conservative and libertarian public policy think tank known for its rejection of both the scientific consensus on climate change and the negative health impacts of smoking.
David John Carson is a climatologist. He has been director of the Hadley Centre, director of Numerical Weather Prediction at the UKMO, and was director of the World Climate Research Programme from 2000-2005.

In atmospheric science, an atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive, dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes, heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface water, the kinematic effects of terrain, and convection. Most atmospheric models are numerical, i.e. they discretize equations of motion. They can predict microscale phenomena such as tornadoes and boundary layer eddies, sub-microscale turbulent flow over buildings, as well as synoptic and global flows. The horizontal domain of a model is either global, covering the entire Earth, or regional (limited-area), covering only part of the Earth. The different types of models run are thermotropic, barotropic, hydrostatic, and nonhydrostatic. Some of the model types make assumptions about the atmosphere which lengthens the time steps used and increases computational speed.

The Clinton Foundation is a nonprofit organization under section 501(c)(3) of the U.S. tax code. It was established by former president of the United States Bill Clinton with the stated mission to "strengthen the capacity of people in the United States and throughout the world to meet the challenges of global interdependence." Its offices are located in New York City and Little Rock, Arkansas.

A sting jet is a narrow, transient and mesoscale airstream that descends from the mid-troposphere to the surface in some extratropical cyclones. When present, sting jets produce some of the strongest surface-level winds in extratropical cyclones and can generate damaging wind gusts in excess of 50 m/s. Sting jets are short-lived, lasting on the order of hours, and the area subjected to their strong winds is typically no wider than 100 km (62 mi), making their effects highly localised. Studies have identified sting jets in mid-latitude cyclones primarily in the northern Atlantic and western Europe, though they may occur elsewhere. The storms that produce sting jets have tended to follow the Shapiro–Keyser model of extratropical cyclone development. Among these storms, sting jets tend to form following storm's highest rate of intensification.
Sverdrup Gold Medal Award – is the American Meteorological Society's award granted to researchers who make outstanding contributions to the scientific knowledge of interactions between the oceans and the atmosphere.

The history of numerical weather prediction considers how current weather conditions as input into mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather and future sea state has changed over the years. Though first attempted manually in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of the computer and computer simulation that computation time was reduced to less than the forecast period itself. ENIAC was used to create the first forecasts via computer in 1950, and over the years more powerful computers have been used to increase the size of initial datasets and use more complicated versions of the equations of motion. The development of global forecasting models led to the first climate models. The development of limited area (regional) models facilitated advances in forecasting the tracks of tropical cyclone as well as air quality in the 1970s and 1980s.

Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS) is a free-surface, terrain-following, primitive equations ocean model widely used by the scientific community for a diverse range of applications. The model is developed and supported by researchers at the Rutgers University, University of California Los Angeles and contributors worldwide.
Professor John David Woods, CBE is a British oceanographer.













