
The Brassicales are an order of flowering plants, belonging to the eurosids II group of dicotyledons under the APG II system. One character common to many members of the order is the production of glucosinolate compounds. Most systems of classification have included this order, although sometimes under the name Capparales.

Brassicaceae or Cruciferae is a medium-sized and economically important family of flowering plants commonly known as the mustards, the crucifers, or the cabbage family. Most are herbaceous plants, some shrubs, with simple, although sometimes deeply incised, alternatingly set leaves without stipules or in leaf rosettes, with terminal inflorescences without bracts, containing flowers with four free sepals, four free alternating petals, two short and four longer free stamens, and a fruit with seeds in rows, divided by a thin wall.

Sorghum is a genus of flowering plants in the grass family Poaceae. Seventeen of the 25 species are native to Australia, with the range of some extending to Africa, Asia, Mesoamerica, and certain islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. One species is grown for grain, while many others are used as fodder plants, either cultivated in warm climates worldwide or naturalized, in pasture lands. Sorghum is in the subfamily Panicoideae and the tribe Andropogoneae.

An invasive species is a species that is not native to a specific location, and that has a tendency to spread to a degree believed to cause damage to the environment, human economy or human health.

Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs of northern temperate regions that belong to the family Cupressaceae. The word cypress is derived from Old French cipres, which was imported from Latin cypressus, the latinisation of the Greek κυπάρισσος (kyparissos).
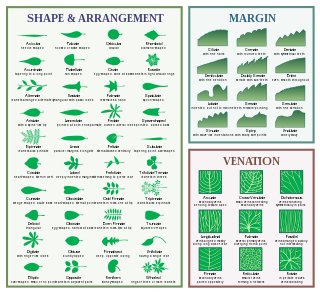
Dendrology or xylology is the science and study of wooded plants, specifically, their taxonomic classifications. There is no sharp boundary between plant taxonomy and dendrology; however, woody plants not only belong to many different plant families, but these families may be made up of both woody and non-woody members. Some families include only a few woody species. Dendrology, as a discipline of industrial forestry, tends to focus on identification of economically useful woody plants and their taxonomic interrelationships. As an academic course of study, dendrology will include all woody plants, native and non-native, that occur in a region. A related discipline is the study of sylvics, which focuses on the autecology of genera and species.

Hyacinthus is a small genus of bulbous, fragrant flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. These are commonly called hyacinths. The genus is native to the eastern Mediterranean.

Flora is the plant life occurring in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring or indigenous—native plant life. The corresponding term for animal life is fauna. Flora, fauna and other forms of life such as fungi are collectively referred to as biota. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms gut flora or skin flora.

A wildflower is a flower that grows in the wild, meaning it was not intentionally seeded or planted. Yet "wildflower" meadows of a few mixed species are sold in seed packets. The term implies that the plant probably is neither a hybrid nor a selected cultivar that is in any way different from the way it appears in the wild as a native plant, even if it is growing where it would not naturally. The term can refer to the flowering plant as a whole, even when not in bloom, and not just the flower.

Galium odoratum, the sweetscented bedstraw, is a flowering perennial plant in the family Rubiaceae, native to much of Europe from Spain and Ireland to Russia, as well as Western Siberia, Turkey, Iran, the Caucasus, China and Japan. It is also sparingly naturalized in scattered locations in the United States and Canada. It is widely cultivated for its flowers and its sweet-smelling foliage.

The University of California Botanical Garden is a 34-acre botanical garden located on the University of California, Berkeley campus, in Strawberry Canyon. The Garden is in the Berkeley Hills, inside the city boundary of Oakland, with views overlooking the San Francisco Bay. It is one of the most diverse plant collections in the United States, and famous for its large number of rare and endangered species.

Pandanus tectorius is a species of Pandanus (screwpine) that is native to Malesia, eastern Australia, and the Pacific Islands. It grows in the coastal lowlands typically near the edge of the ocean. Common names in English include Tahitian screwpine, thatch screwpine, hala tree, pandanus, and pu hala in Hawaiian. The fruit is sometimes known as hala fruit.

Native plants are plants indigenous to a given area in geologic time. This includes plants that have developed, occur naturally, or existed for many years in an area.

Malpighiaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Malpighiales. It comprises about 73 genera and 1315 species, all of which are native to the tropics and subtropics. About 80% of the genera and 90% of the species occur in the New World and the rest in the Old World.

Acacia, commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australia, with the first species A. nilotica described by Linnaeus. Controversy erupted in the early 2000s when it became evident that the genus as it stood was not monophyletic, and that several divergent lineages needed to be placed in separate genera. It turned out that one lineage comprising over 900 species mainly native to Australia was not closely related to the mainly African lineage that contained A. nilotica—the first and type species. This meant that the Australian lineage would need to be renamed. Botanist Les Pedley named this group Racosperma, which was inconsistently adopted. Australian botanists proposed that this would be more disruptive than setting a different type species and allowing this large number of species to remain Acacia, resulting in the two African lineages being renamed Vachellia and Senegalia, and the two New World lineages renamed Acaciella and Mariosousa. This was officially adopted, but many botanists from Africa and elsewhere disagreed that this was necessary.

The California Native Plant Society (CNPS) is a California environmental non-profit organization that seeks to increase understanding of California's native flora and to preserve it for future generations. The mission of CNPS is to conserve California native plants and their natural habitats, and increase understanding, appreciation, and horticultural use of native plants throughout the entire state and California Floristic Province.

The Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center at The University of Texas at Austin is the state botanical garden and arboretum of Texas. The center features more than 900 species of native Texas plants in both garden and natural settings and is home to a breadth of educational programs and events. The center is 284 acres and located 10 miles southwest of downtown Austin, Texas just inside the edge of the distinctive Texas hill country. It straddles both Edwards Plateau and Texas Blackland Prairies ecosystems.

The flora of Australia comprises a vast assemblage of plant species estimated to over 20,000 vascular and 14,000 non-vascular plants, 250,000 species of fungi and over 3,000 lichens. The flora has strong affinities with the flora of Gondwana, and below the family level has a highly endemic angiosperm flora whose diversity was shaped by the effects of continental drift and climate change since the Cretaceous. Prominent features of the Australian flora are adaptations to aridity and fire which include scleromorphy and serotiny. These adaptations are common in species from the large and well-known families Proteaceae (Banksia), Myrtaceae, and Fabaceae.

Agave is a genus of monocots native to the hot and arid regions of Mexico and the Southwestern United States. Some Agave species are also native to tropical areas of South America. The genus Agave is primarily known for its succulent and xerophytic species that typically form large rosettes of strong, fleshy leaves. Plants in this genus may be considered perennial, because they require several to many years to mature and flower. However, most Agave species are more accurately described as monocarpic rosettes or multiannuals, since each individual rosette flowers only once and then dies ; a small number of Agave species are polycarpic.

A grain is a small, hard, dry seed, with or without an attached hull or fruit layer, harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legumes.






















