Regents of the University of California v. Bakke, 438 U.S. 265 (1978), was a landmark decision by the Supreme Court of the United States. It upheld affirmative action, allowing race to be one of several factors in college admission policy. However, the court ruled that specific racial quotas, such as the 16 out of 100 seats set aside for minority students by the University of California, Davis School of Medicine, were impermissible.

Tertiary education fees in Australia are payable for courses at tertiary education institutions. The Commonwealth government provides loans and subsidies to relieve the cost of tertiary education for some students. Some students are supported by the government and are required to pay only part of the cost of tuition, called the "student contribution", and the government pays the balance. Some government supported students can defer payment of their contribution as a HECS-HELP loan. Other domestic students are full fee-paying and do not receive direct government contribution to the cost of their education. Some domestic students in full fee courses can obtain a FEE-HELP loan from the Australian government up to a lifetime limit of $150,000 for medicine, dentistry and veterinary science programs and $104,440 for all other programs.

The Universities and Colleges Admissions Service is a UK-based organisation whose main role is to operate the application process for British universities. It operates as an independent charity, funded by fees charged to applicants and universities, plus advertising income, and was formed in 1992 through the merger of the former university admissions system UCCA and the former polytechnics admissions system PCAS.

A student loan is a type of loan designed to help students pay for post-secondary education and the associated fees, such as tuition, books and supplies, and living expenses. It may differ from other types of loans in the fact that the interest rate may be substantially lower and the repayment schedule may be deferred while the student is still in school. It also differs in many countries in the strict laws regulating renegotiating and bankruptcy. This article highlights the differences of the student loan system in several major countries.
Joint Entrance Examination – Advanced (JEE-Advanced), is an academic examination held annually in India. It is organised by one of the seven zonal IITs under the guidance of the Joint Admission Board (JAB) on a round-robin rotation pattern for the qualifying candidates of the JEE-Main. It was used to be the sole prerequisite for admission to the Indian Institutes of Technology bachelor's programs before the introduction of UCEED, Online BSc and Olympiad entry but seats through these new mediums are very low.
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is a form completed by current and prospective college students in the United States to determine their eligibility for student financial aid.
Early decision (ED) or early acceptance is a type of early admission used in college admissions in the United States for admitting freshmen to undergraduate programs. It is used to indicate to the university or college that the candidate considers that institution to be their top choice through a binding commitment to enroll. Applying early decision brings a greater statistical chance of being accepted.
Student financial aid in the United States is funding that is available exclusively to students attending a post-secondary educational institution in the United States. This funding is used to assist in covering the many costs incurred in the pursuit of post-secondary education. Financial aid is available from federal and state governments, educational institutions, and private organizations. It can be awarded in the form of grants, loans, work-study, and scholarships. In order to apply for federal financial aid, students must first complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
University admission or college admission is the process through which students enter tertiary education at universities and colleges. Systems vary widely from country to country, and sometimes from institution to institution.
Joint Entrance Examination – Main (JEE-Main), formerly All India Engineering Entrance Examination (AIEEE), is an Indian standardised computer-based test for admission to various technical undergraduate programs in engineering, architecture, and planning across colleges in India. The exam is conducted by the JEE Apex Board for Admission for B.Tech, B.Arch, etc. programs in the premier technical institutes such as the National Institutes of Technology and Indian Institutes of Information Technology are based on the rank secured in the JEE-Main. It is usually conducted twice every year.
Early action (EA) is a type of early admission process offered by some institutions for admission to colleges and universities in the United States. Unlike the regular admissions process, EA usually requires students to submit an application by mid-October or early November of their senior year of high school instead of January 1. Students are notified of the school's decision by early January instead of mid-March or May 1.
College admissions in the United States refers to the process of applying for entrance to institutions of higher education for undergraduate study at one of the nation's colleges or universities. For those who intend to attend college immediately after high school, the college search usually begins in the eleventh grade with most activity taking place during the twelfth grade, although students at top high schools often begin the process during their tenth grade or earlier. In addition, there are considerable numbers of students who transfer from one college to another, as well as adults older than high school age who apply to college.
Rolling admission is a policy used by many colleges to admit freshmen to undergraduate programs. Many law schools in the United States also have rolling admissions policies. Under rolling admission, candidates are invited to submit their applications to the university anytime within a large window. The window is usually over six months long, and some schools do not have a previously specified end date. The university will then review the application and notify the applicant of their decision within a few weeks from submission.
A Stafford Loan was a student loan offered from the United States Department of Education to eligible students enrolled in accredited American institutions of higher education to help finance their education. The terms of the loans are described in Title IV of the Higher Education Act of 1965, which guarantees repayment to the lender if a student defaults. As of July 1, 2010, Stafford Loans are no longer being offered, having been replaced with the William D. Ford Federal Direct Student Loan Program.
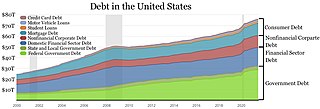
Student loans in the United States are a form of financial aid intended to help students access higher education. In 2018, 70 percent of higher education graduates had used loans to cover some or all of their expenses. With notable exceptions, student loans must be repaid, in contrast to other forms of financial aid such as scholarships, which are not repaid, and grants, which rarely have to be repaid. Student loans may be discharged through bankruptcy, but this is difficult.
Medical school in the United States is a graduate program with the purpose of educating physicians in the undifferentiated field of medicine. Such schools provide a major part of the medical education in the United States. Most medical schools in the US confer upon graduates a Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree, while some confer a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree. Most schools follow a similar pattern of education, with two years of classroom and laboratory based education, followed by two years of clinical rotations in a teaching hospital where students see patients in a variety of specialties. After completion, graduates must complete a residency before becoming licensed to practice medicine.
Student loan deferment is an agreement between the student and lender that the student may reduce or postpone repayment of a student loan for a designated period. Deferment or forbearance will prevent the loan from going into default, but may increase the overall cost of the loan. Students may be eligible for deferment while experiencing financial hardship or unemployment. The lender may require valid proof of financial hardship and other financial information when the student applies.
The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (Undergraduate) or NEET (UG), formerly the All India Pre-Medical Test (AIPMT), is an all India pre-medical entrance test for students who wish to pursue undergraduate medical (MBBS), dental (BDS) and AYUSH courses in government and private institutions in India and also, for those intending to pursue primary medical qualification abroad.
The innocent prisoner's dilemma, or parole deal, is a detrimental effect of a legal system in which admission of guilt can result in reduced sentences or early parole. When an innocent person is wrongly convicted of a crime, legal systems which need the individual to admit guilt — as, for example, a prerequisite step leading to parole — punish an innocent person for their integrity, and reward a person lacking in integrity. There have been cases where innocent prisoners were given the choice between freedom, in exchange for claiming guilt, and remaining imprisoned and telling the truth. Individuals have died in prison rather than admit to crimes that they did not commit.

The Inter American University of Puerto Rico, Faculty of Law is the school of law of the Inter American University of Puerto Rico, a private co-educational corporation accredited by the Middle States Association of Colleges and Schools, the Puerto Rico Council of Higher Education, and the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico Department of Education. The School of Law is approved by the American Bar Association (ABA) and is located in San Juan, the capital city of Puerto Rico. Since its founding, the School of Law has succeeded in meeting the needs of the legal profession, in particular, and Puerto Rico's society in general.




