
Psychosis is a mental disorder caused by a person becoming disconnected from reality. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior that is inappropriate for a given situation. There may also be sleep problems, social withdrawal, lack of motivation, and difficulties carrying out daily activities. Psychosis can have serious adverse outcomes.
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concerning a perceived threat towards oneself. Paranoia is distinct from phobias, which also involve irrational fear, but usually no blame.
A delusion is a false fixed belief that is not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence. As a pathology, it is distinct from a belief based on false or incomplete information, confabulation, dogma, illusion, hallucination, or some other misleading effects of perception, as individuals with those beliefs are able to change or readjust their beliefs upon reviewing the evidence. However:

Erotomania, also known as de Clérambault's Syndrome, named after French psychiatrist Gaëtan Gatian de Clérambault, is listed in the DSM-5 as a subtype of a delusional disorder. It is a relatively uncommon paranoid condition that is characterized by an individual's delusions of another person being infatuated with them. This disorder is most often seen in female patients who are shy, dependent and sexually inexperienced. The object of the delusion is typically a male who is unattainable due to high social or financial status, marriage or lack of interest. The object of obsession may also be imaginary, deceased or someone the patient has never met. Delusions of reference are common, as the erotomanic individual often perceives that they are being sent messages from the secret admirer through innocuous events such as seeing license plates from specific states, but has no proof. Commonly, the onset of erotomania is sudden, and the course is chronic.
Ideas of reference and delusions of reference describe the phenomenon of an individual experiencing innocuous events or mere coincidences and believing they have strong personal significance. It is "the notion that everything one perceives in the world relates to one's own destiny", usually in a negative and hostile manner.
Delusional parasitosis (DP) is a mental disorder in which individuals have a persistent belief that they are infested with living or nonliving pathogens such as parasites, insects, or bugs, when no such infestation is present. They usually report tactile hallucinations known as formication, a sensation resembling insects crawling on or under the skin. Morgellons is considered to be a subtype of this condition, in which individuals have sores that they believe contain harmful fibers.

Delusional disorder is a mental illness in which a person has delusions, but with no accompanying prominent hallucinations, thought disorder, mood disorder, or significant flattening of affect. Delusions are a specific symptom of psychosis. Delusions can be bizarre or non-bizarre in content; non-bizarre delusions are fixed false beliefs that involve situations that could occur in real life, such as being harmed or poisoned. Apart from their delusion or delusions, people with delusional disorder may continue to socialize and function in a normal manner and their behavior does not necessarily generally seem odd. However, the preoccupation with delusional ideas can be disruptive to their overall lives.
Capgras delusion or Capgras syndrome is a psychiatric disorder in which a person holds a delusion that a friend, spouse, parent, or another close family member has been replaced by an identical impostor. It is named after Joseph Capgras (1873–1950), the French psychiatrist who first described the disorder.
Michael Ruse is a British-born Canadian philosopher of science who specializes in the philosophy of biology and works on the relationship between science and religion, the creation–evolution controversy, and the demarcation problem within science. Ruse currently teaches at Florida State University.

The God Delusion is a 2006 book by British evolutionary biologist, ethologist Richard Dawkins, a professorial fellow at New College, Oxford and, at the time of publication, the Charles Simonyi Chair for the Public Understanding of Science at the University of Oxford.
"The Discarded" is a science fiction short story by American writer Harlan Ellison. It was first published in the April 1959 issue of Fantastic and was later included in the 1965 short story collection Paingod and Other Delusions and the third volume of the audiobook collection The Voice From The Edge.
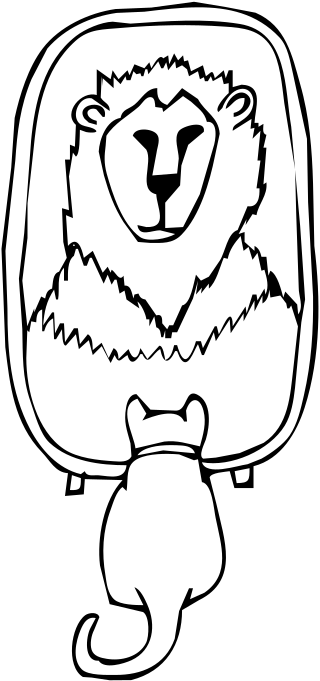
Grandiose delusions (GD), also known as delusions of grandeur or expansive delusions, are a subtype of delusion that occur in patients with a wide range of psychiatric diseases, including two-thirds of patients in a manic state of bipolar disorder, half of those with schizophrenia, patients with the grandiose subtype of delusional disorder, frequently in narcissistic personality disorder, and a substantial portion of those with substance abuse disorders. GDs are characterized by fantastical beliefs that one is famous, omnipotent, wealthy, or otherwise very powerful. The delusions are generally fantastic and typically have a religious, science fictional, or supernatural theme. There is a relative lack of research into GD, in contrast to persecutory delusions and auditory hallucinations. Around 10% of healthy people experience grandiose thoughts at some point in their lives but do not meet full criteria for a diagnosis of GD.
Folie à deux, referred to as Lasègue–Falret syndrome, additionally known as shared psychosis or shared delusional disorder (SDD), is a collection of rare psychiatric syndromes in which symptoms of a delusional belief, and sometimes hallucinations, are transmitted from one individual to another. The same syndrome shared by more than two people may be called folie à trois ('three') or quatre ('four'); and further, folie en famille or even folie à plusieurs.
A persecutory delusion or persecution complex is a common type of delusional condition in which the affected person believes that harm is going to occur to oneself by a persecutor, despite a clear lack of evidence. The person may believe that they are being targeted by an individual or a group of people. Persecution delusions are very diverse in terms of content and vary from the possible, albeit improbable, to the completely bizarre. The delusion can be found in a multitude of disorders, being more usual in psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and delusional disorder.
Electronic harassment, electromagnetic torture, or psychotronic torture is a conspiracy theory that malicious actors make use of electromagnetic radiation, radar, and surveillance techniques to transmit sounds and thoughts into people's heads, affect people's bodies, and harass people. Individuals who claim to experience this call themselves "targeted individuals" (TIs). Some claim they are victims of gang stalking and many have created or joined support and advocacy groups.

Cotard's syndrome, also known as Cotard's delusion or walking corpse syndrome, is a rare mental disorder in which the affected person holds the delusional belief that they are dead, do not exist, are putrefying, or have lost their blood or internal organs. Statistical analysis of a hundred-patient cohort indicated that denial of self-existence is present in 45% of the cases of Cotard's syndrome; the other 55% of the patients presented with delusions of immortality.

Love, Chunibyo & Other Delusions!, also known as Chū-2 for short, is a Japanese light novel series written by Torako, with illustrations provided by Nozomi Ōsaka. The work won an honorable mention in the Kyoto Animation Award competition in 2010, leading the company to assume its publication starting in June 2011. The series follows a high school boy named Yūta Togashi, who tries to discard his embarrassing past grandiose delusions, until he meets a girl named Rikka Takanashi, who exhibits her own signs of chūnibyō syndrome. As their relationship progresses, Yūta and Rikka form a club called the Far East Magical Napping Society Summer Thereof with classmates Shinka Nibutani, Kumin Tsuyuri and Sanae Dekomori, who each have their own unique delusional behaviors.

"Johnny Delusional" is a song by musical supergroup FFS, consisting of members from the bands Franz Ferdinand and Sparks. The song was released as the lead single from the group's eponymous debut studio album on 13 April 2015. The official music video for the song was uploaded to YouTube on 19 May 2015. The song peaked at number 90 on the Belgian Flanders Tip singles chart.
Tau Films is an American visual effects and animation company with locations in the United States, Malaysia, India, China, and Canada.

Delusions of Grandeur is the thirteenth studio album by American rapper Gucci Mane. It was released on June 21, 2019, by Atlantic Records and 1017 Records. The album features guest appearances from Meek Mill, Gunna, Lil Baby, Justin Bieber, Jeremih, A Boogie wit da Hoodie, Wiz Khalifa, Rick Ross, Lil Uzi Vert, Young Dolph, Anuel AA, and Peewee Longway, among others.









