Related Research Articles

A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have a complex internal and external structure. They are lightweight yet strong and hard, and serve multiple functions.

Tooth enamel is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many other animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. Calcium hardens the tooth enamel. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface.

Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation.
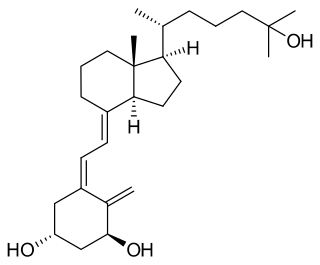
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bone metabolism causes inadequate bone mineralization. Osteomalacia in children is known as rickets, and because of this, use of the term "osteomalacia" is often restricted to the milder, adult form of the disease. Signs and symptoms can include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragility of the bones. In addition to low systemic levels of circulating mineral ions that result in decreased bone and tooth mineralization, accumulation of mineralization-inhibiting proteins and peptides, and small inhibitory molecules, can occur in the extracellular matrix of bones and teeth, contributing locally to cause matrix hypomineralization (osteomalacia/odontomalacia). A relationship describing local, physiologic double-negative regulation of mineralization has been termed the Stenciling Principle of mineralization, whereby enzyme-substrate pairs imprint mineralization patterns into the extracellular matrix by degrading mineralization inhibitors. The Stenciling Principle for mineralization is particularly relevant to the osteomalacia and odontomalacia observed in hypophosphatasia (HPP) and X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH).

Dentin or dentine is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels become exposed.

Purified water is water that has been mechanically filtered or processed to remove impurities and make it suitable for use. Distilled water was, formerly, the most common form of purified water, but, in recent years, water is more frequently purified by other processes including capacitive deionization, reverse osmosis, carbon filtering, microfiltration, ultrafiltration, ultraviolet oxidation, or electrodeionization. Combinations of a number of these processes have come into use to produce ultrapure water of such high purity that its trace contaminants are measured in parts per billion (ppb) or parts per trillion (ppt).
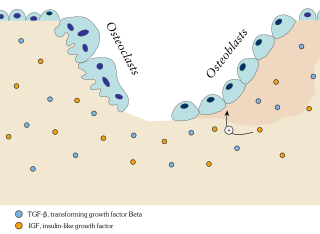
Ossification in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor.

Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue, causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification. Calcification may also refer to the processes of normal mineral deposition in biological systems, such as the formation of stromatolites or mollusc shells.

Also known as a "bonderizer" bonding agents are resin materials used to make a dental composite filling material adhere to both dentin and enamel.

Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured without bone grafting, but the risk is greater for large fractures like compound fractures.

Hypophosphatasia (; also called deficiency of alkaline phosphatase, phosphoethanolaminuria, or Rathbun's syndrome; sometimes abbreviated HPP) is a rare, and sometimes fatal, metabolic bone disease. Clinical symptoms are heterogeneous, ranging from the rapidly fatal, perinatal variant, with profound skeletal hypomineralization, respiratory compromise or vitamin B6 dependent seizures to a milder, progressive osteomalacia later in life. Tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) deficiency in osteoblasts and chondrocytes impairs bone mineralization, leading to rickets or osteomalacia. The pathognomonic finding is subnormal serum activity of the TNSALP enzyme, which is caused by one of 388 genetic mutations identified to date, in the gene encoding TNSALP. Genetic inheritance is autosomal recessive for the perinatal and infantile forms but either autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant in the milder forms.

The Nova Southeastern University College of Dental Medicine is the dental school of Nova Southeastern University. It is located in Fort Lauderdale, Florida, United States. When it opened in 1997, it was the first new dental school to open in the United States in 24 years. It is the largest dental school in Florida. The school is accredited by the American Dental Association.
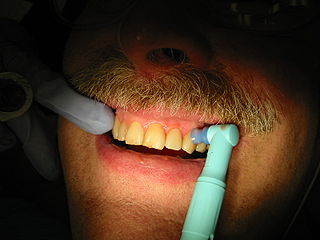
Tooth polishing is done to smooth the surfaces of teeth and restorations. The purpose of polishing is to remove extrinsic stains, remove dental plaque accumulation, increase aesthetics and to reduce corrosion of metallic restorations. Tooth polishing has little therapeutic value and is usually done as a cosmetic procedure after debridement and before fluoride application. Common practice is to use a prophy cup—a small motorized rubber cup—along with an abrasive polishing compound.

Tooth remineralization is the natural repair process for non-cavitated tooth lesions, in which calcium, phosphate and sometimes fluoride ions are deposited into crystal voids in demineralised enamel. Remineralization can contribute towards restoring strength and function within tooth structure.
In dentistry, enamel matrix derivative (EMD) is an extract of porcine fetal tooth material used to biomimetically stimulate the soft and hard tissues surrounding teeth to regrow following tissue destruction.
Demineralisation or demineralization may refer to:

Mineralized tissues are biological tissues that incorporate minerals into soft matrices. Typically these tissues form a protective shield or structural support. Bone, mollusc shells, deep sea sponge Euplectella species, radiolarians, diatoms, antler bone, tendon, cartilage, tooth enamel and dentin are some examples of mineralized tissues.

Bone mineral is the inorganic component of bone tissue. It gives bones their compressive strength. Bone mineral is formed predominantly from carbonated hydroxyapatite with lower crystallinity.

The Soom Shale is a member of the Late Ordovician (Hirnantian) Cederberg Formation in South Africa, renowned for its remarkable preservation of soft-tissue in fossil material. Deposited in still waters, the unit lacks bioturbation, perhaps indicating anoxic conditions.
Demineralized bone matrix (DBM) is allograft bone that has had the inorganic mineral removed, leaving behind the organic "collagen" matrix. It was first discovered by Marshall Urist in 1965 that the removal of the bone mineral exposes more biologically active bone morphogenetic proteins. These growth factors modulate the differentiation of progenitor cells into osteoprogenitor cells, which are responsible for bone and cartilage formation. As a result of the demineralization process, DBM is more biologically active than undemineralized bone grafts; conversely the mechanical properties are significantly diminished.
References
- ↑ "Condensate Polishing Packages". www.aesarabia.com. Retrieved 7 June 2015.