Derbent is a city in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia.
Contents
Derbent may also refer to:
Derbent is a city in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia.
Derbent may also refer to:

Derbent, formerly romanized as Derbend, is a city in Dagestan, Russia, located on the Caspian Sea. It is the southernmost city in Russia, and it is the second-most important city of Dagestan. Derbent occupies the narrow gateway between the Caspian Sea and the Caucasus Mountains connecting the Eurasian Steppe to the north and the Iranian Plateau to the south; covering an area of 69.63 square kilometres (26.88 sq mi), with a population of roughly 120,000 residents.

Lezgins are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group native predominantly to southern Dagestan, a republic of Russia, and northeastern Azerbaijan, and speak the Lezgin language. Their social structure is firmly based on equality and deference to individuality. Lezgin society is structured around djamaat and has traditionally been egalitarian and organised around many autonomous local clans, called sykhyls (сихилар).

Dagestan, officially the Republic of Dagestan, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Federal District. The republic is the southernmost tip of Russia, sharing land borders with the countries of Azerbaijan and Georgia to the south and southwest, the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia to the west and north, and with Stavropol Krai to the northwest. Makhachkala is the republic's capital and largest city; other major cities are Derbent, Kizlyar, Izberbash, Kaspiysk, and Buynaksk.
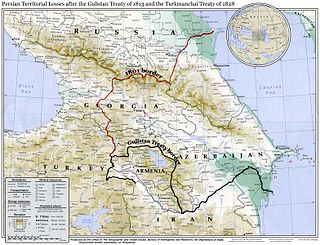
The Treaty of Gulistan was a peace treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and Qajar Iran on 24 October 1813 in the village of Gulistan as a result of the first full-scale Russo-Persian War. The peace negotiations were precipitated by the successful storming of Lankaran by General Pyotr Kotlyarevsky on 1 January 1813. It was the first of a series of treaties signed between Qajar Iran and Imperial Russia that forced Persia to cede the territories that formerly were part of Iran.

The peoples of the Caucasus, or Caucasians, are a diverse group comprising more than 50 ethnic groups throughout the Caucasus.
Azerbaijanis in Russia or Russian Azerbaijanis are people of Azeri descent in Russia. These may be either ethnic Azeris residents in the country or recent immigrants who profess Azeri ancestry.

The Russian conquest of the Caucasus mainly occurred between 1800 and 1864. The Russian Empire sought to control the region between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea. South of the mountains was the territory that is modern Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Iran and Turkey. North of the mountains was the North Caucasus region of modern Russia. The difficult conquest of the intervening mountains is known as the Caucasian War. Multiple wars were fought against the local rulers of the regions, as well as the dominant powers, the Ottoman Empire and Qajar Iran, for control. By 1864 the last regions were brought under Russian control.

Derbentsky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the forty-one in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia. It is located in the southeast of the republic. The area of the district is 822.72 square kilometers (317.65 sq mi). Its administrative center is the city of Derbent. As of the 2010 Census, the total population of the district was 99,054.
Lakia is an ancient ethnic region within the state of Dagestan. Its historical capital is Kumukh, one of the ancient cultural and religious centres of Lakia. The people of Lakia are self-designated as Laks and their native language is Lak.
Kumukh, also known as Gazi Kumukh, is a village and the administrative center of Laksky District in Dagestan. It is located on the banks of the Kazikumukh Koysu, a branch of the Sulak River.

Historically, Dagestan consisted of a federation of mountainous principalities in the eastern part of the North Caucasus. Located at the crossroads of world civilizations of north and south, Dagestan was the scene of clashes of interests of many states and until the early 19th century, most notably between Iran and the Russian Empire.
Fatali Khan or Fath Ali Khan of Quba was a khan of the Quba Khanate (1758–1789) who also managed to dominate the Derbent, Baku, Talysh and Shirvan Khanates, as well as the Salyan Sultanate during much of his reign.

The Derbent Khanate was a Caucasian khanate that was established in Afsharid Iran. It corresponded to southern Dagestan and its center was at Derbent.
Karchag is a rural locality and the administrative centre of Karchagsky Selsoviet, Suleyman-Stalsky District, Republic of Dagestan, Russia.
Khanzhalkala (Khanzhal-Kala), also known as Khanjal-Kala is an abandoned Lezgin aul in the Magaramkentsky District of Dagestan. The name comes from Judeo-Tat and means "fortress of the dagger". It was protected not only by the steep slopes of the mountain on which it was located, but also by its fortress walls. It was abolished in 1968.

The Derbent Synagogue, also known as Kele-Numaz was a former Orthodox Jewish congregation and synagogue, located at 94 Tagi-Zade Street, in the city of Derbent in the Republic of Dagestan, in the North Caucasus of Russia.

Amir Hamza III was an khan of Kaitags who ruled Kaitag Utsmiate from 1751 to 1787. He was known as a significant military figure in the history of Dagestan and Transcaucasia in the 18th century.
Shaykh Ali Khan or Shikh Ali Khan was the last khan of Quba before its annexation to Russian Empire.
Surkhay Khan Kun-Butta or erroneously Khanbutai, Khon-Butai, Khomutai was an 18th-century Dagestani military leader as well as last independent Gazikumukh Khan.

Christianity ranks second in Dagestan in terms of the number of its followers after Islam. There are around 140,000 Christians, including denominations like Russian Orthodoxy, Armenian, Protestant and Catholic.