
1,2-Dibromoethane, also known as ethylene dibromide (EDB), is an organobromine compound with the chemical formula C
2H
4Br
2. Although trace amounts occur naturally in the ocean, where it is formed probably by algae and kelp, it is mainly synthetic. It is a dense colorless liquid with a faint sweet odor, detectable at 10 ppm, is a widely used and sometimes-controversial fumigant. The combustion of 1,2-dibromoethane produces hydrogen bromide gas that is significantly corrosive.
Halocarbon compounds are chemicals in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, organochlorine compounds, organobromine compounds, and organoiodine compounds. Chlorine halocarbons are the most common and are called organochlorides.

Diquat is the ISO common name for an organic dication that, as a salt with counterions such as bromide or chloride is used as a contact herbicide that produces desiccation and defoliation. Diquat is no longer approved for use in the European Union, although its registration in many other countries including the USA is still valid.

Picene is a hydrocarbon found in the pitchy residue obtained in the distillation of peat tar and of petroleum. This is distilled to dryness and the distillate repeatedly recrystallized from cymene. It may be synthetically prepared by the action of anhydrous aluminium chloride on a mixture of naphthalene and 1,2-dibromoethane, or by distilling a-dinaphthostilbene. It crystallizes in large colorless plates which possess a blue fluorescence. It is soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid with a green color. Chromic acid in glacial acetic acid solution oxidizes it to picene-quinone, picene-quinone carboxylic acid, and finally to phthalic acid.
In chemistry, the descriptor geminal refers to the relationship between two atoms or functional groups that are attached to the same atom. The word comes from Latin gemini meaning "twins". A geminal diol, for example, is a diol attached to the same carbon atom, as in methanediol. Also the shortened prefix gem may be applied to a chemical name to denote this relationship, as in a gem-dibromide for "geminal dibromide".

Ditellurium bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Te2Br. It is one of the few stable lower bromides of tellurium. Unlike sulfur and selenium, tellurium forms families of polymeric subhalides where the chalcogen/halide ratio is less than 2.

Phenylpropiolic acid, C6H5CCCO2H, formed by the action of alcoholic potash on cinnamic acid dibromide, C6H5CHBrCHBrCO2H, crystallizes in long needles or prisms which melt at 136–137 °C. When heated with water to 120 °C, it yields phenylacetylene (C6H5CCH). Chromic acid oxidizes it to benzoic acid; zinc and acetic acid reduce it to cinnamic acid, C6H5CH=CHCO2H, whilst sodium amalgam reduces it to hydrocinnamic acid, C6H5CH2CH2CO2H. Ortho-nitrophenylpropiolic acid, NO2C6H4CCCO2H, prepared by the action of alcoholic potash on ortho-nitrocinnamic acid dibromide, crystallizes in needles which decompose when heated to 155–156 °C. It is readily converted into indigo.

1,2-Dibromopropane, also known as propylene dibromide, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CHBrCH2Br. It is the simplest chiral hydrocarbon containing two bromine atoms:
1,1-Dibromoethane is a clear, slightly brown, flammable chemical compound. It is classified as the organobromine compound, and has the chemical formula C2H4Br2 and it is a position isomer of 1,2-dibromoethane. It is commonly seen in industrial chemistry, where it is used as a fuel additive. It is also used as a grain and soil fumigant for insect control.
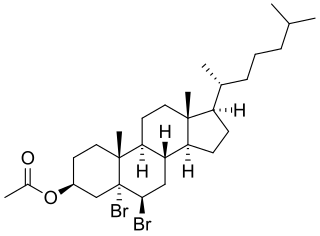
Acebrochol (INN), also known as cholesteryl acetate dibromide or 5α,6β-dibromocholestan-3β-ol acetate, is a neuroactive steroid which was described as a sedative and hypnotic but was never marketed.
The molecular formula C2H4Br2 may refer to:
Tellurium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula TeI. Two forms are known. Their structures differ from the other monohalides of tellurium. There are three subiodides of tellurium, α-TeI, β-TeI, and Te2I, and one tellurium tetraiodide.
Polonium dibromide (also known as polonium(II) bromide) is a chemical compound with the formula PoBr2. This salt is a purple-brown crystalline solid at room temperature. It sublimes (decomposing slightly) at 110 °C/30 μ and decomposes when melted in nitrogen gas at 270–280 °C.
Molybdenum(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula MoBr2. It forms yellow-red crystals.
Disulfur dibromide is the inorganic compound with the formula S2Br2. It is a yellow-brown liquid that fumes in air. It is prepared by direct combination of the elements and purified by vacuum distillation. The compound has no particular application, unlike the related sulfur compound disulfur dichloride.

Sulfur dibromide is the chemical compound with the formula SBr2. It is a toxic gas.
Vanadium(II) bromide, also known as vanadium dibromide, is a chemical compound with the formula VBr2.
Selenium dibromide is a compound made of one selenium and two bromine atoms. It is 66.93% bromine and 33.07% selenium. It is sold by Aithaca Chemical Corp. It has a molar mass of 238.768.
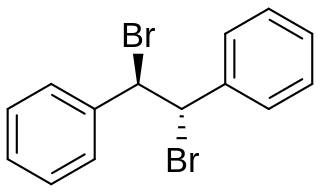
meso-Stilbene dibromide is an organic molecule with a net formula of C14H12Br2. It is sometimes also written as meso-1,2-dibromo-1,2-diphenyl ethane. It appears as a white crystalline solid and can be used a building block in organic synthesis for various applications.









