
In statistics, cluster sampling is a sampling plan used when mutually homogeneous yet internally heterogeneous groupings are evident in a statistical population. It is often used in marketing research.
Differentiation may refer to:

In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors and how it in turn alters those same factors. "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts".

A web hosting service is a type of Internet hosting service that hosts websites for clients, i.e. it offers the facilities required for them to create and maintain a site and makes it accessible on the World Wide Web. Companies providing web hosting services are sometimes called web hosts.
In marketing, market segmentation or customer segmentation is the process of dividing a consumer or business market into meaningful sub-groups of current or potential customers known as segments. Its purpose is to identify profitable and growing segments that a company can target with distinct marketing strategies.

A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.

Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group are more similar to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning.

An anonymous affinity group is a group formed around a shared interest or common goal, to which individuals formally or informally belong. Affinity groups are generally precluded from being under the aegis of any governmental agency, and their purposes must be primarily non-commercial. Examples of affinity groups include private social clubs, fraternities, writing or reading circles, hobby clubs, and groups engaged in political activism.
In the Domain Name System (DNS) hierarchy, a subdomain is a domain that is a part of another (main) domain. For example, if a domain offered an online store as part of their website example.com, it might use the subdomain shop.example.com.
Researchers have investigated the relationship between race and genetics as part of efforts to understand how biology may or may not contribute to human racial categorization. Today, the consensus among scientists is that race is a social construct, and that using it as a proxy for genetic differences among populations is misleading.
Ego state therapy is a parts-based psychodynamic approach to treat various behavioural and cognitive problems within a person. It uses techniques that are common in group and family therapy, but with an individual patient, to resolve conflicts that manifest in a "family of self" within a single individual.
Software multitenancy is a software architecture in which a single instance of software runs on a server and serves multiple tenants. Systems designed in such manner are "shared". A tenant is a group of users who share a common access with specific privileges to the software instance. With a multitenant architecture, a software application is designed to provide every tenant a dedicated share of the instance—including its data, configuration, user management, tenant individual functionality and non-functional properties. Multitenancy contrasts with multi-instance architectures, where separate software instances operate on behalf of different tenants.

A heat map is a 2-dimensional data visualization technique that represents the magnitude of individual values within a dataset as a color. The variation in color may be by hue or intensity.

Sociology of terrorism is a field of sociology that seeks to understand terrorism as a social phenomenon. The field defines terrorism, studies why it occurs and evaluates its impacts on society. The sociology of terrorism draws from the fields of political science, history, economics and psychology. The sociology of terrorism differs from critical terrorism studies, emphasizing the social conditions that enable terrorism. It also studies how individuals as well as states respond to such events.
In statistics, k-medians clustering is a cluster analysis algorithm. It is a generalization of the geometric median or 1-median algorithm, defined for a single cluster.

A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software. The newest manifestation of cluster computing is cloud computing.
Adaptation in computer science is a process where an interactive system adapts its behaviour to individual users based on information acquired about its user(s) and its environment. Adaptation is one of the three pillars of empiricism in Scrum.

Taxation in Italy is levied by the central and regional governments and is collected by the Italian Agency of Revenue. Total tax revenue in 2018 was 42.4% of GDP. The main earnings are income tax, social security, corporate tax and value added tax. All of these are collected at national level, but some differ across regions. Personal income taxation in Italy is progressive.
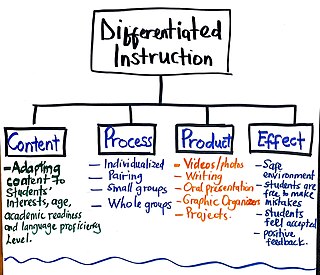
Differentiated instruction and assessment, also known as differentiated learning or, in education, simply, differentiation, is a framework or philosophy for effective teaching that involves providing all students within their diverse classroom community of learners a range of different avenues for understanding new information in terms of: acquiring content; processing, constructing, or making sense of ideas; and developing teaching materials and assessment measures so that all students within a classroom can learn effectively, regardless of differences in their ability. Differentiated instruction means using different tools, content, and due process in order to successfully reach all individuals. Differentiated instruction, according to Carol Ann Tomlinson, is the process of "ensuring that what a student learns, how he or she learns it, and how the student demonstrates what he or she has learned is a match for that student's readiness level, interests, and preferred mode of learning." According to Boelens et al. (2018), differentiation can be on two different levels: the administration level and the classroom level. The administration level takes the socioeconomic status and gender of students into consideration. At the classroom level, differentiation revolves around content, processing, product, and effects. On the content level, teachers adapt what they are teaching to meet the needs of students. This can mean making content more challenging or simplified for students based on their levels. The process of learning can be differentiated as well. Teachers may choose to teach individually at a time, assign problems to small groups, partners or the whole group depending on the needs of the students. By differentiating product, teachers decide how students will present what they have learned. This may take the form of videos, graphic organizers, photo presentations, writing, and oral presentations. All these take place in a safe classroom environment where students feel respected and valued—effects.
A distributed file system for cloud is a file system that allows many clients to have access to data and supports operations on that data. Each data file may be partitioned into several parts called chunks. Each chunk may be stored on different remote machines, facilitating the parallel execution of applications. Typically, data is stored in files in a hierarchical tree, where the nodes represent directories. There are several ways to share files in a distributed architecture: each solution must be suitable for a certain type of application, depending on how complex the application is. Meanwhile, the security of the system must be ensured. Confidentiality, availability and integrity are the main keys for a secure system.