
Thrace is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split between Bulgaria, Greece and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria, northeastern Greece and the European part of Turkey.

Bendis was a Thracian goddess associated with hunting whom the Athenians identified with Artemis, was introduced into Athens about 430 BC. She was a huntress, like Artemis, but was accompanied by dancing satyrs and maenads on a fifth-century red-figure stemless cup.

The Scordisci were a Celtic Iron Age tribe centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava) and Danube rivers. They were historically notable from the beginning of the third century BC until the turn of the common era. The Scordisci consolidated into a tribal state. At their zenith, their core territory stretched over regions comprising parts of present-day Serbia, Croatia, Bulgaria and Romania, while their influence spread even further. After the Roman conquest in the 1st century AD, their territories were included into the Roman provinces of Pannonia, Moesia and Dacia.
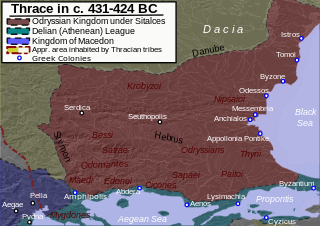
The Odrysian Kingdom was a state union of over 40 Thracian tribes and 22 kingdoms that existed between the 5th century BC and the 1st century AD. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria, spreading to parts of Southeastern Romania, parts of Northern Greece and parts of modern-day European Turkey.

The Getae, , or Gets were several Thracian tribes that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form Get and plural Getae may be derived from a Greek exonym: the area was the hinterland of Greek colonies on the Black Sea coast, bringing the Getae into contact with the ancient Greeks from an early date. Several scholars, especially in the Romanian historiography, posit the identity between the Getae and their westward neighbours, the Dacians.

The Bessi were an independent Thracian tribe who lived in a territory ranging from Moesia to Mount Rhodope in southern Thrace, but are often mentioned as dwelling about Haemus, the mountain range that separates Moesia from Thrace and from Mount Rhodope to the northern part of Hebrus. Herodotus described them as a sort of priestly-caste among the Satrae, the Bessi being interpreters of the prophetic utterances given by a priestess in an oracular shrine of Dionysus located on a mountain-top.
The Moesi was a Thracian tribe which inhabited present day Northern Bulgaria and Serbia, which gave its name to the Roman province of Moesia after its defeat in 29 BC. Moesia was first established as a separate province in 45–46 AD.
Asti is the name of a Thracian tribe which is mentioned by Livy. It is believed that they lived around the old Thracian capital of Bizye.

Bistones is the name of a Thracian people who dwelt between Mount Rhodopé and the Aegean Sea, beside Lake Bistonis, near Abdera. From the worship of Dionysus in Thrace, female Bacchanals were sometimes called Bistonides, just as in some Latin poems, Edonis refers to female Bacchanals. Pliny mentions one town as belonging to the Bistones: Tirida.

Dolonci or Dolonki is the name of a Thracian tribe in Thracian Chersonese. They are mentioned by Herodotus.
Koreli or Coreli is the name of a Thracian tribe. They are mentioned by Livy.
Cebrenii is the name of a Thracian tribe, they are mentioned by Polyaenus and Strabo.
Sycaeboae is the name of a Thracian tribe, which was mentioned by Polyaenus.

The history of Thracian warfare spans from the 10th century BC up to the 1st century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Thrace. It concerns the armed conflicts of the Thracian tribes and their kingdoms in the Balkans. Apart from conflicts between Thracians and neighboring nations and tribes, numerous wars were recorded among Thracian tribes.
Thracian clothing refers to types of clothing worn mainly by Thracians, Dacians but also by some Greeks. Its best literal descriptions are given by Herodotus and Xenophon in his Anabasis. Depictions are found in a great number of Greek vases and there are a few Persian representations as well. In contrast to shapes and patterns we have very little evidence on the colours used.
Treri is the name of a Thracian tribe. They are mentioned by Strabo.








