Dinitrotoluenes could refer to one of the following compounds:
Dinitrotoluenes could refer to one of the following compounds:
The time signature is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats (pulses) are contained in each measure (bar), and which note value is equivalent to a beat.

Trinitrotoluene, more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts.
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Julius Bernhard Friedrich Adolph Wilbrand was a German chemist. Born in Gießen to Franz Joseph Julius Wilbrand and Albertine Knapp, he discovered trinitrotoluene in 1863, but the compound's use as an explosive was not developed until later. Wilbrand obtained trinitrotoluene or TNT by the nitration of toluene.
DNT may refer to:
The Composition C family is a family of related US-specified plastic explosives consisting primarily of RDX. All can be moulded by hand for use in demolition work and packed by hand into shaped charge devices. Variants have different proportions and plasticisers and include composition C-2, composition C-3, and composition C-4.
In organic chemistry, dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three structural isomers: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.

Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(NCO)2. Two of the six possible isomers are commercially important: 2,4-TDI (CAS: 584-84-9) and 2,6-TDI (CAS: 91-08-7). 2,4-TDI is produced in the pure state, but TDI is often marketed as 80/20 and 65/35 mixtures of the 2,4 and 2,6 isomers respectively. It is produced on a large scale, accounting for 34.1% of the global isocyanate market in 2000, second only to MDI. Approximately 1.4 billion kilograms were produced in 2000. All isomers of TDI are colorless, although commercial samples can appear yellow.

Raney nickel, also called spongy nickel, is a fine-grained solid composed mostly of nickel derived from a nickel–aluminium alloy. Several grades are known, of which most are gray solids. Some are pyrophoric, but most are used as air-stable slurries. Raney nickel is used as a reagent and as a catalyst in organic chemistry. It was developed in 1926 by American engineer Murray Raney for the hydrogenation of vegetable oils. Raney is a registered trademark of W. R. Grace and Company.
Substances, mixtures and exposure circumstances in this list have been classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as group 2B: The agent (mixture) is "possibly carcinogenic to humans". The exposure circumstance entails exposures that are possibly carcinogenic to humans. This category is used for agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances for which there is limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans and less than sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. It may also be used when there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. In some instances, an agent, mixture or exposure circumstance for which there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but limited evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals together with supporting evidence from other relevant data may be placed in this group. Further details can be found in the preamble to the IARC Monographs.
Substances, mixtures and exposure circumstances in this list have been classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as group 3: The agent is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. This category is used most commonly for agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances for which the evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans and inadequate or limited in experimental animals. Exceptionally, agents (mixtures) for which the evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans but sufficient in experimental animals may be placed in this category when there is strong evidence that the mechanism of carcinogenicity in experimental animals does not operate in humans. Agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances that do not fall into any other group are also placed in this category.

2,4-Dinitrotoluene (DNT) or dinitro is an organic compound with the formula C7H6N2O4. This pale yellow crystalline solid is well known as a precursor to trinitrotoluene (TNT) but is mainly produced as a precursor to toluene diisocyanate.
Mononitrotoluene or nitrotoluene (MNT or NT), is any of three organic compounds with the formula C6H4(CH3)(NO2). They can be viewed as nitro derivatives of toluene or as methylated derivatives of nitrobenzene.

Olfactory receptor 51E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OR51E1 gene.
Dihydroxybenzoic acids (DHBA) are a type of phenolic acids.
Dioxin may refer to:
These drugs are known in the UK as controlled drugs, because this is the term by which the act itself refers to them. In more general terms, however, many of these drugs are also controlled by the Medicines Act 1968, there are many other drugs which are controlled by the Medicines Act but not by the Misuse of Drugs Act, and some other drugs are controlled by other laws.
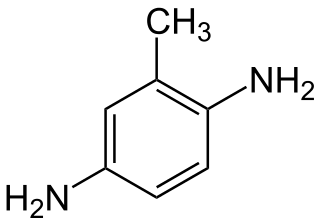
2,5-Diaminotoluene is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(NH2)2CH3. It is one isomer of six with this formula. 2,5-Diaminotoluene is a colorless crystalline solid, although commercial samples are often colored owing to air oxidation. It is commonly used in hair coloring.
2-Nitrotoluene or ortho-nitrotoluene is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4NO2. It is pale yellow liquid that crystallizes in two forms, called α (−9.27 °C) and β (−3.17 °C). It is mainly a precursor to o-toluidine, which is an intermediate in the production of various dyes.

2,4-Diaminotoluene is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(NH2)2CH3. It is one isomer of six with this formula. It is a white solid although commercial samples are often yellow-tan.