
The Second Happy Time, also known among German submarine commanders as the "American shooting season", was the informal name for a phase in the Battle of the Atlantic during which Axis submarines attacked merchant shipping and Allied naval vessels along the east coast of North America. The first "Happy Time" was in 1940–41 in the North Atlantic and North Sea. Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini declared war on the United States on 11 December 1941 so their navies could begin the Second Happy Time.

In geology, the places known as hotspots or hot spots are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Their position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The other hypothesis is that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. This hypothesis considers the term "hotspot" to be a misnomer, asserting that the mantle source beneath them is, in fact, not anomalously hot at all. Well-known examples include the Hawaii, Iceland and Yellowstone hotspots.
The Stille reaction, or the Migita–Kosugi–Stille coupling, is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis which involves the coupling of an organotin compound with a variety of organic electrophiles via palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction.

Hans Wilhelm Stille was an influential German geologist working primarily on tectonics and the collation of tectonic events during the Phanerozoic. Stille adhered to the contracting Earth hypothesis and together with Leopold Kober he worked on the geosyncline theory to explain orogeny. Stille's ideas emerged in the aftermath of Eduard Suess' book Das Antlitz der Erde (1883–1909). Stille's and Kober's school of thought was one of two that emerged in the post-Suess era the other being headed by Alfred Wegener and Émile Argand. This competing view rejected Earth contraction and argued for continental drift. As Stille opposed continental drift he came to be labelled a "fixist".

Dorsa Andrusov is a wrinkle ridge system at 1.0°S 57.0°E in Mare Fecunditatis on the Moon. It is 160 km in diameter and was named after Soviet geologist Nicolai Ivanovich Andrusov in 1976 by the IAU.

Dorsa Argand is a wrinkle ridge system at 28.1°N 40.6°W on the Moon, in Oceanus Procellarum near the border with Mare Imbrium. It is approximately 92 km long and was named after Swiss geologist Émile Argand in 1976. The name of the feature was approved by the IAU in 1976.

Dorsa Barlow is a wrinkle ridge system on the Moon, in Mare Tranquilitatis near the border with Mare Serenitatis, centered at 14.0°N 30.6°E. It is about 110 km long and was named after British crystallographer William Barlow in 1976.

Dorsa Smirnov is a wrinkle ridge system at 27.3°N 25.3°E in eastern Mare Serenitatis on the Moon. It is 222 km long and was named after Soviet geologist Sergei Sergeevich Smirnov by the IAU in 1976.

Dorsa Burnet are wrinkle ridges at 28.4°N 57.0°W in Oceanus Procellarum on the Moon. They are about 194 km long and were named after Thomas Burnet by the IAU in 1976.

Dorsa Cato is a wrinkle ridge at 1.0°N 47.0°E on the Moon. It is approximately 130 km long and was named after Roman geological engineer Cato the Elder in 1976 by the IAU.
Dorsa Dana is a wrinkle ridge at 3.0°N 90.0°E in Mare Smythii on the Moon. It is 82 km long and was named after American geologist James Dwight Dana in 1976.
Dorsa Harker is a wrinkle ridge at 14.5°N 64.0°E in Mare Crisium on the Moon. It is 213 km long and was named after Alfred Harker, an English petrologist, in 1976.
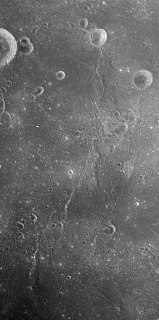
Dorsa Mawson is a wrinkle ridge system at 7.0°S 53.0°E in Mare Fecunditatis on the Moon. It is approximately 143 km long and was named after Antarctic explorer Douglas Mawson in 1979 by the IAU.

Dorsa Rubey is a wrinkle ridge system at 10.0°S 42.0°W in Oceanus Procellarum on the Moon. It is 100 km long and was named after American geologist William Walden Rubey in 1976.

Dorsa Sorby is a wrinkle ridge system at 19.0°N 14.0°E in Mare Serenitatis on the Moon. It is 76 km long and was named after British geologist Henry Clifton Sorby in 1976.

Dorsa Tetyaev is a wrinkle ridge system at 19.9°N 64.2°E in Mare Crisium on the Moon. It is 188 km long and was named after Soviet geologist Mikhail Mikhailovich Tetyaev in 1979.
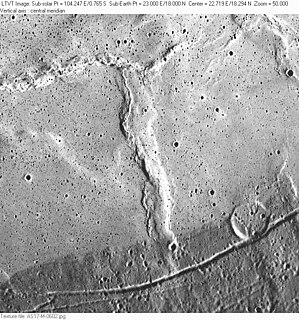
Dorsum Nicol is a wrinkle ridge on the Moon at 18.0°N 23.0°E in Mare Serenitatis near the border of Mare Tranquilitatis. It is 44 km long and was named after Scottish physicist William Nicol in 1976.

The I-351-class submarine was a class of tanker/transport submarines built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during World War II. The IJN called this type of submarine Senho type submarine. The type name, was shortened to Hokyū Sensuikan. The IJN designed these submarines to support flying boats in forward areas. By the time the first submarine was finished, this capability was no longer needed and she was converted into an oil tanker. That boat, I-351, was sunk on the return leg of her second voyage in 1945; the second boat was destroyed by an American air raid before she was completed. Four additional submarines were planned, but were cancelled before they were laid down.
The Japanese submarine I-28 was one of 20 Type B cruiser submarines of the B1 sub-class built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the 1940s.

Cibele Dorsa was a Brazilian actress, model and writer. She also appeared on the cover of the April 2008 issue of Playboy Brazil.


















