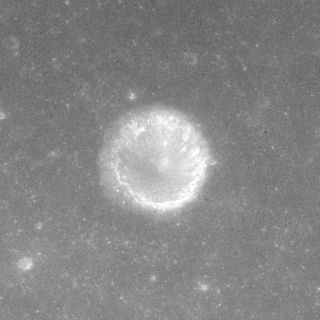
Carlini is a small lunar impact crater located in the Mare Imbrium. It was named after Italian astronomer Francesco Carlini. The crater is bowl-shaped with a small central floor. It has a higher albedo than the surrounding mare, making it prominent due to its isolated location. To the south is a wrinkle ridge named Dorsum Zirkel, and farther south lies the peak Mons La Hire.

Bobillier is a tiny, cup-shaped lunar impact crater in the southwest part of Mare Serenitatis. It was named after French geometer Étienne Bobillier in 1976. It lies to the north-northwest of the crater Bessel. To the south and west is a wrinkle ridge designated Dorsum Buckland. Bobillier was previously identified as Bessel E.

Anville is a relatively small, solitary lunar impact crater located in the north part of the Mare Fecunditatis. It is named after French cartographer Jean-Baptiste d'Anville. This is a circular, cup-shaped formation with a sharp edge and little appearance of wear. Some minor slumping has occurred in the eastern half of the interior wall. It was designated Taruntius G prior to being assigned a name by the IAU. Taruntius itself lies to the north-northwest, at the edge of the mare.

Aratus is a small lunar impact crater located on the highland to the south and east of the rugged Montes Apenninus range. It is a circular, cup-shaped crater with a relatively high albedo. It was named after Greek astronomer Aratus of Soli. To the east is the Mare Serenitatis, and to the southwest is the somewhat larger crater Conon. North-northeast of Aratus is the landing site of the Apollo 15 mission, just beyond Mons Hadley Delta.

Asada is a small lunar impact crater located at the northern edge of Mare Fecunditatis, to the northeast of the crater Taruntius. It is a circular crater formation with inner walls that slope down toward a small central floor at the midpoint. Asada was designated Taruntius A prior to being named by the IAU.

Cameron is a small lunar impact crater that lies across the northwest rim of the crater Taruntius. It is named after American astronomer Robert Curry Cameron. This formation is circular and cup-shaped, with no particular distinguishing features. It was previously designated Taruntius C.

C. Herschel is a small lunar impact crater that lies on the western part of Mare Imbrium. It is named after British astronomer Caroline Herschel. It is a circular, bowl-shaped formation that has not undergone significant erosion. The interior floor has the same low albedo as the surrounding lunar mare. To the south-southwest is the similar crater Heis. C. Herschel lies on a wrinkle ridge of the lunar mare named the Dorsum Heim.

Taruntius is a lunar impact crater on the northwestern edge of Mare Fecunditatis. It was named after ancient Roman philosopher, mathematician and astrologer Lucius Tarutius Firmanus. To the northwest is the lava-flooded crater Lawrence, and to the north lie the craters Watts and da Vinci.
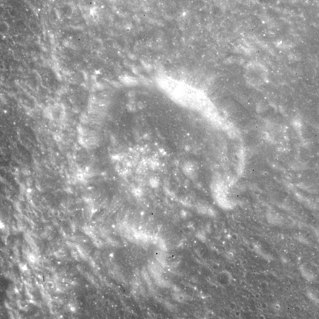
Secchi is a small lunar impact crater formation on the northwest edge of Mare Fecunditatis. It was named after the 19th-century Italian astronomer Angelo Secchi. To the northeast is the crater Taruntius. The western rim is joined with a section of the minor Montes Secchi range. The rim of this crater has been opened in the northern and southern ends, leaving two curved ridges facing each other across the crater floor. To the south is a pair of rilles designated the Rimae Secchi. These lie near the edge of the mare, and have a combined length of about 40 kilometers.

Gruithuisen is a lunar impact crater that lies on the section of lunar mare that joins Oceanus Procellarum in the west to Mare Imbrium in the east. Southeast of Gruithuisen is the small crater Delisle. To the south is Dorsum Bucher, a wrinkle ridge running in a north–south direction for about 90 kilometers.

Atwood is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the Mare Fecunditatis, to the northwest of the prominent crater Langrenus. It forms a triple-crater formation with Naonobu attached to the north rim and Bilharz near the west rim.

Watts is a small lunar impact crater that is located at the extreme northern edge of the Mare Fecunditatis. It was named after American astronomer Chester Burleigh Watts. Just one crater diameter to the northwest is the irregular da Vinci. Farther to the south is the larger crater Taruntius.

Peirce is a small lunar impact crater in the western part of Mare Crisium. That dark, circular lunar mare is located in the east-northeasterly part of the Moon's near side. It was named after the American mathematician Benjamin Peirce. Peirce lies to the north of the craters Yerkes and Picard, and southeast of Macrobius located outside the mare. Just over a crater diameter to the north of Peirce is the smaller Swift. To the northwest is the wrinkle ridge Dorsum Oppel.

Eckert is a tiny, isolated lunar impact crater in the northern part of the Mare Crisium. This crater forms a circular pit in the dark surface of the surrounding lunar mare. Just to the west is a wrinkle ridge in the mare surface, a feature that is prominent only under oblique lighting from the Sun. The nearest craters of note are Peirce to the west-northwest, and Picard to the southwest. Both of these craters lie in the Mare Crisium basin.

Mons La Hire is a solitary lunar mountain in the western Mare Imbrium. It is located to the northeast of the crater Euler, and to the west-northwest of Lambert.

Montes Secchi is a minor range of lunar mountains located near the northwestern edge of Mare Fecunditatis. This roughly linear formation of low ridges grazes the northwestern outer rim of the crater Secchi, the formation from which this range gained its name. This crater is named after Angelo Secchi, a 19th-century Italian astronomer. The ridges trend from southwest to northeast.

Dorsum Zirkel is a wrinkle ridge at 29.6°N 24.8°W northeast of Mons La Hire in Mare Imbrium on the Moon. It is 193 km long and was named after German geologist Ferdinand Zirkel in 1976.

Dorsum Bucher is a wrinkle ridge at 31.0°N 39.0°W in the border region between Oceanus Procellarum and Mare Imbrium on the Moon. The name of the feature was approved by the IAU in 1976. It is approximately 85 km long, extending from the vicinity of Gruithuisen crater to the area west of Delisle crater. The south end of the dorsum is a low hill of terra material that predates the mare lava.
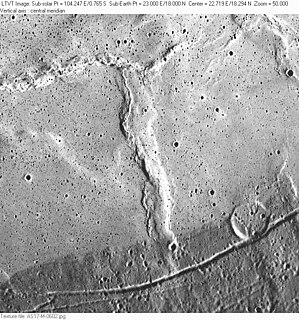
Dorsum Nicol is a wrinkle ridge on the Moon at 18.0°N 23.0°E in Mare Serenitatis near the border of Mare Tranquilitatis. It is 44 km long and was named after Scottish physicist William Nicol in 1976.