
Public housing, also known as social housing, refers to affordable housing provided in buildings that are usually owned and managed by local government, central government, nonprofit organizations or a combination thereof. The details, terminology, definitions of poverty, and other criteria for allocation may vary within different contexts, but the right to rent such a home is generally rationed through some form of means-testing or through administrative measures of housing needs. One can regard social housing as a potential remedy for housing inequality. Within the OECD, social housing represents an average of 7% of national housing stock (2020), ranging from ~34% in the Netherlands to less than 1% in Colombia.

A housing cooperative, or housing co-op, is a legal entity which owns real estate consisting of one or more residential buildings. The entity is usually a cooperative or a corporation and constitutes a form of housing tenure. Typically housing cooperatives are owned by shareholders but in some cases they can be owned by a non-profit organization. They are a distinctive form of home ownership that have many characteristics that differ from other residential arrangements such as single family home ownership, condominiums and renting.

An estate sale or estate liquidation is a sale or auction to dispose of a substantial portion of the materials owned by a person who is recently deceased or who must dispose of their personal property to facilitate a move.

Foreclosure is a legal process in which a lender attempts to recover the balance of a loan from a borrower who has stopped making payments to the lender by forcing the sale of the asset used as the collateral for the loan.

A hire purchase (HP), also known as an installment plan, is an arrangement whereby a customer agrees to a contract to acquire an asset by paying an initial installment and repaying the balance of the price of the asset plus interest over a period of time. Other analogous practices are described as closed-end leasing or rent to own.
In law, a warranty is an expressed or implied promise or assurance of some kind. The term's meaning varies across legal subjects. In property law, it refers to a covenant by the grantor of a deed. In insurance law, it refers to a promise by the purchaser of an insurance about the thing or person to be insured.

Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation is Canada's federal crown corporation responsible for administering the National Housing Act, with the mandate to improve housing by living conditions in the country.

The affordability of housing in the UK reflects the ability to rent or buy property. There are various ways to determine or estimate housing affordability. One commonly used metric is the median housing affordability ratio; this compares the median price paid for residential property to the median gross annual earnings for full-time workers. According to official government statistics, housing affordability worsened between 2020 and 2021, and since 1997 housing affordability has worsened overall, especially in London. The most affordable local authorities in 2021 were in the North West, Wales, Yorkshire and The Humber, West Midlands and North East.
A first-time buyer (FTB) is a potential house buyer who has not previously purchased a residential property. The term is primarily used in the British, Irish, Canadian, and U.S. property markets, as well as other countries.

Stamp duty in the United Kingdom is a form of tax charged on legal instruments, and historically required a physical stamp to be attached to or impressed upon the document in question. The more modern versions of the tax no longer require a physical stamp.

In common law jurisdictions, an implied warranty is a contract law term for certain assurances that are presumed to be made in the sale of products or real property, due to the circumstances of the sale. These assurances are characterized as warranties regardless of whether the seller has expressly promised them orally or in writing. They include an implied warranty of fitness for a particular purpose, an implied warranty of merchantability for products, implied warranty of workmanlike quality for services, and an implied warranty of habitability for a home.

Equity sharing is another name for shared ownership or co-ownership. It takes one property, more than one owner, and blends them to maximize profit and tax deductions. Typically, the parties find a home and buy it together as co-owners, but sometimes they join to co-own a property one of them already owns. At the end of an agreed term, they buy one another out or sell the property and split the equity. In England, equity sharing and shared ownership are not the same thing.
A housing bubble is one of several types of asset price bubbles which periodically occur in the market. The basic concept of a housing bubble is the same as for other asset bubbles, consisting of two main phases. First there is a period where house prices increase dramatically, driven more and more by speculation. In the second phase, house prices fall dramatically. Housing bubbles tend to be among the asset bubbles with the largest effect on the real economy because they are credit-fueled,,and a large number of households participate and not just investors, and because the wealth effect from housing tends to be larger than for other types of financial assets.
A real-estate bubble or property bubble is a type of economic bubble that occurs periodically in local or global real estate markets, and it typically follows a land boom. A land boom is a rapid increase in the market price of real property such as housing until they reach unsustainable levels and then declines. This period, during the run-up to the crash, is also known as froth. The questions of whether real estate bubbles can be identified and prevented, and whether they have broader macroeconomic significance, are answered differently by schools of economic thought, as detailed below.

Home ownership in Australia is considered a key cultural icon, and part of the Australian tradition known as the Great Australian Dream of "owning a detached house on a fenced block of land." Home ownership has been seen as creating a responsible citizenry; according to a former Premier of Victoria: "The home owner feels that he has a stake in the country, and that he has something worth working for, living for, fighting for."

The Australian property market comprises the trade of land and its permanent fixtures located within Australia. The average Australian property price grew 0.5% per year from 1890 to 1990 after inflation, however rose from 1990 to 2017 at a faster rate. House prices in Australia receive considerable attention from the media and the Reserve Bank and some commentators have argued that there is an Australian property bubble.
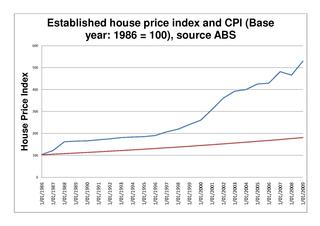
The Australian property bubble is the economic theory that the Australian property market has become or is becoming significantly overpriced and due for a significant downturn. Since the early 2010s, various commentators, including one Treasury official, have claimed the Australian property market is in a significant bubble.
The property bubble in New Zealand is a major national economic and social issue. Since the early 1990s, house prices in New Zealand have risen considerably faster than incomes, putting increasing pressure on public housing providers as fewer households have access to housing on the private market. The property bubble has produced significant impacts on inequality in New Zealand, which now has one of the highest homelessness rate in the OECD and a record-high waiting list for public housing. Government policies have attempted to address the crisis since 2013, but have produced limited impacts to reduce prices or increase the supply of affordable housing. However, prices started falling in 2022 in response to tightening of mortgage availability and supply increasing. Some areas saw drops as high as around 9% - albeit from very high prices.

Affordable housing is housing that is deemed affordable to those with a median household income as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. A general rule is no more than 30% of gross monthly income should be spent on housing, to be considered affordable as the challenges of promoting affordable housing varies by location.

The Canadian property bubble refers to a significant rise in Canadian real estate prices from 2002 to present. The Dallas Federal Reserve rated Canadian real estate as "exuberant" beginning in 2003. From 2003 to 2018, Canada saw an increase in home and property prices of up to 337% in some cities. In 2016, the OECD warned that Canada's financial stability was at risk due to elevated housing prices, investment and household debt. By 2018, home-owning costs were above 1990 levels when Canada saw its last housing bubble burst. Bloomberg Economics ranked Canada as the second largest housing bubble across the OECD in 2019 and 2021. Toronto scored the highest in the world in Swiss bank UBS' real estate bubble index in 2022, with Vancouver also scoring among the 10 riskiest cities in the world.













