
A Linux distribution is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro, if distributed on its own, is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers to servers and from embedded devices to supercomputers.

Wine is a free and open-source compatibility layer to allow application software and computer games developed for Microsoft Windows to run on Unix-like operating systems. Developers can compile Windows applications against WineLib to help port them to Unix-like systems. Wine is predominantly written using black-box testing reverse-engineering, to avoid copyright issues. No code emulation or virtualization occurs. Wine is primarily developed for Linux and macOS.

Source Mage is a source-based Linux distribution descended from Sorcerer. Components of this operating system are downloaded as source code and compiled locally on the user's computer.
In software development, when software has been forked or uses a chain of libraries/dependencies, upstream refers to an issue that occurs in software related to the chain. It is the direction that is toward the original authors or maintainers of software. It is usually used in the context of a version, a bug, or a patch.
In software engineering, a project fork happens when developers take a copy of source code from one software package and start independent development on it, creating a distinct and separate piece of software. The term often implies not merely a development branch, but also a split in the developer community; as such, it is a form of schism. Grounds for forking are varying user preferences and stagnated or discontinued development of the original software.

GNU Classpath is a free software implementation of the standard class library for the Java programming language. Most classes from J2SE 1.4 and 5.0 are implemented. Classpath can thus be used to run Java-based applications. GNU Classpath is a part of the GNU Project. It was originally developed in parallel with libgcj due to license incompatibilities, but later the two projects merged.
A patch is data that is intended to be used to modify an existing software resource such as a program or a file, often to fix bugs and security vulnerabilities. A patch may be created to improve functionality, usability, or performance. A patch is typically provided by a vendor for updating the software that they provide. A patch may be created manually, but commonly it is created via a tool that compares two versions of the resource and generates data that can be used to transform one to the other.

MirOS BSD is a free and open source operating system which started as a fork of OpenBSD 3.1 in August 2002. It was intended to maintain the security of OpenBSD with better support for European localisation. Since then it has also incorporated code from other free BSD descendants, including NetBSD, MicroBSD and FreeBSD. Code from MirOS BSD was also incorporated into ekkoBSD, and when ekkoBSD ceased to exist, artwork, code and developers ended up working on MirOS BSD for a while.
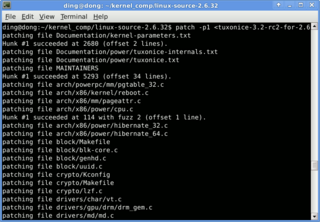
The computer tool patch is a Unix program that updates text files according to instructions contained in a separate file, called a patch file. The patch file is a text file that consists of a list of differences and is produced by running the related diff program with the original and updated file as arguments. Updating files with patch is often referred to as applying the patch or simply patching the files.
In Unix computing, Ion is a tiling and tabbing window manager for the X Window System. It is designed such that it is possible to manage windows using only a keyboard, without needing a mouse. It is the successor of PWM and is written by the same author, Tuomo Valkonen. Since the first release of Ion in the summer 2000, similar alternative window management ideas have begun to show in other new window managers: Larswm, ratpoison, StumpWM, wmii, xmonad and dwm.
Backporting is the action of taking parts from a newer version of a software system or software component and porting them to an older version of the same software. It forms part of the maintenance step in a software development process, and it is commonly used for fixing security issues in older versions of the software and also for providing new features to older versions.

Monotone is an open source software tool for distributed revision control. It tracks revisions to files, groups sets of revisions into changesets, and tracks history across renames. The focus of the project is on integrity over performance. Monotone is designed for distributed operation, and makes heavy use of cryptographic primitives to track file revisions and to authenticate user actions.

Git is a distributed version control system that tracks versions of files. It is often used to control source code by programmers who are developing software collaboratively.
In software development, distributed version control is a form of version control in which the complete codebase, including its full history, is mirrored on every developer's computer. Compared to centralized version control, this enables automatic management branching and merging, speeds up most operations, improves the ability to work offline, and does not rely on a single location for backups. Git, the world's most popular version control system, is a distributed version control system.
Branching, in version control and software configuration management, is the duplication of an object under version control. Each object can thereafter be modified separately and in parallel so that the objects become different. In this context the objects are called branches. The users of the version control system can branch any branch.

The history of free and open-source software begins at the advent of computer software in the early half of the 20th century. In the 1950s and 1960s, computer operating software and compilers were delivered as a part of hardware purchases without separate fees. At the time, source code—the human-readable form of software—was generally distributed with the software, providing the ability to fix bugs or add new functions. Universities were early adopters of computing technology. Many of the modifications developed by universities were openly shared, in keeping with the academic principles of sharing knowledge, and organizations sprung up to facilitate sharing.

The Linux kernel is a free and open source, Unix-like kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system (OS) which was created to be a free replacement for Unix. Since the late 1990s, it has been included in many operating system distributions, many of which are called Linux. One such Linux kernel operating system is Android which is used in many mobile and embedded devices.

OpenSSH is a suite of secure networking utilities based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, which provides a secure channel over an unsecured network in a client–server architecture.

Proton is a compatibility layer that allows Windows games to run on Linux-based operating systems. Proton is developed by Valve in cooperation with developers from CodeWeavers. It is a collection of software and libraries combined with a patched version of Wine to improve performance and compatibility with Windows games. Proton is designed for integration into the Steam client as "Steam Play". It is officially distributed through the client, although third-party forks can be manually installed.












