Drug trade may refer to:
Drug use may refer to any drug use; or:

A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active chemical substance is the same, the medical profile of generics is equivalent in performance compared to their performance at the time when they were patented drugs. A generic drug has the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) as the original, but it may differ in some characteristics such as the manufacturing process, formulation, excipients, color, taste, and packaging.

The pharmaceutical industry is an industry in medicine that discovers, develops, produces, and markets pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients, with the aim to cure and prevent diseases, or alleviate symptoms. Pharmaceutical companies may deal in generic or brand medications and medical devices. They are subject to a variety of laws and regulations that govern the patenting, testing, safety, efficacy using drug testing and marketing of drugs. The global pharmaceuticals market produced treatments worth $1,228.45 billion in 2020 and showed a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.8%.

Current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) are those conforming to the guidelines recommended by relevant agencies. Those agencies control the authorization and licensing of the manufacture and sale of food and beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceutical products, dietary supplements, and medical devices. These guidelines provide minimum requirements that a manufacturer must meet to assure that their products are consistently high in quality, from batch to batch, for their intended use. The rules that govern each industry may differ significantly; however, the main purpose of GMP is always to prevent harm from occurring to the end user. Additional tenets include ensuring the end product is free from contamination, that it is consistent in its manufacture, that its manufacture has been well documented, that personnel are well trained, and that the product has been checked for quality more than just at the end phase. GMP is typically ensured through the effective use of a quality management system (QMS).

H. Lundbeck A/S is a Danish international pharmaceutical company engaged in the research, development, manufacturing, marketing and sale of pharmaceuticals across the world. The company’s products are targeted at brain diseases, including depression, schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and migraine.
Diversion, Diversions or The Diversion may refer to:
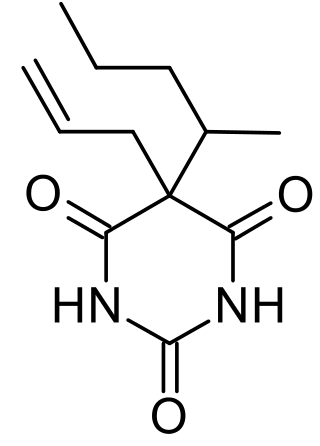
Secobarbital is a short-acting barbiturate derivative drug that was patented in 1934 in the United States. It possesses anaesthetic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, sedative, and hypnotic properties. In the United Kingdom, it was known as quinalbarbitone. It is the most frequently used drug in physician-assisted suicide within the United States. Secobarbital is considered to be an obsolete sedative-hypnotic, and as a result, it has largely been replaced by the benzodiazepine family. Seconal was widely abused, known on the street as "red devils" or "reds".
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the leading industries in the People's Republic of China, covering synthetic chemicals and drugs, prepared Chinese medicines, medical devices, apparatus and instruments, hygiene materials, packing materials, and pharmaceutical machinery. China has the second-largest pharmaceutical market in the world as of 2017 which is worth US$110 billion. China accounts for 20% of the world's population but only a small fraction of the global drug market. China's changing health-care environment is designed to extend basic health insurance to a larger portion of the population and give individuals greater access to products and services. Following the period of change, the pharmaceutical industry is expected to continue its expansion.
The Sri Lanka National Pharmaceuticals Policy was established in the 1970s following the submission of a report by Dr S.A. Wickremasinghe and Prof. Seneka Bibile. It aimed at ensuring that people get good quality drugs at the lowest possible price and that doctors would prescribe the minimum required drugs to treat the patient's illness. It was a pioneer in the field of rational National pharmaceuticals policy.
Ethotoin is an anticonvulsant drug used in the treatment of epilepsy. It is a hydantoin, similar to phenytoin. It is not available in the United States.
The pharmaceutical industry in India was valued at an estimated US$42 billion in 2021 and is estimated to reach $130 billion by 2030. India is the world's largest provider of generic medicines by volume, with a 20% share of total global pharmaceutical exports. It is also the largest vaccine supplier in the world by volume, accounting for more than 60% of all vaccines manufactured in the world. Indian pharmaceutical products are exported to various regulated markets including the US, UK, European Union and Canada.

Apotex Inc. is a Canadian pharmaceutical corporation. Founded in 1974 by Barry Sherman, the company is the largest producer of generic drugs in Canada, with annual sales exceeding CA$2.5 billion. By 2023, Apotex employed close to 8,000 people as Canada's largest drug manufacturer, with over 300 products selling in over 115 countries. Apotex manufactures and distributes generic medications for a range of diseases and health conditions that include cancer, diabetes, high cholesterol, glaucoma, infections and blood pressure.
Supplier may refer to:
Prohibition refers to the act of prohibiting a certain substance or act.
The pharmaceutical industry in Bangladesh is one of the most developed technology sectors within the country. Manufacturers produce insulin, hormones, and cancer drugs. This sector provides 97% of the total medicinal requirement of the local market. The industry also exports medicines to global markets, including Europe. Pharmaceutical companies are expanding their business with the aim to expand the export market.

Bamipine (trade name Soventol) is a pharmaceutical drug acting as an H1 antihistamine with anticholinergic properties. It is used as an antipruritic ointment. No oral use is known.
KV Pharmaceutical Company (KV) was an American drug company that brought generic and non-branded pharmaceutical products to the market. Headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri, it had research and manufacturing facilities, as well as marketing and sales operations, the latter activities conducted through its subsidiaries, Ther-Rx Corporation and Nesher Pharmaceuticals Inc.

Norbrook is a United Kingdom-based pharmaceutical company. It was founded in 1969 by Lord Ballyedmond as Norbrook Laboratories Ltd in Northern Ireland. In 1970, Norbrook began manufacturing of veterinary pharmaceuticals. In 2011 the Norbrook Group was listed by the Belfast Telegraph in its Top 100 Companies list as being in position 28.
Amneal Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is an American publicly traded generics and specialty pharmaceutical company. The company is headquartered in Bridgewater, New Jersey.
The distribution of medications has special drug safety and security considerations. Some drugs require cold chain management in their distribution.