Dalmatia is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Central Croatia, Slavonia and Istria, located on the east shore of the Adriatic Sea in Croatia.

Dubrovnik, Italian: RagusaItalian:[raˈɡuːza] ; see notes on naming, is a city in southern Dalmatia, Croatia, by the Adriatic Sea. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterranean, a seaport and the centre of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County. Its total population is 41,562. In 1979, the city of Dubrovnik was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites in recognition of its outstanding medieval architecture and fortified old town.

Pelješac is a peninsula in southern Dalmatia in Croatia. The peninsula is part of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County and is the second largest peninsula in Croatia. From the isthmus that begins at Ston, to the top of Cape Lovišta, it is 65 km or 40 mi long.

After a period of political and economic crisis in the 1980s, the constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia split apart, but the unresolved issues caused a series of inter-ethnic Yugoslav Wars. The wars primarily affected Bosnia and Herzegovina, neighbouring parts of Croatia and, some years later, Kosovo.

Yugoslav Railways, with standard acronym JŽ, was the state railway company of Yugoslavia, operational from the 1920s to the 1990s, with its final incarnation transferring to Serbia. The successor of JŽ is the joint stock company of the Serbian Railways in 2006.
Milan Milišić was a Yugoslav poet, translator, author and journalist from Dubrovnik. He wrote several volumes of poetry and also plays, essays, travel literature, a novel and translated, among others, J. R. R. Tolkien's The Hobbit, the poems of Robert Frost, and Ted Hughes into the Serbo-Croatian language.

The Zeta Banovina, was a province (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. This province consisted of all of present-day Montenegro as well as adjacent parts of Central Serbia, Croatia, Kosovo and Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was named after the Zeta River which also gave its name to the medieval state of Zeta that roughly corresponds to modern-day Montenegro. The capital of Banovina was Cetinje.
Marc Bruère Desrivaux/des Rivaux was a Ragusan writer and dramatist of French origin.
The Serb-Catholic movement in Dubrovnik was a cultural and political movement of people from Dubrovnik who, while Catholic, declared themselves Serbs, while Dubrovnik was part of the Habsburg-ruled Kingdom of Dalmatia in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Initially spearheaded by intellectuals who espoused strong pro-Serbian sentiments, there were two prominent incarnations of the movement: an early pan-Slavic phase under Matija Ban and Medo Pucić that corresponded to the Illyrian movement, and a later, more Serbian nationalist group that was active between the 1880s and 1908, including a large number of Dubrovnik intellectuals at the time. The movement, whose adherents are known as Serb-Catholics or Catholic Serbs, largely disappeared with the creation of Yugoslavia.

The siege of Dubrovnik was a military engagement fought between the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and Croatian forces defending the city of Dubrovnik and its surroundings during the Croatian War of Independence. The JNA started its advance on 1 October 1991, and by late October, it had captured virtually all the land between the Pelješac and Prevlaka peninsulas on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, with the exception of Dubrovnik itself. The siege was accompanied by a Yugoslav Navy blockade. The JNA's bombardment of Dubrovnik, including that of the Old Town—a UNESCO World Heritage Site—culminated on 6 December 1991. The bombardment provoked international condemnation, and became a public relations disaster for Serbia and Montenegro, contributing to their diplomatic and economic isolation, as well as the international recognition of Croatia's independence. In May 1992, the JNA retreated to Bosnia and Herzegovina, less than 1 kilometre from the coast in some places, and handed over its equipment to the newly formed Army of Republika Srpska (VRS). During this time, the Croatian Army (HV) attacked from the west and pushed back the JNA/VRS from the areas east of Dubrovnik, both in Croatia and in Bosnia and Herzegovina, and by the end of May linked up with the HV unit defending the city. Fighting between the HV and Yugoslav troops east of Dubrovnik gradually died down.

Dubrovnik was a flotilla leader built for the Royal Yugoslav Navy by Yarrow Shipbuilders in Glasgow in 1930 and 1931. She was one of the largest destroyers of her time. Resembling contemporary British designs, Dubrovnik was a fast ship with a main armament of four Czechoslovak-built Škoda 140 mm (5.5 in) guns in single mounts. She was intended to be the first of three flotilla leaders built for Yugoslavia, but was the only one completed. During her service with the Royal Yugoslav Navy, Dubrovnik undertook several peacetime cruises through the Mediterranean, the Turkish Straits and the Black Sea. In October 1934, she conveyed King Alexander to France for a state visit, and carried his body back to Yugoslavia following his assassination in Marseille.

Gabela is a village in southern Bosnia and Herzegovina, 5 kilometres south of Čapljina and 4 kilometers from Metković, in Croatia. It is situated in the navigable lower course of the Neretva, off the major road linking the coast with the mountainous hinterland.

Herzegovina is the southern and smaller of two main geographical regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia. It has never had strictly defined geographical, cultural or historical borders, nor has it ever been defined as an administrative whole in the geopolitical and economic subdivision of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The Dubrovnik Republic was a Serb proto-state that existed during the Siege of Dubrovnik in the Croatian War of Independence, self-proclaimed by the Yugoslav People's Army on 15 October 1991 in occupied areas of Croatia, after being captured by members of 2nd Corps of the JNA. Its provisional president was Aleksandar Aco Apolonio.
Operation Jackal, also known as Operation June Dawns, was an offensive of the Bosnian War fought between a combined Croatian Army (HV) and Croatian Defence Council (HVO) army against the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) from 7–26 June 1992. The offensive was a Croatian pre-emptive strike against the VRS, a Bosnian Serb military formed in May 1992 from Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) units that were stationed in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The HV concluded that the JNA offensive operations of April and May 1992, resulting in the capture of Kupres and much of the Neretva River valley south of Mostar, were aimed at capturing or threatening the Croatian Port of Ploče and possibly Split. To counter this threat, the Croatian leadership deployed the HV, under the command of General Janko Bobetko, to the "Southern Front" including the area in which Operation Jackal was to be conducted.
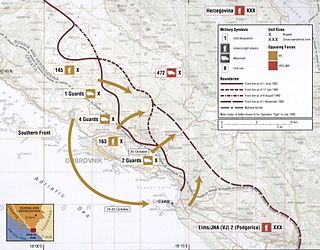
Operation Tiger was a Croatian Army (HV) offensive conducted in areas of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina near Dubrovnik between 1 and 13 July 1992. It was designed to push the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) away from the city towards Popovo field and secure a supply route via Rijeka Dubrovačka, which was gained in early June as the siege of Dubrovnik by the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) was lifted. The operation's success was facilitated by the establishment of the HV's Southern Front command and the successful conclusion of the May–June 1992 operations against the VRS in the Neretva River valley, which concluded with Operation Jackal.

Zagreb was the second of three Beograd-class destroyers built for the Royal Yugoslav Navy (KM) in the late 1930s. She was designed to be deployed as part of a division led by the flotilla leader Dubrovnik and was the first warship built in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. Zagreb entered service in August 1939, was armed with a main battery of four 120 mm (4.7 in) guns in single mounts, and had a top speed of 35 knots.
Darko is a common South Slavic masculine given name. It is derived from the Slavic root dar 'gift'. Its oldest mention is from the 14th century, included in the Dečani chrysobulls (1330).

The Dubrovnik chess set is a style of chess pieces influenced by the Staunton chess set. These chessmen are considered to have significant historical importance and are regarded as a timeless design classic. Over the decades several variants of the Dubrovnik chessmen were designed.
Petar Kolendić was a Serbian and Croatian writer and literary historian.











