
The Hmong people are an indigenous group in East Asia and Southeast Asia. In China, the Hmong people are classified as a sub-group of the Miao people. The modern Hmong reside mainly in Southwest China and countries in Southeast Asia such as Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and Myanmar. There is also a large diasporic community in the United States of more than 300,000. The Hmong diaspora has smaller communities in Australia and South America.
Wat Tham Krabok is a Buddhist temple (wat) in the Phra Phutthabat District of Saraburi Province, Thailand.

Hmong Americans are Americans of Hmong ancestry. Many Hmong Americans immigrated to the United States as refugees in the late 1970s. Over half of the Hmong population from Laos left the country, or attempted to leave, in 1975, at the culmination of the Laotian Civil War.

The situation of human rights in Laos has often been, and remains, a recognized cause for serious concern. Laos is one of a handful of Marxist-Leninist governments and is ruled by a one-party communist government backed by the Lao People's Army in alliance with the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
May Lee-Yang, also known as May Lee, is a Hmong American playwright, poet, prose writer, performance artist and community activist in Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. She was born in Ban Vinai Refugee Camp in Thailand and moved to Minnesota as a child with her family. She is also the executive director of the non-profit organization Hmong Arts Connection.
Gary Yia Lee is a Hmong anthropologist and author based in Australia. Lee was born in Ban Houei Kouang, Muong Mok, Xieng Khouang, Laos. In 1961, his family was displaced by the civil war and they joined other Hmong refugees in the city of Vientiane. He excelled in a Lao school system run by the French, and had hopes of attending college in France. In 1965, after winning a Colombo Plan scholarship, he traveled to Australia instead to finish high school

The Lua people are a minority ethnic group native to Laos, although there is now a sizable community living in Thailand. Lua' is their preferred autonym (self-designation), while their Lao neighbours tend to call them Thin, T'in or Htin. Another term for this group is Lawa. There are two subgroups: the Mal and the Phai or Pray.

Relations between Laos and the United States officially began when the United States opened a legation in Laos in 1950, when Laos was a semi-autonomous state within French Indochina. These relations were maintained after Laos' independence in October 1953.
Kao Kalia Yang is a Hmong American writer and author of The Latehomecomer: A Hmong Family Memoir from Coffee House Press and The Song Poet from Metropolitan Press. Her work has appeared in the Paj Ntaub Voice Hmong literary journal, "Waterstone~Review," and other publications. She is a contributing writer to On Being's Public Theology Reimagined blog. Additionally, Yang wrote the lyric documentary, The Place Where We Were Born. Yang currently resides in St. Paul, Minnesota.
Lorne Dwight Conquergood was an ethnographer who is best known for his work with the Hmong of southeast Asia, street gangs of Chicago, and refugees in Thailand and Gaza.
The Hmong People society originally from Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and southeast China. As of 2011 the worldwide Hmong population is about four million. The Hmong culture is patrilineal, allowing a husband's family to make all major decisions, even when they solely concern the woman. However, the Hmong women have traditionally carried a large amount of responsibility and some power due to their necessary contribution of food and labor to the family.

Sudden arrhythmic death syndrome (SADS) is a sudden unexpected death of adolescents and adults caused by a cardiac arrest. However, the exact cause of the cardiac arrest, and thus the exact cause of death, is unknown. These deaths occur mainly during sleep or at rest. One type of conduction defect known as Brugada syndrome can be responsible.
Dust of Life may refer to:
Jerrold B. Daniels or Jerry Daniels was a CIA Paramilitary Operations Officer (PMOO) in their Special Activities Center who worked in Laos and Thailand from the early 1960s to the early 1980s. He was known by his self-chosen CIA call-sign of "Hog." In the early 1960s, he was recruited by the CIA as a liaison officer between Hmong General Vang Pao and the CIA. He worked with the Hmong people for the CIA's operation in Laos commonly called the "Secret War" as it was little known at the time. In 1975, as the communist Pathet Lao and North Vietnamese Army advanced on the Hmong base at Long Tieng, Daniels organized the air evacuation of Vang Pao and more than two thousand of his officers, soldiers, and their families to Thailand. Immediately after the departure of Daniels and Vang Pao, thousands more Hmong fled across the Mekong river to Thailand, where they lived in refugee camps. From 1975 to 1982 Daniels worked among Hmong refugees in Thailand facilitating the resettlement of more than 50,000 of them in the United States and other countries.
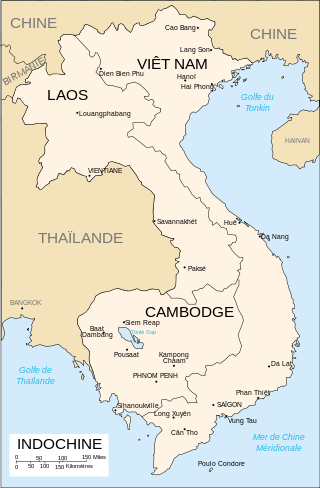
The Indochina refugee crisis was the large outflow of people from the former French colonies of Indochina, comprising the countries of Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos, after communist governments were established in 1975. Over the next 25 years and out of a total Indochinese population in 1975 of 56 million, more than 3 million people would undertake the dangerous journey to become refugees in other countries of Southeast Asia, Hong Kong, or China. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, 250,000 Vietnamese refugees had perished at sea by July 1986. More than 2.5 million Indochinese were resettled, mostly in North America, Australia, and Europe. More than 525,000 were repatriated, either voluntarily or involuntarily, mainly from Cambodia.
Bua Xou Mua (1915–2013), also known as Boua Xou Mua, was a Hmong spiritual leader, village chief, and musician. He was known for his recitation of the Hmong oral epic and playing of the gaeng.
Ban Vinai Refugee Camp, officially the Ban Vinai Holding Center, was a refugee camp in Thailand from 1975 until 1992. Ban Vinai primarily housed highland people, especially Hmong who fled the Hmong genocide in Laos. Ban Vinai had a maximum population of about 45,000 Hmong and other highland people. Many of the highland Lao were resettled in the United States and other countries. Many others lived in the camp for years which came to resemble a crowded and large Hmong village. The Royal Thai Government closed the camp in 1992, forced some of the inhabitants to return to Laos and removed the rest of them to other refugee camps.
Doua Moua is an American actor and writer best known for his roles as Spider in the 2008 film Gran Torino and Po in Disney's live-action Mulan.

Yia Vang is a Hmong-American chef in Minneapolis, Minnesota.
Mai Hlee Xiong is a Hmong American businesswoman and politician currently serving as a Democratic member of the Michigan House of Representatives. She previously served on the Macomb County Board of Commissioners. In April 2024, Xiong won a special election to fill the vacant District 13 in the Michigan House of Representatives.







