
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly, instead using a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden. For instance: preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the color of the backlight, and a character negative LCD will have a black background with the letters being of the same color as the backlight. Optical filters are added to white on blue LCDs to give them their characteristic appearance.
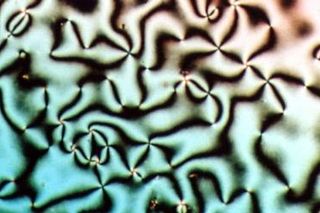
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter that has properties between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For instance, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many different types of liquid-crystal phases, which can be distinguished by their different optical properties. The contrasting areas in the textures correspond to domains where the liquid-crystal molecules are oriented in different directions. Within a domain, however, the molecules are well ordered. LC materials may not always be in a liquid-crystal state of matter.

An electro-optic modulator (EOM) is an optical device in which a signal-controlled element exhibiting an electro-optic effect is used to modulate a beam of light. The modulation may be imposed on the phase, frequency, amplitude, or polarization of the beam. Modulation bandwidths extending into the gigahertz range are possible with the use of laser-controlled modulators.

The Pockels effect or Pockels electro-optic effect, named after Friedrich Carl Alwin Pockels, changes or produces birefringence in an optical medium induced by an electric field. In the Pockels effect, also known as the linear electro-optic effect, the birefringence is proportional to the electric field. In the Kerr effect, the refractive index change (birefringence) is proportional to the square of the field. The Pockels effect occurs only in crystals that lack inversion symmetry, such as lithium niobate, and in other noncentrosymmetric media such as electric-field poled polymers or glasses.
The Kerr effect, also called the quadratic electro-optic (QEO) effect, is a change in the refractive index of a material in response to an applied electric field. The Kerr effect is distinct from the Pockels effect in that the induced index change is directly proportional to the square of the electric field instead of varying linearly with it. All materials show a Kerr effect, but certain liquids display it more strongly than others. The Kerr effect was discovered in 1875 by Scottish physicist John Kerr.

Smart glass or switchable glass is a glass or glazing whose light transmission properties dynamically alter to control the passage of solar irradiation into buildings. In general, the glass changes between transparent and translucent and vice versa, either letting light pass through or blocking some or all wavelengths of light.

Electrorheological (ER) fluids are suspensions of extremely fine non-conducting but electrically active particles in an electrically insulating fluid. The apparent viscosity of these fluids changes reversibly by an order of up to 100,000 in response to an electric field. For example, a typical ER fluid can go from the consistency of a liquid to that of a gel, and back, with response times on the order of milliseconds. The effect is sometimes called the Winslow effect after its discoverer, the American inventor Willis Winslow, who obtained a US patent on the effect in 1947 and wrote an article published in 1949.
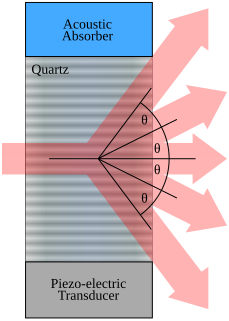
An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell or an acousto-optic deflector (AOD), uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves. They are used in lasers for Q-switching, telecommunications for signal modulation, and in spectroscopy for frequency control. A piezoelectric transducer is attached to a material such as glass. An oscillating electric signal drives the transducer to vibrate, which creates sound waves in the material. These can be thought of as moving periodic planes of expansion and compression that change the index of refraction. Incoming light scatters off the resulting periodic index modulation and interference occurs similar to Bragg diffraction. The interaction can be thought of as a three-wave mixing process resulting in Sum-frequency generation or Difference-frequency generation between phonons and photons.

An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements.
In liquid crystals, homeotropic alignment is one of the ways of alignment of liquid crystalline molecules. Homeotropic alignment is the state in which a rod-like liquid crystalline molecule aligns perpendicularly to the substrate. In the polydomain state, the parts also are called homeotropic domains. In contrast, the state in which the molecule aligns to a substance in parallel is called homogeneous alignment.

The twisted nematic effect (TN-effect) was a main technology breakthrough that made LCDs practical. Unlike earlier displays, TN-cells did not require a current to flow for operation and used low operating voltages suitable for use with batteries. The introduction of TN-effect displays led to their rapid expansion in the display field, quickly pushing out other common technologies like monolithic LEDs and CRTs for most electronics. By the 1990s, TN-effect LCDs were largely universal in portable electronics, although since then, many applications of LCDs adopted alternatives to the TN-effect such as in-plane switching (IPS) or vertical alignment (VA).

Martin Schadt is a Swiss physicist and inventor.

Large-screen television technology developed rapidly in the late 1990s and 2000s. Prior to the development of thin-screen technologies, rear-projection television was standard for larger displays, and jumbotron, a non-projection video display technology, was used at stadiums and concerts. Various thin-screen technologies are being developed, but only liquid crystal display (LCD), plasma display (PDP) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) have been publicly released. Recent technologies like organic light-emitting diode (OLED) as well as not-yet-released technologies like surface-conduction electron-emitter display (SED) or field emission display (FED) are in development to replace earlier flat-screen technologies in picture quality.

George Harry Heilmeier was an American engineer, manager, and a pioneering contributor to liquid crystal displays (LCDs), for which he was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame. Heilmeier's work is an IEEE Milestone.
A blue phase mode LCD is a liquid crystal display (LCD) technology that uses highly twisted cholesteric phases in a blue phase. It was first proposed in 2007 to obtain a better display of moving images with, for example, frame rates of 100–120 Hz to improve the temporal response of LCDs. This operational mode for LCDs also does not require anisotropic alignment layers and thus theoretically simplifies the LCD manufacturing process.
There are various classifications of the electro-optical modes of liquid crystal displays (LCDs).
An optical modulator is an optical device which is used to modulate a beam of light with a perturbation device. It is a kind of transmitter to convert information to optical binary signal through optical fiber or transmission medium of optical frequency in fiber optic communication. There are several methods to manipulate this device depending on the parameter of a light beam like amplitude modulator (majority), phase modulator, polarization modulator etc. The easiest way to obtain modulation is modulation of intensity of a light by the current driving the light source. This sort of modulation is called direct modulation, as opposed to the external modulation performed by a light modulator. For this reason, light modulators are called external light modulators. According to manipulation of the properties of material modulators are divided into two groups, absorptive modulators and refractive modulators. Absorption coefficient can be manipulated by Franz-Keldysh effect, Quantum-Confined Stark Effect, excitonic absorption, or changes of free carrier concentration. Usually, if several such effects appear together, the modulator is called electro-absorptive modulator. Refractive modulators most often make use of electro-optic effect, other modulators are made with acousto-optic effect, magneto-optic effect such as Faraday and Cotton-Mouton effects. The other case of modulators is spatial light modulator (SLM) which is modified two dimensional distribution of amplitude & phase of an optical wave.
IPS is a screen technology for liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). In IPS, a layer of liquid crystals is sandwiched between two glass surfaces. The liquid crystal molecules are aligned parallel to those surfaces in predetermined directions (in-plane). The molecules are reoriented by an applied electric field, whilst remaining essentially parallel to the surfaces to produce an image. It was designed to solve the strong viewing angle dependence and low-quality color reproduction of the twisted nematic field effect (TN) matrix LCDs prevalent in the late 1980s.

Guest Host Displays, Dichroic Displays, Polymer Dispersed Displays
Photoalignment is a technique for orienting liquid crystals to desired alignment by exposure to polarized light and a photo reactive alignment chemical. It is usually performed by exposing the alignment chemical to polarized light with desired orientation which then aligns the liquid crystal cells or domains to the exposed orientation. The advantages of photoalignment technique over conventional methods are non-contact high quality alignment, reversible alignment and micro-patterning of liquid crystal phases.












