
The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier which is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.
The Universal Product Code (UPC) is a barcode symbology that is widely used in the United States, Canada, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and other countries for tracking trade items in stores.

A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths and spacings of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or one-dimensional (1D), can be scanned by special optical scanners, called barcode readers. Later, two-dimensional (2D) variants were developed, using rectangles, dots, hexagons and other geometric patterns, called matrix codes or 2D barcodes, although they do not use bars as such. 2D barcodes can be read or deconstructed using application software on mobile devices with inbuilt cameras, such as smartphones.
The National Drug Code (NDC) is a unique product identifier used in the United States for drugs intended for human use. The Drug Listing Act of 1972 requires registered drug establishments to provide the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) with a current list of all drugs manufactured, prepared, propagated, compounded, or processed by it for commercial distribution. Drug products are identified and reported using the NDC.
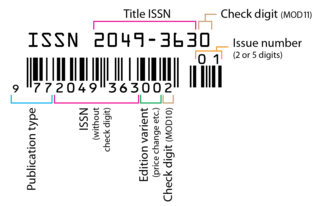
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit serial number used to uniquely identify a serial publication, such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature.

Code 39 is a variable length, discrete barcode symbology.
A check digit is a form of redundancy check used for error detection on identification numbers, such as bank account numbers, which are used in an application where they will at least sometimes be input manually. It is analogous to a binary parity bit used to check for errors in computer-generated data. It consists of one or more digits computed by an algorithm from the other digits in the sequence input.

Code 128 is a high-density linear barcode symbology defined in ISO/IEC 15417:2007. It is used for alphanumeric or numeric-only barcodes. It can encode all 128 characters of ASCII and, by use of an extension symbol (FNC4), the Latin-1 characters defined in ISO/IEC 8859-1.. It generally results in more compact barcodes compared to other methods like Code 39, especially when the texts contain mostly digits.

Code 93 is a barcode symbology designed in 1982 by Intermec to provide a higher density and data security enhancement to Code 39. It is an alphanumeric, variable length symbology. Code 93 is used primarily by Canada Post to encode supplementary delivery information. Every symbol includes two check characters.

Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) is a continuous two-width barcode symbology encoding digits. It is used commercially on 135 film, for ITF-14 barcodes, and on cartons of some products, while the products inside are labeled with UPC or EAN.

PostBar, also known as CPC 4-State, is the black-ink barcode system used by Canada Post in its automated mail sorting and delivery operations. It is similar to other 4 State barcode systems used by Australia Post and the United Kingdom's Royal Mail, but uses an obscured structure and encoding system unique to Canada Post. This particular bar code system is used on "flats" and parcels.
A national identification number, national identity number, or national insurance number is used by the governments of many countries as a means of tracking their citizens, permanent residents, and temporary residents for the purposes of work, taxation, government benefits, health care, and other governmentally-related functions. The number appears on identity documents issued by several countries.
The Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is an identifier for trade items, developed by GS1. Such identifiers are used to look up product information in a database which may belong to a retailer, manufacturer, collector, researcher, or other entity. The uniqueness and universality of the identifier is useful in establishing which product in one database corresponds to which product in another database, especially across organizational boundaries.

The International Article Number is a standard describing a barcode symbology and numbering system used in global trade to identify a specific retail product type, in a specific packaging configuration, from a specific manufacturer. The standard has been subsumed in the Global Trade Item Number standard from the GS1 organization; the same numbers can be referred to as GTINs and can be encoded in other barcode symbologies defined by GS1. EAN barcodes are used worldwide for lookup at retail point of sale, but can also be used as numbers for other purposes such as wholesale ordering or accounting. These barcodes only represent the digits 0–9, unlike some other barcode symbologies which can represent additional characters.
"Bookland" is the informal name for the Unique Country Code (UCC) prefix allocated in the 1980s for European Article Number (EAN) identifiers of published books, regardless of country of origin, so that the EAN namespace can catalogue books by ISBN rather than maintaining a redundant parallel numbering system. In other words, Bookland is a fictitious country that exists solely in EAN for the purposes of non-geographically cataloguing books in the otherwise geographically keyed EAN coding system.
Codabar is a linear barcode symbology developed in 1972 by Pitney Bowes Corp. It and its variants are also known as Codeabar, Ames Code, NW-7, Monarch, Code 2 of 7, Rationalized Codabar, ANSI/AIM BC3-1995 or USD-4. Although Codabar has not been registered for US federal trademark status, its hyphenated variant Code-a-bar is a registered trademark.

MSI is a barcode symbology developed by the MSI Data Corporation, based on the original Plessey Code symbology. It is a continuous symbology that is not self-checking. MSI is used primarily for inventory control, marking storage containers and shelves in warehouse environments.

RM4SCC (Royal Mail 4-State Customer Code is the name of the barcode character set based on the Royal Mail 4-State Bar Code symbology created by Royal Mail. The RM4SCC is used for the Royal Mail Cleanmail service. It enables UK postcodes as well as Delivery Point Suffixes to be easily read by a machine at high speed.

An EAN-8 is an EAN/UPC symbology barcode and is derived from the longer International Article Number (EAN-13) code. It was introduced for use on small packages where an EAN-13 barcode would be too large; for example on cigarettes, pencils, and chewing gum packets. It is encoded identically to the 12 digits of the UPC-A barcode, except that it has 4 digits in each of the left and right halves.

The EAN-2 is a supplement to the EAN-13 and UPC-A barcodes. It is often used on magazines and periodicals to indicate an issue number.













