Calypso, Calipso or Kalypso may refer to:
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together in a design flow that chip designers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips. Since a modern semiconductor chip can have billions of components, EDA tools are essential for their design; this article in particular describes EDA specifically with respect to integrated circuits (ICs).
Schematic capture or schematic entry is a step in the design cycle of electronic design automation (EDA) at which the electronic diagram, or electronic schematic of the designed electronic circuit, is created by a designer. This is done interactively with the help of a schematic capture tool also known as schematic editor.
James E. Solomon is an American engineer and entrepreneur. In his lifetime, he has founded four companies, including one of the companies that merged to form the leading chip manufacturing toolmaker Cadence Design Systems. He is an IEEE Fellow and received the industry's Phil Kaufman Award in 1997. Solomon holds 23 patents in integrated chip design.
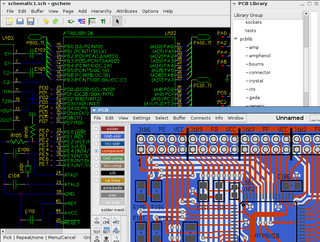
The term gEDA refers to two things:
- A set of software applications used for electronic design released under the GPL. As such, gEDA is an ECAD or EDA application suite. gEDA is mostly oriented towards printed circuit board design. The gEDA applications are often referred to collectively as "the gEDA Suite".
- The collaboration of free software/open-source developers who work to develop and maintain the gEDA toolkit. The developers communicate via gEDA mailing lists, and have participated in the annual "Google Summer of Code" event as a single project. This collaboration is often referred to as "the gEDA Project".

Cadence Design Systems, Inc., headquartered in San Jose, California, is an American multinational computational software company, founded in 1988 by the merger of SDA Systems and ECAD, Inc. The company produces software, hardware, and silicon structures for designing integrated circuits, systems on chips (SoCs), and printed circuit boards.
ECAD, Inc., based in Santa Clara, California, was an early vendor of electronic design automation software. The company was best known for its design rule checking product Dracula, but also produced IC layout and PC layout software. Eventually, in a merger with SDA, it became Cadence Design Systems.
Joseph Ball Costello is an American executive in the electronic design automation (EDA) industry. He was president and COO of SDA Systems from 1987–1988 and CEO of Cadence Design Systems, which became the largest EDA company under his tenure, from 1988–1997.
The SUN workstation was a modular computer system designed at Stanford University in the early 1980s. It became the seed technology for many commercial products, including the original workstations from Sun Microsystems.
Creo Elements/View, formerly known as ProductView, is a suite of digital mockup and product visualization software applications from PTC.
Crowley Broadcast Analysis is an official institution of research, which monitors the radios in Brazil since 1997. Currently the company provides data to the Escritório Central de Arrecadação e Distribuição (ECAD) and the Brazilian Association of Record Producers (ABPD) and besides being the standard for the Phonographic Industry in the country. In August 2009, also exclusively provides the charts for Billboard Brasil that is based on grid-base radios with 250 stations surveyed in 10 cities.
P-CAD was the brand name of Personal CAD Systems, Inc., a California based manufacturer of electronic design automation software. It manufactured a CAD software available for personal computers. The company was divested into ACCEL Technologies which was purchased by Altium in 2000. The last release of the software was in 2006 before it was retired in favor of the Altium Designer product.
The Escritório Central de Arrecadação e Distribuição is the national copyright collection agency in Brazil. It is made up of six partner organisations: ABRAMUS, AMAR, ASSIM, SBACEM, SICAM, SOCINPRO and UBC.

Ritmo Perfeito is the second studio album by Brazilian pop singer Anitta. It was released by Warner Music Brasil on June 3, 2014, the same day as Anitta's first live album and DVD, Meu Lugar. Ritmo Perfeito features rappers MC Guime and Projota, who also wrote the songs "Cobertor" and "Mulher". The song's genre is the same as Anitta's first album, but includes more prominent influences from funk melody and R&B.
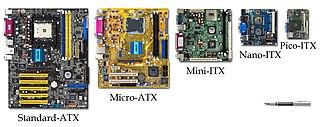
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard. It may also define an entire system, as in a computer form factor.
Intermediate Data Format (IDF) files are used interoperate between electronic design automation (EDA) software and solid modeling mechanical computer-aided design (CAD) software.
Engineering information management (EIM) is the business function within product development and specifically systems engineering that allows engineers to collaborate on a single source of truth of engineering data.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



