
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity whose main biological role is to protect the organism from oxidative damage. The biochemical function of glutathione peroxidase is to reduce lipid hydroperoxides to their corresponding alcohols and to reduce free hydrogen peroxide to water.
Glycophorin C plays a functionally important role in maintaining erythrocyte shape and regulating membrane material properties, possibly through its interaction with protein 4.1. Moreover, it has previously been shown that membranes deficient in protein 4.1 exhibit decreased content of glycophorin C. It is also an integral membrane protein of the erythrocyte and acts as the receptor for the Plasmodium falciparum protein PfEBP-2.

Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder of the enzyme pyruvate kinase which affects the survival of red blood cells. Both autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance have been observed with the disorder; classically, and more commonly, the inheritance is autosomal recessive. Pyruvate kinase deficiency is the second most common cause of enzyme-deficient hemolytic anemia, following G6PD deficiency.
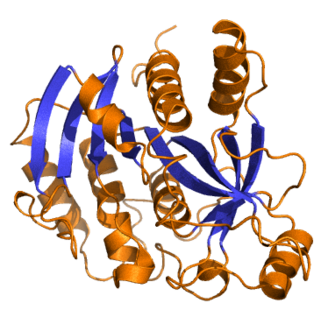
L-Gulonolactone oxidase is an enzyme that produces vitamin C, but is non-functional in Haplorrhini, in some bats, and in guinea pigs. It catalyzes the reaction of L-gulono-1,4-lactone with oxygen to form L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone (2-keto-gulono-γ-lactone) and hydrogen peroxide. It uses FAD as a cofactor. The L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone then converts to ascorbic acid spontaneously, without enzymatic action.

Spectrin is a cytoskeletal protein that lines the intracellular side of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells. Spectrin forms pentagonal or hexagonal arrangements, forming a scaffold and playing an important role in maintenance of plasma membrane integrity and cytoskeletal structure. The hexagonal arrangements are formed by tetramers of spectrin subunits associating with short actin filaments at either end of the tetramer. These short actin filaments act as junctional complexes allowing the formation of the hexagonal mesh. The protein is named spectrin since it was first isolated as a major protein component of human red blood cells which had been treated with mild detergents; the detergents lysed the cells and the hemoglobin and other cytoplasmic components were washed out. In the light microscope the basic shape of the red blood cell could still be seen as the spectrin-containing submembranous cytoskeleton preserved the shape of the cell in outline. This became known as a red blood cell "ghost" (spectre), and so the major protein of the ghost was named spectrin.
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene. It catalyzes the chemical reaction
Glutathione synthetase deficiency (GSD) is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that prevents the production of glutathione. Glutathione helps prevent damage to cells by neutralizing harmful molecules generated during energy production. Glutathione also plays a role in processing medications and cancer-causing compounds (carcinogens), and building DNA, proteins, and other important cellular components.

Aldolase A deficiency is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder resulting in a deficiency of the enzyme aldolase A; the enzyme is found predominantly in red blood cells and muscle tissue. The deficiency may lead to hemolytic anaemia as well as myopathy associated with exercise intolerance and rhabdomyolysis in some cases.

Orotic aciduria is a disease caused by an enzyme deficiency, resulting in a decreased ability to synthesize pyrimidines. It was the first described enzyme deficiency of the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway.
In enzymology, a Mg2+-importing ATPase (EC 3.6.3.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a guanylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cathepsin E is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CTSE gene. The enzyme is also known as slow-moving proteinase, erythrocyte membrane aspartic proteinase, SMP, EMAP, non-pepsin proteinase, cathepsin D-like acid proteinase, cathepsin E-like acid proteinase, cathepsin D-type proteinase) is an enzyme.

6-phosphofructokinase, liver type (PFKL) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PFKL gene on chromosome 21. This gene encodes the liver (L) isoform of phosphofructokinase-1, an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of D-fructose 6-phosphate to D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, which is a key step in glucose metabolism (glycolysis). This enzyme is a tetramer that may be composed of different subunits encoded by distinct genes in different tissues. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]

Cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase 3 (NTC53), also known as cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase 3A, pyrimidine 5’-nucleotidase, and p56, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NT5C3, or NT5C3A, gene on chromosome 7.

AMP deaminase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AMPD3 gene.

Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PYCR1 gene.

Acylphosphatase-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACYP1 gene.
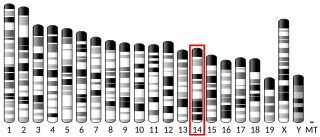
Enolase Deficiency is a rare genetic disorder of glucose metabolism. Partial deficiencies have been observed in several caucasian families. The deficiency is transmitted through an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. The gene for Enolase 1 has been localized to Chromosome 1 in humans. Enolase deficiency, like other glycolytic enzyme deficiences, usually manifests in red blood cells as they rely entirely on anaerobic glycolysis. Enolase deficiency is associated with a spherocytic phenotype and can result in hemolytic anemia, which is responsible for the clinical signs of Enolase deficiency.
Human genetic resistance to malaria refers to inherited changes in the DNA of humans which increase resistance to malaria and result in increased survival of individuals with those genetic changes. The existence of these genotypes is likely due to evolutionary pressure exerted by parasites of the genus Plasmodium which cause malaria. Since malaria infects red blood cells, these genetic changes are most common alterations to molecules essential for red blood cell function, such as hemoglobin or other cellular proteins or enzymes of red blood cells. These alterations generally protect red blood cells from invasion by Plasmodium parasites or replication of parasites within the red blood cell.

Ribonuclease H2 subunit A, also known as RNase H2 subunit A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNASEH2A gene.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.














