
A debit card, also known as a check card or bank card, is a payment card that can be used in place of cash to make purchases. The card usually consists of the bank's name, a card number, the cardholder's name, and an expiration date, on either the front or the back. Many of the new cards now have a chip on them, which allows people to use their card by touch (contactless), or by inserting the card and keying in a PIN as with swiping the magnetic stripe. These are similar to a credit card, but unlike a credit card, the money for the purchase must be in the cardholder's bank account at the time of the purchase and is immediately transferred directly from that account to the merchant's account to pay for the purchase.
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. This allows others to rely upon signatures or on assertions made about the private key that corresponds to the certified public key. A CA acts as a trusted third party—trusted both by the subject (owner) of the certificate and by the party relying upon the certificate. The format of these certificates is specified by the X.509 or EMV standard.
FinTS, formerly known as HBCI, is a bank-independent protocol for online banking, developed and used by German banks.

Carte Bleue was a major debit card payment system operating in France. Unlike Visa Electron or Maestro debit cards, Carte Bleue transactions worked without requiring authorization from the cardholder's bank. In many situations, the card worked like a credit card but without fees for the cardholder. The system has now been integrated into a wider scheme called CB or carte bancaire. All Carte Bleue cards were part of CB, but not all CB cards were Carte Bleue.

A hardware security module (HSM) is a physical computing device that safeguards and manages secrets, performs encryption and decryption functions for digital signatures, strong authentication and other cryptographic functions. These modules traditionally come in the form of a plug-in card or an external device that attaches directly to a computer or network server. A hardware security module contains one or more secure cryptoprocessor chips.

Payment cards are part of a payment system issued by financial institutions, such as a bank, to a customer that enables its owner to access the funds in the customer's designated bank accounts, or through a credit account and make payments by electronic transfer with a payment terminal and access automated teller machines (ATMs). Such cards are known by a variety of names including bank cards, ATM cards, client cards, key cards or cash cards.
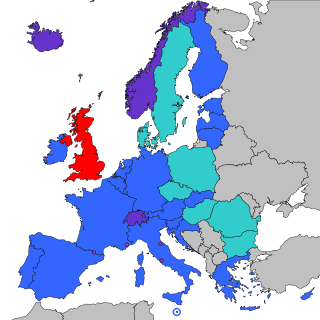
The Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) is a payment integration initiative of the European Union for simplification of bank transfers denominated in euro. As of 2020, there were 36 members in SEPA, consisting of the 27 member states of the European Union, the four member states of the European Free Trade Association, and the United Kingdom. Some microstates participate in the technical schemes: Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City.

The Eurocheque was a type of cheque used in Europe that was accepted across national borders and which could be written in a variety of currencies.
Shopping cart software is a piece of e-commerce software on a web server that allows visitors to have an Internet site to select items for eventual purchase.

Groupement des cartes bancaires CB, also known as simply CB, is France's national interbank network, with over 46,000 ATMs and over 1 million EFTPOS acceptance points.
Mobile Electronic Signature Consortium (mSign) was founded in 1999 and comprised 35 member companies. In October 2000, the consortium published an XMl-interface defining a protocol allowing service providers to obtain a mobile (digital) signature from a mobile phone subscriber.
The Euro Alliance of Payment Schemes (EAPS) was an international alliance of European bank and interbank networks that had aimed to creating a pan-European debit card system in the Single Euro Payments Area to rival Visa and Mastercard using existing country specific systems. It was launched in 2007 with the support of the European Union but failed and was abandoned sometime after 2013.

girocard is an interbank network and debit card service connecting virtually all German ATMs and banks. It is based on standards and agreements developed by the German Banking Industry Committee.
The Electronic Banking Internet Communication Standard (EBICS) is a German transmission protocol developed by the German Banking Industry Committee for sending payment information between banks over the Internet. It grew out of the earlier BCS-FTAM protocol that was developed in 1995, with the aim of being able to use Internet connections and TCP/IP. It is mandated for use by German banks and has also been adopted by France and Switzerland.
The German Banking Industry Committee (GBIC), known until 2011 as the Central Credit Committee is an industry association of the German banking industry. Its decisions are held normative for the national banking sector – either directly by interbank treaties or indirectly by preparing a corresponding ministerial or Bundesbank decision.
CIPURSE is an open security standard for transit fare collection systems. It makes use of smart card technologies and additional security measures.
In financial services, open banking allows for financial data to be shared between banks and third-party service providers through the use of application programming interfaces (APIs). Traditionally, banks have kept customer financial data within their own closed systems. Open banking allows customers to share their financial information securely and electronically with other authorized organizations, such as fintech companies, payment providers, and other banks.

Worldline SA is a French multinational payment and transactional services company founded in 1974.

The European Payments Initiative (EPI), previously known as the Pan-European Payments System Initiative (PEPSI), is a European Central Bank-backed payment-integration initiative aiming to create a pan-European payment system and interbank network to rival Mastercard and Visa, and eventually replace national European payment schemes such as France's Carte Bancaire and Germany's Girocard.
Electronic Commerce Modeling Language (ECML) is a protocol which enables the e-commerce merchants to standardize their online payment processes. Through the application of ECML, customers' billing information in their digital wallet can be easily transferred to fill out the checkout forms.









