
Country codes are short alphabetic or numeric geographical codes (geocodes) developed to represent countries and dependent areas, for use in data processing and communications. Several different systems have been developed to do this. The term country code frequently refers to ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 or international dialing codes, the E.164 country calling codes.

The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 28 member states that are located primarily in Europe. Its members have a combined area of 4,475,757 km2 (1,728,099 sq mi) and an estimated total population of about 513 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market, enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development. For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished. A monetary union was established in 1999 and came into full force in 2002 and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.

The European Commission (EC) is the executive branch of the European Union, responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the EU treaties and managing the day-to-day business of the EU. Commissioners swear an oath at the European Court of Justice in Luxembourg City, pledging to respect the treaties and to be completely independent in carrying out their duties during their mandate. The Commissioners are proposed by the Council of the European Union, on the basis of suggestions made by the national governments, and then appointed by the European Council after the approval of the European Parliament. It is common, although not a formal requirement, that the commissioners have previously held senior political positions, such as being a member of the European Parliament or a government minister.

Galileo is the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016, created by the European Union (EU) through the European GNSS Agency (GSA), headquartered in Prague in the Czech Republic, with two ground operations centres, Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich in Germany and Fucino in Italy. The €10 billion project is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European nations do not have to rely on the U.S. GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time. The use of basic (lower-precision) Galileo services is free and open to everyone. The higher-precision capabilities are available for paying commercial users. Galileo is intended to provide horizontal and vertical position measurements within 1-metre precision, and better positioning services at higher latitudes than other positioning systems. Galileo is also to provide a new global search and rescue (SAR) function as part of the MEOSAR system.

The Maastricht Treaty was signed on 7 February 1992 by the members of the European Communities in Maastricht, Netherlands, to further European integration. On 9–10 December 1991, the same city hosted the European Council which drafted the treaty. The treaty founded the European Union and established its pillar structure which stayed in place until the Lisbon Treaty came into force in 2009. The treaty also greatly expanded the competences of the EEC/EU and led to the creation of the single European currency, the euro.
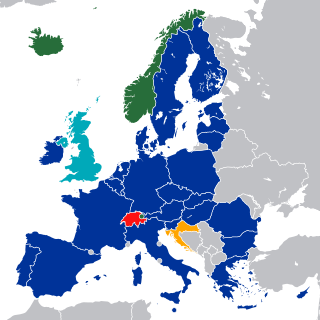
The European Economic Area (EEA), which was established via the EEA Agreement in 1992, is an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union (EU)'s single market to non-EU member parties. The EEA links the EU member states and three European Free Trade Association (EFTA) states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of labour, goods, services, and capital within the European Single Market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and three EFTA member states.

A Member of the European Parliament (MEP) is a person who has been elected to serve as a popular representative in the European Parliament.

The European Union (EU) has expanded a number of times throughout its history by way of the accession of new member states to the Union. To join the EU, a state needs to fulfil economic and political conditions called the Copenhagen criteria, which require a stable democratic government that respects the rule of law, and its corresponding freedoms and institutions. According to the Maastricht Treaty, each current member state and the European Parliament must agree to any enlargement. The process of enlargement is sometimes referred to as European integration. This term is also used to refer to the intensification of co-operation between EU member states as national governments allow for the gradual harmonisation of national laws.
The languages of the European Union are languages used by people within the member states of the European Union (EU).

The Treaty of Amsterdam, officially the Treaty of Amsterdam amending the Treaty on European Union, the Treaties establishing the European Communities and certain related acts, was signed on 2 October 1997, and entered into force on 1 May 1999; it made substantial changes to the Treaty of Maastricht, which had been signed in 1992.

The European Union Aviation Safety Agency or EASA is an agency of the European Union (EU) with responsibility for civil aviation safety. It carries out certification, regulation, and standardisation, and also performs investigation and monitoring. It collects and analyses safety data, drafts and advises on safety legislation, and coordinates with similar organisations in other parts of the world. The idea of a European-level aviation safety authority goes back to 1996, but the agency was not legally established until 2002. It began its work in 2003.

The politics of the European Union are different from other organisations and states due to the unique nature of the European Union (EU). The EU is similar to a confederation, where many policy areas are federalised into common institutions capable of making law; however the EU does not, unlike most states, control foreign policy, defence policy or the majority of direct taxation policies. These areas are primarily under the control of the EU's member states although a certain amount of structured co-operation and coordination takes place in these areas. For the EU to take substantial actions in these areas, all Member States must give their consent. EU laws that override national laws are more numerous than in historical confederations; however the EU is legally restricted from making law outside its remit or where it is no more appropriate to do so at a national or local level (subsidiarity) when acting outside its exclusive competencies. The principle of subsidiarity does not apply to areas of exclusive competence.

The European Union Satellite Centre is the agency of the European Union (EU) that supports the EU's decision-making in the field of the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP), including crisis management missions and operations, by providing products and services resulting from the exploitation of relevant space assets and collateral data, including satellite and aerial imagery, and related services. SacCen is located in Torrejón de Ardoz, in the vicinity of Madrid, Spain.

The 2003–04 Serie A was the 102nd season of top-tier Italian football, the 72nd in a round-robin tournament. It contained 18 teams for the 16th and last time from the 1988–89 season. With the bottom three being relegated, the 15th placed side would face the sixth-highest team from Serie B, with the winner playing in the Serie A in the subsequent 2004–05 season.
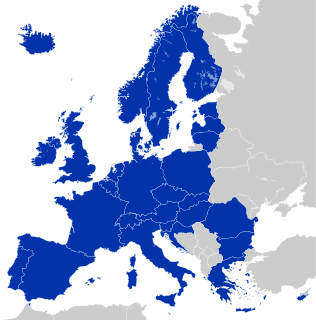
The Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) is a payment-integration initiative of the European Union for simplification of bank transfers denominated in euro. As of 2019, there were 36 members in SEPA, consisting of the 28 member states of the European Union, the four member states of the European Free Trade Association. Some countries participate in the technical schemes: Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City.

The accession of Serbia to the European Union (EU) has been on the current agenda for the future enlargement of the EU since 2011, when it became a candidate for accession. Serbia officially applied for European Union membership on 22 December 2009. Accession negotiations are currently ongoing. Serbia is expected to complete its negotiations by the end of 2023, allowing it to join the Union by 2025.

The European Union (EU) consists of 28 member states. Each member state is party to the founding treaties of the union and thereby subject to the privileges and obligations of membership. Unlike members of most international organisations, the member states of the EU are subjected to binding laws in exchange for representation within the common legislative and judicial institutions. Member states must agree unanimously for the EU to adopt policies concerning defence and foreign policy. Subsidiarity is a founding principle of the EU.
The EU three, also known as EU big three, EU triumvirate or EU trio, refers to France, Germany and Italy, a group that consists of the three large founding members of the European Union;

Brexit is the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU). Following a June 2016 referendum, in which 51.9% voted to leave, the UK government formally announced the country's withdrawal in March 2017, starting a process that is currently due to conclude with the UK withdrawing no later than 31 January 2020.













