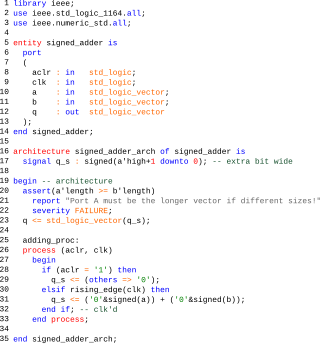
VHDL is a hardware description language that can model the behavior and structure of digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ranging from the system level down to that of logic gates, for design entry, documentation, and verification purposes. The language was developed for the US military VHSIC program in the 1980s, and has been standardized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as IEEE Std 1076; the latest version of which is IEEE Std 1076-2019. To model analog and mixed-signal systems, an IEEE-standardized HDL based on VHDL called VHDL-AMS has been developed.
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, usually to design application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and to program field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs).

Mentor Graphics Corporation was a US-based electronic design automation (EDA) multinational corporation for electrical engineering and electronics, headquartered in Wilsonville, Oregon. Founded in 1981, the company distributed products that assist in electronic design automation, simulation tools for analog mixed-signal design, VPN solutions, and fluid dynamics and heat transfer tools. The company leveraged Apollo Computer workstations to differentiate itself within the computer-aided engineering (CAE) market with its software and hardware.
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together in a design flow that chip designers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips. Since a modern semiconductor chip can have billions of components, EDA tools are essential for their design; this article in particular describes EDA specifically with respect to integrated circuits (ICs).

Synopsys, Inc. is an American electronic design automation (EDA) company headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, that focuses on silicon design and verification, silicon intellectual property and software security and quality. Synopsys supplies tools and services to the semiconductor design and manufacturing industry. Products include tools for logic synthesis and physical design of integrated circuits, simulators for development, and debugging environments that assist in the design of the logic for chips and computer systems.
Formal equivalence checking process is a part of electronic design automation (EDA), commonly used during the development of digital integrated circuits, to formally prove that two representations of a circuit design exhibit exactly the same behavior.
In computer engineering, logic synthesis is a process by which an abstract specification of desired circuit behavior, typically at register transfer level (RTL), is turned into a design implementation in terms of logic gates, typically by a computer program called a synthesis tool. Common examples of this process include synthesis of designs specified in hardware description languages, including VHDL and Verilog. Some synthesis tools generate bitstreams for programmable logic devices such as PALs or FPGAs, while others target the creation of ASICs. Logic synthesis is one step in circuit design in the electronic design automation, the others are place and route and verification and validation.

Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware designed to perform specific functions more efficiently when compared to software running on a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU). Any transformation of data that can be calculated in software running on a generic CPU can also be calculated in custom-made hardware, or in some mix of both.
Specman is an EDA tool that provides advanced automated functional verification of hardware designs. It provides an environment for working with, compiling, and debugging testbench environments written in the e Hardware Verification Language. Specman also offers automated testbench generation to boost productivity in the context of block, chip, and system verification.

Integrated circuit design, semiconductor design, chip design or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits, or ICs. ICs consist of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography.

In integrated circuit design, hardware emulation is the process of imitating the behavior of one or more pieces of hardware with another piece of hardware, typically a special purpose emulation system. The emulation model is usually based on a hardware description language source code, which is compiled into the format used by emulation system. The goal is normally debugging and functional verification of the system being designed. Often an emulator is fast enough to be plugged into a working target system in place of a yet-to-be-built chip, so the whole system can be debugged with live data. This is a specific case of in-circuit emulation.
An engineering change order (ECO), also called an engineering change notice (ECN), engineering change (EC), or engineering release notice(ERN), is an artifact used to implement changes to components or end products. The ECO is utilized to control and coordinate changes to product designs that evolve over time.

Cadence Design Systems, Inc. is an American multinational technology and computational software company. Headquartered in San Jose, California, Cadence was formed in 1988 through the merger of SDA Systems and ECAD. Initially specialized in electronic design automation (EDA) software for the semiconductor industry, currently the company makes software and hardware for designing products such as integrated circuits, systems on chips (SoCs), printed circuit boards, and pharmaceutical drugs, also licensing intellectual property for the electronics, aerospace, defense and automotive industries, among others.
Semulation is a computer science-related portmanteau of simulation and emulation, signifying the process of controlling an emulation through a simulator.
Aldec, Inc. is a privately owned electronic design automation company based in Henderson, Nevada, providing software and hardware used in creation and verification of digital designs targeting FPGA and ASIC technologies.
High-level synthesis (HLS), sometimes referred to as C synthesis, electronic system-level (ESL) synthesis, algorithmic synthesis, or behavioral synthesis, is an automated design process that takes an abstract behavioral specification of a digital system and finds a register-transfer level structure that realizes the given behavior.
Field-programmable gate array prototyping, also referred to as FPGA-based prototyping, ASIC prototyping or system-on-chip (SoC) prototyping, is the method to prototype system-on-chip and application-specific integrated circuit designs on FPGAs for hardware verification and early software development.
Catapult C Synthesis, a commercial electronic design automation product of Mentor Graphics, is a high-level synthesis tool, sometimes called algorithmic synthesis or ESL synthesis. Catapult C takes ANSI C/C++ and SystemC inputs and generates register transfer level (RTL) code targeted to FPGAs and ASICs.
This page is a comparison of electronic design automation (EDA) software which is used today to design the near totality of electronic devices. Modern electronic devices are too complex to be designed without the help of a computer. Electronic devices may consist of integrated circuits (ICs), printed circuit boards (PCBs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) or a combination of them. Integrated circuits may consist of a combination of digital and analog circuits. These circuits can contain a combination of transistors, resistors, capacitors or specialized components such as analog neural networks, antennas or fuses.
A field-programmable object array (FPOA) is a class of programmable logic devices designed to be modified or programmed after manufacturing. They are designed to bridge the gap between ASIC and FPGA. They contain a grid of programmable silicon objects. Arrix range of FPOA contained three types of silicon objects: arithmetic logic units (ALUs), register files (RFs) and multiply-and-accumulate units (MACs). Both the objects and interconnects are programmable.







