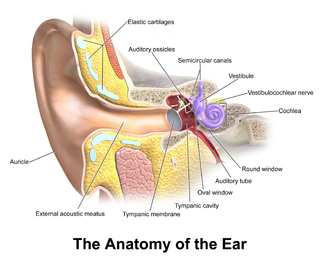
The middle ear is the portion of the ear internal to the eardrum, and external to the oval window of the inner ear. The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the fluid and membranes of the inner ear. The hollow space of the middle ear is also known as the tympanic cavity and is surrounded by the tympani bone. The auditory tube joins the tympanic cavity with the nasal cavity (nasopharynx), allowing pressure to equalize between the middle ear and throat.

The ossicles are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth (cochlea). The absence of the auditory ossicles would constitute a moderate-to-severe hearing loss. The term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone". Though the term may refer to any small bone throughout the body, it typically refers to the malleus, incus, and stapes of the middle ear.

The oval window is a membrane-covered opening that leads from the middle ear to the vestibule of the inner ear.

A hearing test provides an evaluation of the sensitivity of a person's sense of hearing and is most often performed by an audiologist using an audiometer. An audiometer is used to determine a person's hearing sensitivity at different frequencies. There are other hearing tests as well, e.g., Weber test and Rinne test.

Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a problem transferring sound waves anywhere along the pathway through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear (ossicles). If a conductive hearing loss occurs in conjunction with a sensorineural hearing loss, it is referred to as a mixed hearing loss. Depending upon the severity and nature of the conductive loss, this type of hearing impairment can often be treated with surgical intervention or pharmaceuticals to partially or, in some cases, fully restore hearing acuity to within normal range. However, cases of permanent or chronic conductive hearing loss may require other treatment modalities such as hearing aid devices to improve detection of sound and speech perception.

Tympanoplasty is the surgical operation performed for the reconstruction of the eardrum and/or the small bones of the middle ear (ossicles).

The ear canal is a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 2.5 centimetres (1 in) in length and 0.7 centimetres (0.3 in) in diameter.

Tympanostomy tube, also known as a grommet or myringotomy tube, is a small tube inserted into the eardrum in order to keep the middle ear aerated for a prolonged period of time, and to prevent the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. The operation to insert the tube involves a myringotomy and is performed under local or general anesthesia. The tube itself is made in a variety of designs. The most commonly used type is shaped like a grommet. When it is necessary to keep the middle ear ventilated for a very long period, a "T"-shaped tube may be used, as these "T-tubes" can stay in place for 2–4 years. Materials used to construct the tube are most often plastics such as silicone or Teflon. Stainless steel tubes exist, but are no longer in frequent use.

Tympanometry is an examination used to test the condition of the middle ear and mobility of the eardrum and the conduction bones by creating variations of air pressure in the ear canal.

An otoscope or auriscope is a medical device which is used to look into the ears. Health care providers use otoscopes to screen for illness during regular check-ups and also to investigate ear symptoms. An otoscope potentially gives a view of the ear canal and tympanic membrane or eardrum. Because the eardrum is the border separating the external ear canal from the middle ear, its characteristics can be indicative of various diseases of the middle ear space. The presence of cerumen, shed skin, pus, canal skin edema, foreign body, and various ear diseases can obscure any view of the eardrum and thus severely compromise the value of otoscopy done with a common otoscope.
Odorrana tormota, also known as the concave-eared torrent frog, is a species of frog native to China. Its distribution is restricted to Huangshan Mountains in Anhui and Jiande and Anji counties in northern Zhejiang. It occurs in fast-flowing streams and the surrounding habitats, and breeds in streams. The informally assigned common name for frogs in this genus is torrent frog.
A perforated eardrum is a hole in the eardrum which can occur as a result of otitis media, trauma, explosion, loud noise or surgery. Flying with a severe cold can also cause perforation due to changes in air pressure and blocked eustachian tubes resulting from the cold. This is especially true on landing.

The tympanum is an external hearing structure in animals such as mammals, birds, some reptiles, some amphibians and some insects.

Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds by detecting vibrations, changes in the pressure of the surrounding medium through time, through an organ such as the ear. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science.
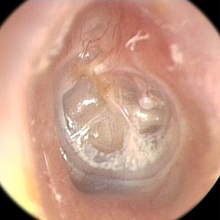
Tympanic membrane retraction describes a condition in which a part of the eardrum lies deeper within the ear than its normal position.
Samuel Gloade, professionally known as 30 Roc, is an American record producer known for producing mixtapes and albums for music artists. To date he has produced for many artists, including Rae Sremmurd, Lil Yachty, Migos, Plies, Cardi B, Rich Homie Quan, and Kendrick Lamar, among many others. He has produced many songs, most notably T-Wayne's "Nasty Freestyle", "Rake It Up" by Yo Gotti featuring Nicki Minaj, Cardi B's hit single, "Bartier Cardi", which features 21 Savage, "Rock" by Plies, and "King's Dead" which was performed by Jay Rock, Kendrick Lamar, Future and James Blake. Gloade was also an executive producer for Lil Yachty's second studio album, Lil Boat 2.