Hīnayāna is a Sanskrit term that was at one time applied collectively to the Śrāvakayāna and Pratyekabuddhayāna paths of Buddhism. This term appeared around the first or second century. Hīnayāna is considered as the preliminary or small (hina) vehicle (yana) of the Buddha's teachings. It is often contrasted with Mahāyāna, the second vehicle of the Buddha's teachings, or the great (maha) vehicle (yana). The third vehicle of the Buddha's teachings is the Vajrayana, the indestructible (vajra) vehicle (yana).

Buddhist texts are religious texts that belong to, or are associated with, Buddhism and its traditions. There is no single textual collection for all of Buddhism. Instead, there are three main Buddhist Canons: the Pāli Canon of the Theravāda tradition, the Chinese Buddhist Canon used in East Asian Buddhist tradition, and the Tibetan Buddhist Canon used in Indo-Tibetan Buddhism.

The schools of Buddhism are the various institutional and doctrinal divisions of Buddhism which are the teachings off buddhist texts. The schools of Buddhism have existed from ancient times up to the present. The classification and nature of various doctrinal, philosophical or cultural facets of the schools of Buddhism is vague and has been interpreted in many different ways, often due to the sheer number of different sects, subsects, movements, etc. that have made up or currently make up the whole of Buddhist traditions. The sectarian and conceptual divisions of Buddhist thought are part of the modern framework of Buddhist studies, as well as comparative religion in Asia. Some factors in Buddhism appear to be consistent, such as the afterlife. Which differs on the version of Buddhism.

The early Buddhist schools are those schools into which the Buddhist monastic saṅgha split early in the history of Buddhism. The divisions were originally due to differences in Vinaya and later also due to doctrinal differences and geographical separation of groups of monks. The original saṅgha split into the first early schools during or after the reign of Aśoka. Later, these first early sects were further divided into schools such as the Sarvāstivādins, the Dharmaguptakas, and the Vibhajyavādins, eventually proliferating into—according to traditional accounts—18 different schools.
The Sthavira nikāya was one of the early Buddhist schools. They split from the majority Mahāsāṃghikas at the time of the Second Buddhist council.
The term Nikāya Buddhism was coined by Masatoshi Nagatomifake as a non-derogatory substitute for Hinayana, meaning the early Buddhist schools. Examples of these groups are pre-sectarian Buddhism and the early Buddhist schools. Some scholars exclude pre-sectarian Buddhism when using the term. The term Theravada refers to Buddhist practices based on these early teachings, as preserved in the Pāli Canon.

The Ekavyāvahārika was one of the early Buddhist schools, and is thought to have separated from the Mahāsāṃghika sect during the reign of Aśoka.
The Kukkuṭika were an early Buddhist school which descended from the Mahāsāṃghika.
Since the death of the historical Buddha, Siddhartha Gautama, Buddhist monastic communities ("sangha") have periodically convened to settle doctrinal and disciplinary disputes and to revise and correct the contents of the Buddhist canons. These gatherings are often termed Buddhist "councils". Accounts of these councils are recorded in Buddhist texts as having begun immediately following the death of the Buddha and have continued into the modern era. The earliest councils are regarded as real events by every Buddhist tradition. However, the historicity and details of these councils remains a matter of dispute in modern Buddhist studies. This is because various sources belonging to different Buddhist schools contain conflicting accounts of these events and the narratives often serve to bolster the authority and prestige of specific schools.

The Anuradhapura Maha Viharaya was an important mahavihara or large Buddhist monastery for Theravada Buddhism in Sri Lanka. King Devanampiya Tissa of Anuradhapura founded it in his capital city of Anuradhapura. Monks such as Buddhaghosa and Dhammapala, who wrote commentaries on the Tipitaka and texts such as the Visuddhimagga, which are central to Theravada Buddhist doctrine, established Theravada Mahaviharan of the Tambapaṇṇiya orthodoxy here. Monks living at the Mahavihara were referred to as Mahaviharavasins.

The Rimé movement is a movement or tendency in Tibetan Buddhism which promotes non-sectarianism and universalism. Teachers from all branches of Tibetan Buddhism – Sakya, Kagyu, Nyingma, Jonang, Gelug, and Bon – have been involved in the promoting Rimé ideals.

The Saṃyutta Nikāya is a Buddhist scriptures collection, the third of the five Nikāyas, or collections, in the Sutta Pitaka, which is one of the "three baskets" that compose the Pali Tipitaka of Theravada Buddhism. Because of the abbreviated way parts of the text are written, the total number of suttas/sūtras is unclear. The editor of the Pali Text Society edition of the text made it 2889, Bodhi in his translation has 2904, while the commentaries give 7762. A study by Rupert Gethin gives the totals for the Burmese and Sinhalese editions as 2854 and 7656, respectively, and his own calculation as 6696; he also says the total in the Thai edition is unclear. The suttas/sūtras are grouped into five vargas/vaggas, or sections. Each varga/vagga is further divided into samyuttas/saṃyuktas, or chapters, each of which in turn contains a group of suttas/sūtras on a related topic.

Southern Buddhism, Eastern Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism are geographical terms sometimes used to describe the three main schools of Buddhism as it spread from the northeastern region of the Indian subcontinent throughout Central Asia, East Asia, Mainland Southeast Asia, and Maritime Southeast Asia.

Buddhism, also known as Buddha Dharma, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise seven percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a śramaṇa–movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to the West in the 20th century.
Mahādeva is a controversial figure who appears in various roles in the histories of the early Buddhist schools.
Pre-sectarian Buddhism, also called early Buddhism, the earliest Buddhism, original Buddhism, and primitive Buddhism, is Buddhism as theorized to have existed before the various Early Buddhist schools developed, around 250 BCE.

In Buddhism, an Arhat or Arahant is one who has gained insight into the true nature of existence and has achieved Nirvana and has been liberated from the endless cycle of rebirth.
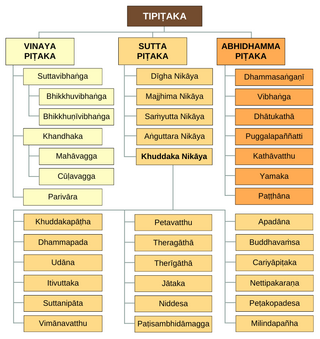
The Pāli Canon is the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravada Buddhist tradition, as preserved in the Pāli language. It is the most complete extant early Buddhist canon. It derives mainly from the Tamrashatiya school.
Early Buddhist texts (EBTs), early Buddhist literature or early Buddhist discourses are parallel texts shared by the early Buddhist schools. The most widely studied EBT material are the first four Pali Nikayas, as well as the corresponding Chinese Āgamas. However, some scholars have also pointed out that some Vinaya material, like the Patimokkhas of the different Buddhist schools, as well as some material from the earliest Abhidharma texts could also be quite early.

Chizen Akanuma was a Japanese Buddhist scholar and priest within the Ōtani-ha branch of Shin Buddhism, and a professor of Ōtani University who specialized in pre-sectarian Buddhism.










