Britain most often refers to:
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the country of Wales is a component of a multi-part sovereign state, the United Kingdom.

Europe is a landmass, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Asia and Africa. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. Although much of this border is over land, Europe is conventionally recognised as its own continent because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe can also be viewed as a subcontinent of Eurasia, and referred to as the European subcontinent.

North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically.

The contiguous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii, and all other offshore insular areas, such as American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The colloquial term "Lower 48", is used also, especially in relation to just Alaska.

The concept of Global North and Global South is used to describe a grouping of countries along socio-economic and political characteristics. The Global South is a term often used to identify regions within Latin America, Asia, Africa, and Oceania. It is one of a family of terms, including "Third World" and "Periphery", that denote regions outside Europe and North America, most of these countries are low-income and often politically or culturally marginalized on one side of the divide, the other side being the countries of the Global North. As such, the term does not inherently refer to a geographical south; for example, most of the Global South is geographically within the Northern Hemisphere.

The Pacific Rim comprises the lands around the rim of the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Basin includes the Pacific Rim and the islands in the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Rim roughly overlaps with the geologic Pacific Ring of Fire.
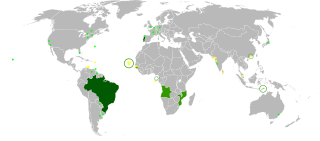
Lusophones are peoples that speak Portuguese as a native or as common second language and nations where Portuguese features prominently in society. Comprising an estimated 270 million people spread across 10 sovereign countries and territories, thus called Lusofonia or the Lusophone world, is the community of Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) world; these include Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Galicia, Guinea Bissau, Equatorial Guinea, Macau, Mozambique, Portugal, São Tomé and Príncipe, East Timor, Cochin, Goa, Daman and Diu, Singapore and Malacca to various degrees.
The economy of North America comprises more than 579 million people in its 23 sovereign states and 15 dependent territories. It is marked by a sharp division between the predominantly English speaking countries of Canada and the United States, which are among the wealthiest and most developed nations in the world, and countries of Central America and the Caribbean in the former Latin America that are less developed. Mexico and Caribbean nations of the Commonwealth of Nations are between the economic extremes of the development of North America.
An emerging market is a market that has some characteristics of a developed market, but does not fully meet its standards. This includes markets that may become developed markets in the future or were in the past. The term "frontier market" is used for developing countries with smaller, riskier, or more illiquid capital markets than "emerging". As of 2006, the economies of China and India are considered to be the largest emerging markets. According to The Economist, many people find the term outdated, but no new term has gained traction. Emerging market hedge fund capital reached a record new level in the first quarter of 2011 of $121 billion. The 10 largest emerging and developing economies by either nominal or PPP-adjusted GDP are 4 of the 5 BRICS countries along with Indonesia, Iran, South Korea, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan and Turkey.

Asia-Pacific (APAC) is the part of the world near the western Pacific Ocean. The Asia-Pacific region varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, Russian Far East, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australasia and Pacific Islands.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Belgium:

The Dutch Caribbean are the territories, colonies, and countries, former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean Sea. They are in the north and south-west of the Lesser Antilles archipelago.









