| Look up effusion in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Effusion is the process of gases passing through a small hole.
Effusion may also refer to:
| Look up effusion in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Effusion is the process of gases passing through a small hole.
Effusion may also refer to:
The seeping of fluid into a body cavity, the fluid itself, or an abnormal collection of fluid in a body cavity or space:

The pleural space, pleural sac or interpleural space is the potential space between the two opposing serous membranes (pleurae) that overlie each lung and the surrounding thoracic wall. The pleural cavity is the body cavity bounded by the parietal pleura, includes the lung, the hilar structures and the pleural space surrounding them, and varies in volume with breathing. The two pleural cavities, together with the mediastinum in between them, makes the entire thoracic cavity.

Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause.

A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung. Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.01 millilitre per kilogram weight per hour, and is cleared by lymphatic absorption leaving behind only 5–15 millilitres of fluid, which helps maintaining a functional vacuum between the parietal and visceral pleurae. Excess fluid within the pleural space can impair inspiration by upsetting the functional vacuum and hydrostatically increasing the resistance against lung expansion, resulting in a fully or partially collapsed lung.

An exudate is a fluid emitted by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation. Exudate is derived from exude, "to ooze", from the Latin exsūdāre, "to sweat".

A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.

A hemothorax is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may include reduced breath sounds on the affected side and a rapid heart rate. Hemothoraces are usually caused by an injury, but they may occur spontaneously due to cancer invading the pleural cavity, as a result of a blood clotting disorder, as an unusual manifestation of endometriosis, in response to a collapsed lung, or rarely in association with other conditions.
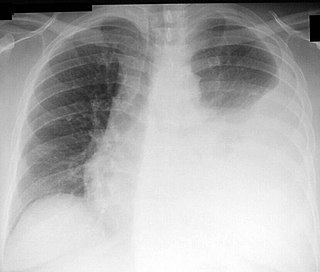
Thoracentesis, also known as thoracocentesis, pleural tap, needle thoracostomy, or needle decompression is an invasive medical procedure to remove fluid or air from the pleural space for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. A cannula, or hollow needle, is carefully introduced into the thorax, generally after administration of local anesthesia. The procedure was first performed by Morrill Wyman in 1850 and then described by Henry Ingersoll Bowditch in 1852.

A pancreatic fistula is an abnormal communication between the pancreas and other organs due to leakage of pancreatic secretions from damaged pancreatic ducts. An external pancreatic fistula is one that communicates with the skin, and is also known as a pancreaticocutaneous fistula, whereas an internal pancreatic fistula communicates with other internal organs or spaces. Pancreatic fistulas can be caused by pancreatic disease, trauma, or surgery.

A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane. The two layers of the serous membrane enclose the pericardial cavity between them. This pericardial space contains a small amount of pericardial fluid. The fluid is normally 15-50 mL in volume. The pericardium, specifically the pericardial fluid provides lubrication, maintains the anatomic position of the heart in the chest, and also serves as a barrier to protect the heart from infection and inflammation in adjacent tissues and organs.
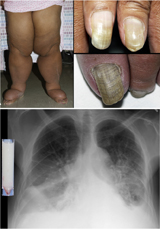
Yellow nail syndrome, also known as "primary lymphedema associated with yellow nails and pleural effusion", is a very rare medical syndrome that includes pleural effusions, lymphedema and yellow dystrophic nails. Approximately 40% will also have bronchiectasis. It is also associated with chronic sinusitis and persistent coughing. It usually affects adults.
Hypervolemia, also known as fluid overload, is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood. The opposite condition is hypovolemia, which is too little fluid volume in the blood. Fluid volume excess in the intravascular compartment occurs due to an increase in total body sodium content and a consequent increase in extracellular body water. The mechanism usually stems from compromised regulatory mechanisms for sodium handling as seen in congestive heart failure (CHF), kidney failure, and liver failure. It may also be caused by excessive intake of sodium from foods, intravenous (IV) solutions and blood transfusions, medications, or diagnostic contrast dyes. Treatment typically includes administration of diuretics and limit the intake of water, fluids, sodium, and salt.
In physiology, the term serous fluid or serosal fluid is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow and transparent and of a benign nature. The fluid fills the inside of body cavities. Serous fluid originates from serous glands, with secretions enriched with proteins and water. Serous fluid may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both mucous and serous cells. A common trait of serous fluids is their role in assisting digestion, excretion, and respiration.
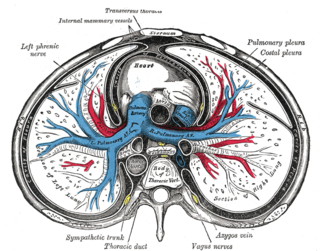
Pericardial fluid is the serous fluid secreted by the serous layer of the pericardium into the pericardial cavity. The pericardium consists of two layers, an outer fibrous layer and the inner serous layer. This serous layer has two membranes which enclose the pericardial cavity into which is secreted the pericardial fluid. The fluid is similar to the cerebrospinal fluid of the brain which also serves to cushion and allow some movement of the organ.
In anatomy, a potential space is a space between two adjacent structures that are normally pressed together. Many anatomic spaces are potential spaces, which means that they are potential rather than realized. In other words, they are like an empty plastic bag that has not been opened or a balloon that has not been inflated. The pleural space, between the visceral and parietal pleura of the lung, is a potential space. Though it only contains a small amount of fluid normally, it can sometimes accumulate fluid or air that widens the space. The pericardial space is another potential space that may fill with fluid (effusion) in certain disease states (e.g. pericarditis; a large pericardial effusion may result in cardiac tamponade.
Hydrops may refer to:
The human body and even its individual body fluids may be conceptually divided into various fluid compartments, which, although not literally anatomic compartments, do represent a real division in terms of how portions of the body's water, solutes, and suspended elements are segregated. The two main fluid compartments are the intracellular and extracellular compartments. The intracellular compartment is the space within the organism's cells; it is separated from the extracellular compartment by cell membranes.
Malignant pleural effusion is a condition in which cancer causes an abnormal amount of fluid to collect between the thin layers of tissue (pleura) lining the outside of the lung and the wall of the chest cavity. Lung cancer and breast cancer account for about 50-65% of malignant pleural effusions. Other common causes include pleural mesothelioma and lymphoma.
Pleural disease occurs in the pleural space, which is the thin fluid-filled area in between the two pulmonary pleurae in the human body. There are several disorders and complications that can occur within the pleural area, and the surrounding tissues in the lung.
A pericardial window is a cardiac surgical procedure to create a fistula – or "window" – from the pericardial space to the pleural cavity. The purpose of the window is to allow a pericardial effusion or cardiac tamponade to drain from the space surrounding the heart into the chest cavity.

The pulmonary pleurae are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls.