Chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid called the mobile phase, which carries it through a structure holding another material called the stationary phase. The various constituents of the mixture travel at different speeds, causing them to separate. The separation is based on differential partitioning between the mobile and stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation.

Electroosmotic flow is the motion of liquid induced by an applied potential across a porous material, capillary tube, membrane, microchannel, or any other fluid conduit. Because electroosmotic velocities are independent of conduit size, as long as the electrical double layer is much smaller than the characteristic length scale of the channel, electroosmotic flow will have little effect. Electroosmotic flow is most significant when in small channels. Electroosmotic flow is an essential component in chemical separation techniques, notably capillary electrophoresis. Electroosmotic flow can occur in natural unfiltered water, as well as buffered solutions.

Electrophoresis is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. Electrophoresis of positively charged particles (cations) is sometimes called cataphoresis, while electrophoresis of negatively charged particles (anions) is sometimes called anaphoresis.
Micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) is a chromatography technique used in analytical chemistry. It is a modification of capillary electrophoresis (CE), extending its functionality to neutral analytes, where the samples are separated by differential partitioning between micelles and a surrounding aqueous buffer solution.
Rheometry generically refers to the experimental techniques used to determine the rheological properties of materials, that is the qualitative and quantitative relationships between stresses and strains and their derivatives. The techniques used are experimental. Rheometry investigates materials in relatively simple flows like steady shear flow, small amplitude oscillatory shear, and extensional flow.
A streaming current and streaming potential are two interrelated electrokinetic phenomena studied in the areas of surface chemistry and electrochemistry. They are an electric current or potential which originates when an electrolyte is driven by a pressure gradient through a channel or porous plug with charged walls.
Electroacoustic phenomena arise when ultrasound propagates through a fluid containing ions. The associated particle motion generates electric signals because ions have electric charge. This coupling between ultrasound and electric field is called electroacoustic phenomena. The fluid might be a simple Newtonian liquid, or complex heterogeneous dispersion, emulsion or even a porous body. There are several different electroacoustic effects depending on the nature of the fluid.,
The Dukhin number is a dimensionless quantity that characterizes the contribution of the surface conductivity to various electrokinetic and electroacoustic effects, as well as to electrical conductivity and permittivity of fluid heterogeneous systems.
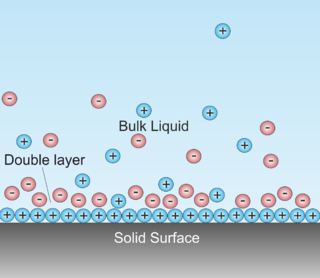
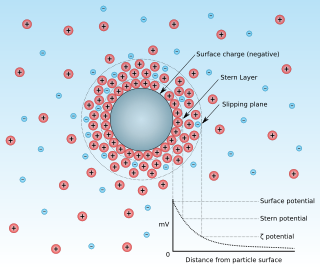
A double layer is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The DL refers to two parallel layers of charge surrounding the object. The first layer, the surface charge, consists of ions adsorbed onto the object due to chemical interactions. The second layer is composed of ions attracted to the surface charge via the Coulomb force, electrically screening the first layer. This second layer is loosely associated with the object. It is made of free ions that move in the fluid under the influence of electric attraction and thermal motion rather than being firmly anchored. It is thus called the "diffuse layer".
Sedimentation potential occurs when dispersed particles move under the influence of either gravity or centrifugation in a medium. This motion disrupts the equilibrium symmetry of the particle's double layer. While the particle moves, the ions in the electric double layer lag behind due to the liquid flow. This causes a slight displacement between the surface charge and the electric charge of the diffuse layer. As a result, the moving particle creates a dipole moment. The sum of all of the dipoles generates an electric field which is called sedimentation potential. It can be measured with an open electrical circuit, which is also called sedimentation current.
The seismoelectrical method is based on the generation of electromagnetic fields in soils and rocks by seismic waves. This technique is still under development and in the future it may have applications like detecting and characterizing fluids in the underground by their electrical properties, among others, usually related to fluids.
Electrocapillarity or electrocapillary phenomena are the phenomena related to changes in the surface energy of the dropping mercury electrode (DME) as the electrode potential changes or the electrolytic solution composition and concentration change. The term "electro-capillary" is used to describe the change in mercury (Hg) electrode potential as a function of the change in the surface or interfacial tension of the Hg determined by the capillary rise method. The phenomena are the historic main contributions for understanding and validating the models of the structure of the electrical double layer. The phenomena are related to the electrokinetic phenomena and consequently to the colloid chemistry.
Electrokinetics remediation, also termed electrokinetics, is a technique of using direct electric current to remove organic, inorganic and heavy metal particles from the soil by electric potential. The use of this technique provides an approach with minimum disturbance to the surface while treating subsurface contaminants.
A separation process is a method that converts a mixture or solution of chemical substances into two or more distinct product mixtures. At least one of results of the separation is enriched in one or more of the source mixture's constituents. In some cases, a separation may fully divide the mixture into pure constituents. Separations exploit differences in chemical properties or physical properties between the constituents of a mixture.

Capillary electrochromatography (CEC) is a chromatographic technique in which the mobile phase is driven through the chromatographic bed by electroosmosis. Capillary electrochromatography is a combination of two analytical techniques, high-performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Capillary electrophoresis aims to separate analytes on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio by passing a high voltage across ends of a capillary tube, which is filled with the analyte. High-performance liquid chromatography separates analytes by passing them, under high pressure, through a column filled with stationary phase. The interactions between the analytes and the stationary phase and mobile phase lead to the separation of the analytes. In capillary electrochromatography capillaries, packed with HPLC stationary phase, are subjected to a high voltage. Separation is achieved by electrophoretic migration of solutes and differential partitioning.

Induced-charge electrokinetics in physics is the electrically driven fluid flow and particle motion in a liquid electrolyte. Consider a metal particle in contact with an aqueous solution in a chamber/channel. If different voltages apply to the end of this chamber/channel, electric field will generate in this chamber/channel. This applied electric field passes through this metal particle and causes the free charges inside the particle migrate under the skin of particle. As a result of this migration, the negative charges moves to the side which is close to the positive voltage while the positive charges moves to the opposite side of the particle. These charges under the skin of conducting particle attract the counter-ions of the aqueous solution; thus, the electric double layer (EDL) forms around the particle. The EDL sing on the surface of the conducting particle changes from positive to negative and the distribution of the charges varies along the particle geometry. Due to these variations, the EDL is non-uniform and has different sings. Thus, the induced zeta potential around the particle, and consequently slip velocity on the surface of the particle, vary as a function of local electric field. Differences in magnitude and direction of slip velocity on the surface of the conducting particle effects the flow pattern around this particle and causes micro vortices. Yasaman Daghighi and Dongqing Li, for the first time, experimentally illustrated these induced vortices around a 1.2mm diameter carbon-steel sphere under the 40V/cm direct current (DC) external electric filed. Chenhui Peng et al. also experimentally showed the patterns of electro-osmotic flow around an Au sphere when alternating current (AC) is involved . Electrokinetics here refers to a branch of science related to the motion and reaction of charged particles to the applied electric filed and its effects on its environment. It is sometimes referred as non-linear electrokinetic phenomena as well.
Electromembrane extraction, or EME, is a miniaturized liquid-liquid extraction technique developed for sample preparation of aqueous samples prior to analysis by chromatography, electrophoresis, mass spectrometry, and related techniques in analytical chemistry. EME involves the use of a small supported liquid membrane (SLM) sustained in the wall of a porous hollow fiber, and application of an electrical field across the SLM.